Port Aggregation & Load Balancing
advertisement

Port Aggregation & Load
Balancing
By:
Joe B., Nabeel O.
Miguel & Mufaddal J.
Objectives
Switch Configuration
Port Aggregatioon
Port Channels
Fast Etherchannels
Load Balancing
Etherchannels
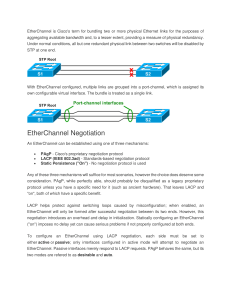
The EtherChannel provides full-duplex
bandwidth up to 800 Mbps (Fast EtherChannel)
or 2 Gbps (Gigabit EtherChannel) between your
switch and another switch or host.
Each EtherChannel can consist of up to eight
compatibly configured Ethernet interfaces. All
interfaces in each EtherChannel must be the
same speed, and all must be configured as
Layer 2 interfaces.
Port Channels
EtherChannel
consists of individual
Fast Ethernet or
Gigabit Ethernet links
bundled into a single
logical link
EtherChannel Modes
Auto Places an interface into a passive negotiating
state, in which the interface responds to PAgP packets it
receives but does not initiate PAgP packet negotiation.
This setting minimizes the transmission of PAgP packets.
Desirable Places an interface into an active negotiating
state, in which the interface initiates negotiations with
other interfaces by sending PAgP packets.
On Forces the interface to channel without PAgP. With
the on mode, a usable EtherChannel exists only when
an interface group in the on mode is connected to
another interface group in the on mode.
Switch Configuration
Switch#config t
Switch(config)#int fa 0/7
Switch(config-if)#channel-group 1 mode desirable
Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel 1
Switch(config-if)#exit
Switch(config)#int fa 0/8
Switch(config-if)#channel-group 1 mode desirable
Switch(config-if)#exit
Switch(config)#int fa 0/9
Switch(config-if)#channel-group 1 mode desirable
Switch(config-if)#exit
Switch Configuration
Switch#sh run
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 1531 bytes
!
version 12.1
no service single-slot-reload-enable
no service pad
service timestamps debug uptime
service timestamps log uptime
no service password-encryption
! hostname Switch
!
!
ip subnet-zero
!
spanning-tree extend system-id
!
!
interface Port-channel1
no ip address
!
interface FastEthernet0/2
no ip address…………
!
interface FastEthernet0/7
no ip address
channel-group 1 mode desirable
!
interface FastEthernet0/8
no ip address
channel-group 1 mode desirable
!
interface FastEthernet0/9
no ip address
channel-group 1 mode desirable
!
interface FastEthernet0/10
no ip address
!......................................
!
interface FastEthernet0/24
no ip address
!
Switch Config. (Cont.)
interface Vlan1
no ip address
no ip route-cache
shutdown
!
ip http server
!
!
line con 0
line vty 5 15
!
End
Switch#config t
Switch(config)#port-channel load-balance
dst-mac
Switch(config)#end
Switch#show etherchannel l
Destination MAC address
Channel-Group
Each EtherChannel has a logical port-channel
interface numbered from 1 to 6.
Load Distribution and Forwarding
Methods
Default EtherChannel Configuration
Channel groups None assigned.
PAgP mode No default.
PAgP learn method Aggregate-port learning
on all interfaces.
PAgP priority 128 on all interfaces. (Changing
this value on Catalyst 2950 switches has no
effect.)
Load balancing Load distribution on the switch
is based on the source-MAC address of the
incoming packet.
Configuring EtherChannels
Configure Layer 2 EtherChannels by
configuring the Ethernet interfaces with the
channel-group interface configuration
command, which creates the port-channel
logical interface.
Note: Layer 2 interfaces must be
connected and functioning for IOS to
create port-channel interfaces
Configuring EtherChannels
Step 1: configure
terminal
Step 2 interface
interface-id
1) Enter global
configuration mode
2) Enter interface
configuration mode, and
specify a physical
interface to configure.
Valid interfaces include
physical interfaces.
Up to eight interfaces of
the same type and speed
can be configured for the
same group.
Configuring EtherChannels
Step 3: channel-group
channel-group-number
mode {auto [non-silent] |
desirable [non-silent] |
on}
Step 4: end
3) Assign the interface to
a channel group, and
specify the PAgP mode.
The default mode is auto
silent.
For channel-groupnumber, the range is 1 to
6. Each EtherChannel
can have up to eight
compatibly configured
Ethernet interfaces.
4) Return to privileged
EXEC mode
Configuring EtherChannels
Step 5: show runningconfig
Step 6: copy runningconfig startup-config
To remove an interface
from the EtherChannel
group, use the no
channel-group interface
configuration command
5) Verify your entries.
6) (Optional) Save your
entries in the
configuration file.
Configuring EtherChannel Load
Balancing
This section describes how to configure
EtherChannel load balancing by using
source-based or destination-based
forwarding methods
Beginning in privileged EXEC mode to
configure EtherChannel load balancing
Configuring EtherChannel Load
Balancing
Step 1: configure terminal
Step 2: port-channel loadbalance {dst-mac | -mac}
Step 3: end
Step 4: show etherchannel
load-balance
Step 5: copy running-config
startup-config
To return EtherChannel load
balancing to the default
configuration, use the no portchannel load-balance global
configuration command.
1) Enter global configuration
mode.
2) Configure an EtherChannel
load-balancing method.
The default is -mac.
3) Return to privileged EXEC
mode
4) Verify your entries
5) (Optional) Save your entries
in the configuration file.
Commands for Displaying
EtherChannel and PAgP Status
show etherchannel
[channel-group-number]
{brief | detail | loadbalance | port | portchannel | summary}
show pagp {channelgroup-number} {counters
| internal | neighbor}
Displays EtherChannel
information in a brief,
detailed, and one-line
summary form. Also
displays the load-balance
or frame-distribution
scheme, port, and portchannel information.
Displays PAgP
information such as traffic
information, the internal
PAgP configuration, and
neighbor information
Little Intro.
Cisco Cluster Management Suite
cisco_cms