Acceleration and Force: Physics Presentation
advertisement

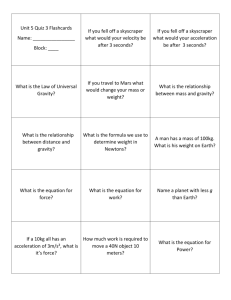
8.2 Acceleration and Force Graph of Speed (distance/time) Speeding up and Slowing down Which car is accelerating? Why it’s m/s2 • a = change in velocity (m/s) • divided by time (s) • _m/s__ = • s m/s X 1/s = m/s2 Balanced and Unbalanced Forces • A balanced force is present when equal forces are applied to each side of an object. • An unbalanced force is present when unequal forces are applied to each side of an object. • In the picture below, the forces are balanced when the horizontal bar is level. • The forces are unbalanced when the horizontal bar is unleveled. . Direction of Forces is Important Total Force Force #2 Force #1 Force #1 Total Force = 0 Force #2 Friction is a Force Force on box by person Force on floor by box Force on person by box Force on box by floor It’s the sum of all the forces that determines the acceleration. Every force has an equal & opposite partner. Friction Mechanism Corrugations in the surfaces grind when things slide. Lubricants fill in the gaps and let things slide more easily. Why Doesn’t Gravity Make the Box Fall? Force of Floor acting on Box Force from floor on box cancels gravity. If the floor vanished, the box would begin to fall. Force of Earth acting on Box (weight) What’s missing in this picture? Force on box by person Force on floor by box Force on person by box Force on box by floor A pair of forces acting between person and floor. Air Resistance – air creates friction What is gravity? Gravity (g) Gravity is a force of attraction between objects. The more massive the object, the greater the pull. However, the object has to be really massive, like Earth, for the pull to be obvious to the casual observer. What are some EFFECTS of gravity? • Weight • Hot air rises, cool air sinks. • Liquids conform to the bottom of a container. • Objects fall. • Liquids of different density settle in layers. Which falls faster? Gravitational Acceleration in Free Fall is 9.8 m/s2