Implementing Spanning Tree
advertisement

Implementing Spanning
Tree
Module 3 - Part 4
Etherchannel
Jane Brooke (Centennial College)
mods by Emerson Hunt
EtherChannel
About EtherChannel
Logical aggregation of
bandwidth
Viewed as one logical port
Bind 2 - 8 ports
by STP, trunking, access
and for administration
Yields 1600Mbps
(FastEther) or
16Gbps(GigabitEther)
Load balancing algorithm
differs by platform
Etherchannel Benefits
Use
all available bandwidth by logically
“bundling” up to eight physical links
The logical Etherchannel can be managed
as a single unit called a port channel or
channel group
Seen as one by
Shutdown/no shutdown
Sh spanning tree
Sh interface trunking
Etherchannel Benefits
Load is balanced across physical links
Although balancing algorithm is not necessarily
optimal
Under some circumstances balancing is uneven
Remaining links continue to operate if a
member of the etherchannel bundle fails
Loss of a line in an etherchannel is not seen by
STA
Failover time is only milliseconds
Used Where?
L2
as trunk between two switches
L3 as connection between two routers
Access link
typically between switch and server with
appropriate NICs (NIC "teaming")
Etherchannel and Servers
Multiple
NICs can be installed in a server
and a higher bandwidth aggregated link
can be formed between the server and the
switch
Known as ``nic teaming``
May not be supported natively by the
server OS
Proper choice of the load balancing
algorithm is important with NIC teaming
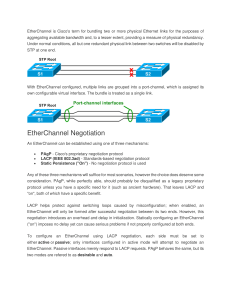
EtherChannel Dynamic Trunk
Negotiation Protocols
PAgP
Cisco proprietary
Sends PAgP packets
across link to negotiate
EtherChannel
LACP
IEEE standard 802.3ad
Sends LACP packets across
link to bundle multiple ports
into a single channel
Use in mixed switch
environment
EtherChannel Interface Modes
ON – Forces EtherChannel ON without PAgP or
LACP negotiation (not recommended)
PAgP
Auto (default PAgP mode)
• interface enters passive negotiating state
• responds to PAgP packets received but doesn’t initiate PAgP
negotiation
Desirable (PAgP mode)
• interface actively negotiates with other interfaces
• PAgP packets are exchanged
LACP
Passive (Default LACP mode)
• port responds to LACP packets received, but it does not initiate
LACP packet negotiation
Active
• port actively negotiates state with other ports by sending LACP
packets
The Defaults
Auto for PAgP and passive for LACP
Best practice is to
Means that by default, links WILL NOT aggregate
automatically
Explicitly set aggregation protocol using the
channel-protocol command
manually configure using the channel-group
command
PAgP is the proprietary default link
aggregation protocol on Cisco switches
Use LACP for vendor neutrality
PAgP
PAgP
packets sent between Etherchannel
ports – negotiate forming channel
Etherchannel seen as single bridge port to
spanning tree
Packets sent every 30 seconds
Multicast out MAC 01-00-0C-CC-CC-CC
Ensures all ports have same speed, duplex
and VLAN info
The Rules
All links in a channel-group must be almost
identical
Speed and duplex
Switch port mode (trunk or access)
If access, belong to same vlan
If trunk, same vlans allowed
Each etherchannel must be assigned a
channel group number (1-64)
Creates a Port-channel interface section in
running config
Guidelines for Configuring
EtherChannel
Guidelines for Configuring
EtherChannel (Cont.)
Interfaces in the same bundle can support varying port
costs
About EtherChannel
Configuration Commands
Configure PAgP
interface range blah blah
channel-protocol pagp
channel-group X mode auto
Configure LACP
interface range blah blah
channel-protocol lacp
channel-group X mode active
Verify
show interfaces fastethernet 0/1 etherchannel
show etherchannel 1 port-channel
show etherchannel 1 summary
Configuring L2 EtherChannel
• Specify the interfaces to configure in the bundle
Switch(config)#interface range interface slot/port - port
• Specify the channel protocol either pagp OR lacp
Switch(config-if-range)#channel-protocol {pagp | lacp}
PAgP is default on Cisco switches.
• Create the port-channel interface and place the interfaces as
members
Switch(config-if-range)#channel-group number mode {auto |
desirable | active | passive | on}
Verifying EtherChannel
Switch#show running-config interface port-channel num
• Displays port-channel information
Switch#show run interface portchannel 1
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 66 bytes
!
interface Port-channel1
switchport mode dynamic desirable
end
Switch#show running-config interface interface x/y
• Displays interface information
Switch#show run interface gig 0/9
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 127 bytes
!
interface GigabitEthernet 0/9
switchport mode dynamic desirable
channel-group 2 mode desirable
channel-protocol pagp
end
Verifying EtherChannel (Cont.)
Switch#show interfaces gigabitethernet 0/9 etherchannel
Port state
= Up Mstr In-Bndl
Channel group = 1
Mode = Desirable-Sl
Gcchange = 0
Port-channel = Po2
GC
= 0x00020001
Pseudo port-channel = Po1
Port index
= 0
Load = 0x00
Flags:
S
A
d
Timers: H
S
-
Device is sending Slow hello.
Device is in Auto mode.
PAgP is down.
Hello timer is running.
Switching timer is running.
C - Device is in Consistent state.
P - Device learns on physical port.
Q - Quit timer is running.
I - Interface timer is running.
Local information:
Port
Gi0/9
Flags State
SC
U6/S7
Timers
H
Hello
Partner PAgP
Interval Count
Priority
30s
1
128
Learning Group
Method Ifindex
Any
15
Partner's information:
Port
Gi0/9
Partner
Name
DSW122
Partner
Device ID
0005.313e.4780
Partner
Port
Gi0/9
Age of the port in the current state: 00d:20h:00m:49s
Partner Group
Age Flags
Cap.
18s SC
20001
Load Balancing
Etherchannel
provides a choice of
algorithms to determine which bundle
member will carry a given frame
Various load-balancing methods are
available (choices are platform dependant)
The default method may lead to some
members being more heavily utilized than
others
Example
Suppose
we have an Etherchannel
connecting a switch to a server
One type of algorithm depends solely on
destination mac address
All frames destined for the same mac address
will use the same wire
Therefore virtually all server bound frames will
use just one wire in the etherchannel
Balancing Methods
src-ip
dst-ip
src-dst-ip
src-mac
dest-mac
src-dst-mac
src-port
dst-port
src-dst-port
Available Methods &
which is the default
vary by platform
Configuring EtherChannel Load
Balancing
Switch(config)#port-channel load-balance type
• Note that this is a global command
• I.e. method cannot be configured on a per-channel basis
• To see the current load balancing method, use the following:
Switch#show etherchannel load-balance
Source XOR Destination IP address
Notes
the
default method will usually result in a
fair balancing
the following command will give some
sense of the fairness of the load balancing
algorithm
show etherchannel port-channel X
Look for the "load" value on each channel
They should be similar
Resources
http://networkers-
online.com/blog/2008/07/etherchannelload-balancing-case-study/
Personal Notes
Etherchannel works (sort of) in Packet Tracer
I have had PT 5.1 crash when playing with
multiple Etherchannels
Packet tracer definitely does not accurately
simulate show command output where port
channels are involved
However, etherchannel also seems a bit
flakey on our equipment
Lab suggests "flapping" the interfaces if the
Etherchannel does not come up