Free Body Diagrams
advertisement

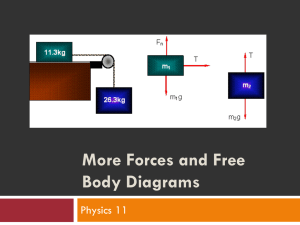
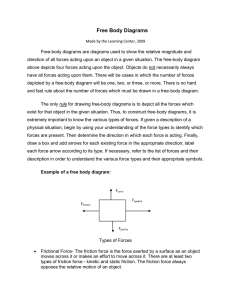
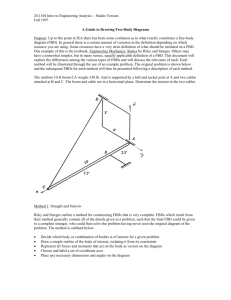
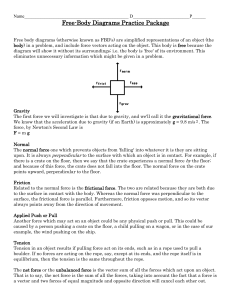
•Free Body Diagrams (FBDs) are tools used to analyze physical situations •FBDs show all the forces acting on a single object As an example of a free-body diagram, consider a 30-newton book resting on a table that weighs 200 newtons. The book is on one corner of the table so that its entire weight is supported by one leg. Because the table is in equilibrium, the net force acting on it must be zero. The weight of the book acts on the table. The weight of the table acts on the floor. The force acting on the table is the reaction to its weight acting on the floor. There are two ways to handle positive and negative directions in a free-body diagram. One way is to make all upward forces positive and all downward forces negative When you solve the problem, if you have chosen correctly, all the values for each force are positive. If one comes out negative, it means the force points in the opposite direction from what you calculated. What forces are acting on objects? •The object itself may be drawn as a circle or box •Draw and label all the external forces on the object • The only “rule” for drawing free-body diagrams is to depict all the forces that exist for that object in the given situation. A circus elephant falls off a tight rope. Neglecting air resistance, draw a free body diagram for the falling elephant. A circus elephant falls off a tight rope. Including air resistance, draw a free body diagram for the falling elephant. A book is at rest on a tabletop. Diagram the forces acting on the book A girl is sitting on a swing at the playground, sketch a FBD of this scenario. •Free Body Diagrams are useful to quickly see if there are unbalanced forces on an object. •If an object is in equilibrium, the net force is zero. •If the forces are unbalanced, then acceleration occurs Let’s calculate the magnitude and directions of this FBD Let’s calculate the magnitude and directions of this FBD Let’s calculate the magnitude and directions of this FBD Suppose three people are trying to keep an injured polar bear in one place. Each person has a long rope attached to the bear. Two people pull on the bear with forces of 100 N each . What force must the third person apply to balance the other two? The bear will not move if the net force is zero.