reviewproblemschapter2
advertisement
EML 3004C
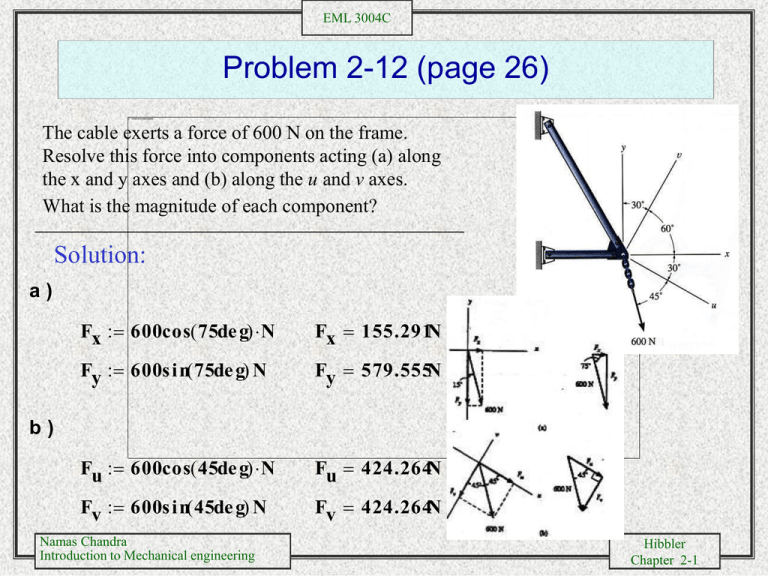
Problem 2-12 (page 26)
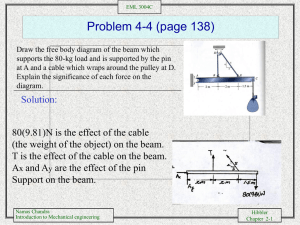
The cable exerts a force of 600 N on the frame.
Resolve this force into components acting (a) along
the x and y axes and (b) along the u and v axes.
What is the magnitude of each component?
Solution:
a)
Fx 600cos( 75de g) N
Fx 155.291N
Fy 600s in( 75de g) N
Fy 579.555N
Fu 600cos( 45de g) N
Fu 424.264N
Fv 600s in( 45de g) N
Fv 424.264N
b)
Namas Chandra
Introduction to Mechanical engineering
Hibbler
Chapter 2-1
EML 3004C
Problem 2-16 (page 26)
If the resultant FR of the two forces acting on the jet
aircraft is to be directed along the positive x axis and have
a magnitude of 10 kN, determine the angle of the cable
attached to the truck at B such that the force FB in this
cable in a minimum. What is the magnitude of force in
each cable when this occurs?
Solution:
90de g 20de g
70de g
3
FB 3.42 10 N
3
Fc 9.397 10 N
FB 10s in( 20de g) 10 N
Fc 10cos( 20de g) 10 N
Namas Chandra
Introduction to Mechanical engineering
3
3
Hibbler
Chapter 2-2
EML 3004C
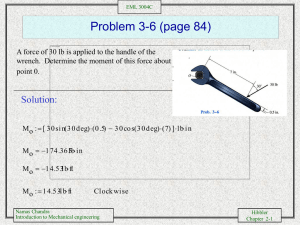
Problem 2-29 (page 35)
Three forces act on the bracket.
Determine the magnitude and orientation
of F2 so that the resultant force is
directed along the positive u axis and has
a magnitude of 50 lb.
Solution:
5
Sum mation of
( 1)
50cos( 25de g) 80 Fs cos 25de g
52
Force s in the
13
X direction.
F2 cos 25de g 54.68
Sum mation of
Force s in the
Namas
Chandra
Hibbler
Y direction.
Introduction to Mechanical engineering
Chapter 2-3
EML 3004C
Problem 2-29 continued
5
Sum m at ion of
50cos( 25de g) 80 Fs cos 25de g
52
Force s in the
13
X dir ection.
F2 cos 25de g 54.68
Sum m at ion of
5
52
Force s in the 50 s in( 25de g) Fs cos 25de g
13
Y dir ection.
F2 s in 25de g 69.13
( 2)
Eq 1 and 2 yields :
tan 25de g 1.2642
25de g 128.34
103de g
Substituting into Eqn 1 or 2 yie lds:
F2 88.1 lb
Namas Chandra
Introduction to Mechanical engineering
Hibbler
Chapter 2-4
EML 3004C
Problem 2-42 (page 47)
The pipe is subjected to the force F which
has components acting along the x, y, z
axes as shown. If the magnitude of F is 12
kN, and α = 120 deg and γ = 45 deg,
determine the magnitudes of its three
components.
Solution:
2 42
2
2
2
cos cos cos 1
2
2
2
cos 120de g cos cos 45de g 1
Fr om the Figure , cos = + 0.5
cos 0.5 plus or m inus
0 de g
Fx F cos
Fx 12 cos 120de g
Fx 6 k N
Fy F cos
Fy 12 cos 60de g
Fx 6 k N
Fz F cos
Fz 12 cos 45de g
Fx 8.49 k N
Namas Chandra
Introduction to Mechanical engineering
Hibbler
Chapter 2-5
EML 3004C
Problem 2-48 (page 55)
Express the position vector r in
Cartesian vector form; then determine
its magnitude and coordinate direction
angles.
Solution:
Pos ition vector:
M agnitude :
Namas Chandra
Introduction to Mechanical engineering
R = (4 - 0) i +[ - 4 - ( - 2)] j + ( 6 - 3) k
= { 4i - 2j + 3k } m
r
2
2
2
4 ( 2) 3
r 5.39 m
Hibbler
Chapter 2-6
EML 3004C
Problem 2-48 continued
Coor dinat e dire ction angles :
R
ur
r
ur
4i 2j 3k
5.385
ur 0.74281i 0.3714j 0.5571k
cos 0.7428
42 de g
cos 0.3714
112 de g
cos 0.5517
56.1 de g
Namas Chandra
Introduction to Mechanical engineering
Hibbler
Chapter 2-7
EML 3004C
Problem 2-59 (page 57)
Express each of the two
forces in Cartesian vector
form and then determine the
magnitude and coordinate
direction angles of the
resultant force.
Solution:
2 59
rab ( 0 4) i ( 8 8) j [ 0 ( 12) ] k
rab ( 4i 0j 12k)ft
rAB
( 4)
2
2
0
( 12)
2
rab
F1v F1
rAB
rAB 12.649ft
4i 0j 12k
12.649
F1v 12
F1v ( 3.79i 11.38k) l b
Namas Chandra
Introduction to Mechanical engineering
Hibbler
Chapter 2-8
EML 3004C
Problem 2.59 continued 1
rac ( 5 4)i ( 8 8) j [ 4 ( 12) ]k
rac ( 9i 16j 16k)ft
rAC
2
2
( 9) ( 16) ( 16)
2
rAC 24.352ft
9i 16j 16k
F1v 18
24.352
rac
F2v F2
rAC
F2v ( 6.65i 11.8j 11.8k) lb
FR F1 F2
FR ( 3.79i 11.38k) ( 6.65i 11.82j 11.82k)
FR ( 10.44i 11.82j 23.21k) lb
Fr
10.442 11.822 23.212
Namas Chandra
Introduction to Mechanical engineering
FR 28.067lb
FR 28.1 lb
Hibbler
Chapter 2-9
EML 3004C
Problem 2-59 continued 2
Coor dinate dir ection angles :
FR
ur
Fr
ur
10.44i 11.82j 23.21k
28.067
ur 0.37i 0.42j 0.82k
cos 0.37
112 de g
cos 0.42
115 de g
cos 0.82
34.2 de g
Namas Chandra
Introduction to Mechanical engineering
Hibbler
Chapter 2-10
EML 3004C
Problem 2-65 (page 59)
The cylindrical vessel is supported by three cables
which are concurrent at point D. Express each force
which the cables exert on the vessel as a Cartesian
vector, and determine the magnitude and coordinate
direction angles of the resultant force.
Solution:
2 65
ra ( 0 0.75) i ( 0 0) j ( 3 0) k
ra ( 0.75i 0j 3k)m
rA
2
2
( 0.75) 0 ( 3)
2
ra
FAv FA
rA
rA 3.0923m
0.75i 0j 3k
3.0923
FAv 6
FAv ( 1.461i 5.82k) k N
Namas Chandra
Introduction to Mechanical engineering
Hibbler
Chapter 2-11
EML 3004C
Problem 2-65 continued 1
rc [ 0 ( 0.75s in 45de g) ]i [ 0 ( 0.75cos 45de g) ] j ( 3 0)k
rc ( 0.5303i 0.5303j 3k)m
rC
2
2
( 0.5303) ( 0.5303) ( 3)
2
rC 3.0923
0.5303i 0.5303j 3k
3.0923
rc
FC v FC
rC
FC v 5
FC v ( 0.857i 0.857j 4.85k) k N
rb [ 0 ( 0.75s in 30de g) ]i [ 0 ( 0.75cos 30de g) ] j ( 3 0)k
rb ( 0.375i 0.6495j 3k)m
rB
2
2
( 0.375) ( 0.6495) ( 3)
rc
FBv FB
rC
2
rB 3.0923
0.375i 0.6495j 3k
3.0923
FBv 8
FBv ( 0.970i 1.68j 7.76k) k N
Namas Chandra
Introduction to Mechanical engineering
Hibbler
Chapter 2-12
EML 3004C
Problem 2-65 continued 2
Res ultant For ce Vector :
FR FA FB FC
FR ( 1.45i 5.8208k) ( 0.97i 1.68j 7.76k) ( 0.85i 0.85j 4.85k)
FR ( 0.3724i 0.8228j 18.4326k) k N
Fr
0.37242 ( 0.8228) 2 18.43262
Namas Chandra
Introduction to Mechanical engineering
FR 18.4547lb
FR 18.5 lb
Hibbler
Chapter 2-13
EML 3004C
Problem 2-65 continued 3
Coor dinate dire ction angle s:
FR
ur
Fr
ur
0.3724i 0.8228j 18.4326k
18.4547
ur 0.02018i 0.04458j 0.9988k
cos 0.02018
88.8 de g
cos 0.04458
92.6 de g
cos 0.9988
2.81 de g
Namas Chandra
Introduction to Mechanical engineering
Hibbler
Chapter 2-14
EML 3004C
Problem 2-78 (page 65)
Determine the magnitudes of the projected
components of the force F={-80i + 30j + 20k} lb in
the direction of the cables AB and AC.
Solution:
uAC
uAB
( 4 0)i ( 3 0)j ( 0 8)k
2
2
( 4 0) ( 3 0) ( 0 8)
uAC
2
( 0 5)i [ 0 ( 4) ]j ( 8 0)k
2
2
( 0 5) [ 0 ( 4) ] ( 8 0)
Namas Chandra
Introduction to Mechanical engineering
2
uAC
4i 3j 8k
89
5i 4j 8k
105
Hibbler
Chapter 2-15
EML 3004C
Problem 2-78 continued
FAC F uAC
4i 3j 8k
FAC ( 80i 30j 20k)
89
FAC
( 80) ( 4) 30 ( 3) 20 ( 8)
lb
89
FAC 26.5lb
FBA F uBA
5i 4j 8k
FBA ( 80i 30j 20k)
105
FBA
( 80) ( 5) 30 ( 4) 20 ( 8)
lb
105
FAC 26.5lb
Namas Chandra
Introduction to Mechanical engineering
Hibbler
Chapter 2-16
EML 3004C
Problem 2-95 (page 68)
Express each of the three forces acting on the
column in Cartesian vector form and
determine the magnitude of the resultant force.
Solution:
F1 ( 140s in( 30de g) i 140cos( 30de g) j
F1 ( 70i 121j) lb
F2 ( 180j) lb
F3 ( 125cos( 45de g) i 125s in( 45de g) j)
FR F1 F2 F3
F3 ( 88.4i 88.4j) lb
FR ( 70i 121.1j) ( 180j) ( 88.4i 88.4j)
FR ( 18.38i 389.63j) lb
M agnitude :
FR
2
( 18.38) ( 398.63)
2
FR 390 lb
Namas Chandra
Introduction to Mechanical engineering
Hibbler
Chapter 2-17