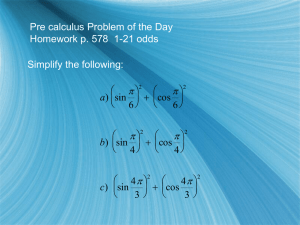
reviewproblemschapter4
advertisement

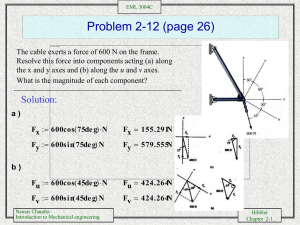
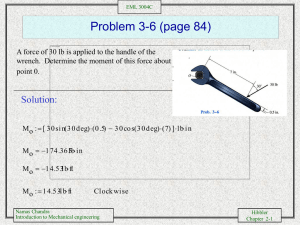
EML 3004C Problem 4-4 (page 138) Draw the free body diagram of the beam which supports the 80-kg load and is supported by the pin at A and a cable which wraps around the pulley at D. Explain the significance of each force on the diagram. Solution: 80(9.81)N is the effect of the cable (the weight of the object) on the beam. T is the effect of the cable on the beam. Ax and Ay are the effect of the pin Support on the beam. Namas Chandra Introduction to Mechanical engineering Hibbler Chapter 2-1 EML 3004C Problem 4-8 (page 139) Draw the free-body diagram of the winch, which consists of a drum radius 4 in. It is pin-connected at it center C, and at its outer rim is a ratchet gear having a mean radius of 6 in. The pawl AB serves as a two-force member (short link) and holds the drum for rotating. Solution: Namas Chandra Introduction to Mechanical engineering Hibbler Chapter 2-2 EML 3004C Problem 4-23 (page 155) The uniform rod AB has a weight of 15 lb. Determine the force in the cable when the rod is in the position shown. Solution: M 0 a F x 0 N B [ 5 sin ( 40 deg ) 15 ( 2.5 cos ( 40 deg ) T cos ( 10 deg ) 8.938 0 Namas Chandra Introduction to Mechanical engineering 0 N B 8.938 lb T 9.08 lb Hibbler Chapter 2-3 EML 3004C Problem 4-32 (page 156) Determine the resultant normal force acting on each set of the wheels of the airplane. There is a set of wheels in the front, A, and a set of wheels under each wing, B. Both wings have total weight of 50 kip and center of gravity at Gw, the fuselage has a weight of 180 kip and center of gravity at Gf, and both engines(one on each side) have a weight 22 kip and center of gravity at Ge. Solution: M 0 a 2 N B ( 40 ) 180000 ( 31 ) 22000 ( 38 ) 50000 ( 40 ) 0 N B 105200 lb F y 0 N A 2 ( 105200 ) 180000 22000 50000 0 N A 41600 lb Namas Chandra Introduction to Mechanical engineering Hibbler Chapter 2-4 EML 3004C Problem 4-57 (page 172) The triangular plate is supported by a balland-socket joint at B and rollers at A and C. Determine the x, y, z components of each reaction at these supports due to the loading shown. Solution: M x 0 C x( 0.6 ) 800 ( 0.3 ) 400 ( 0.3 ) 0 C x 600 N M y 0 B x( 0.8 ) 600 ( 0.4 ) 400 ( 0.4 ) 0 B x 500 N F x 0 A z 600 500 800 400 600 0 A z 700 N F x 0 B x 0 Namas Chandra Introduction to Mechanical engineering F y 0 B y 0 Hibbler Chapter 2-5 EML 3004C Problem 4-70 (page 174) Cable BC and DE can support a max. tension fo 700 lb before it breaks. Determine the greatest weight W that can be suspended from the end of the boom. Also, determine the x, y, z components of reaction at the ball-andsocket joint A. Solution: Assuming failure at cable BC T BC 700 2i 3j 6k 2 2 2 2 ( 3) 6 3i 6j 2k 2 2 2 ( 3 ) ( 6 ) 2 T DE T DE F A A x i A y j A z k Namas Chandra Introduction to Mechanical engineering T BC ( 200i 300j 600 k ) lb T DE 3 7 T DE i 6 7 T DE j 2 7 T DE k W ( W k ) lb Hibbler Chapter 2-6 EML 3004C Problem 4-70 (continued) Force Summation F 0 ( 200i 300j 600 k ) 3 T i 6 T j 2 T k A i A j A k 0 x DE DE DE y z 7 7 7 200 3 T i 300 6 T j 600 2 T A A DE z DE y DE A z W 0 7 7 7 Equilizing i, j, k components F x 0 200 F y 0 300 F z 0 600 3 7 T DE A x 0 6 7 Namas Chandra Introduction to Mechanical engineering 2 7 T DE A y 0 T DE A z W 0 Hibbler Chapter 2-7 EML 3004C Problem 4-70 (continued) Moment Summation M a 0 ( 3j ) 3 T i 6 T j 2 T k ( 8 j) ( W k ) 0 DE DE DE 7 7 7 1800 12 T i 18 T k 0 8W 600 DE DE 7 7 Equating i and k components M x 0 M z 0 1800 12 7 18 7 T DE 8W 0 T DE 600 0 Solving Equations T DE 233.33 lb 233.33 700 lb so assumption OK W 275 lb A z 392 lb A x 100 lb Namas Chandra Introduction to Mechanical engineering A y 500 lb Hibbler Chapter 2-8 EML 3004C Problem 4-78 (page 189) The car has a weight of 4000 lb and a center of gravity at G. If it pulls off the side of a road, determine the greatest angle of tilt, , it can have without slipping or tipping over. The coeffiecient of static friction between its wheels and the ground is 0.4. Solution: Equilibrium F x. 0 4000 sin F a F b 0 F y. 0 M a 0 N A N B 4000 cos 0 N B ( 8 ) 4000 2 sin 4000 4 cos 0 Assuming Slipping occurs. Therefore: F A 0.4 N A F B 0.4 N B Substituting N A 1484.6 lb N B 2228.3 lb 21.8 deg Namas Chandra Introduction to Mechanical engineering Hibbler Chapter 2-9 EML 3004C Problem 4-85 (page 190) The two stone blocks have weights of Wa=600lb and Wb=500lb. Determine the smallest horizontal force P that must be applied to block A in order to move it. The coeffeicient of the static friction between the blocks is 0.3 and between the floor and each block is 0.4. Solution: Case I: Block A and Block B move together: F x 0 N ( 600 500 ) 0 N 1100 lb F y 0 0 0.5 ( 1100 ) P P 550 lb Namas Chandra Case II: Only block A moves Introduction to Mechanical engineering Hibbler Chapter 2-10 EML 3004C Problem 4-85 continued F y 0 Case II: Only block A moves F x. 0 N 600 cos ( 20 deg ) P cos ( 70 deg ) 0 F y. 0 P sin ( 70 deg ) 600 sin ( 20 deg ) 0.3 N 0 Solving P 447.2 lb N 716.8 lb Choose the smalles P among the two cases: P 447 lb Namas Chandra Introduction to Mechanical engineering Hibbler Chapter 2-11 EML 3004C Problem 4-110 (page 194) Determine the angle at which the applied force P should act on the log so that the magnitude of P is as small as possible for pulling the log up the incline. What is the corresponding value of P? The log weighs W and the slope is known. Express the answer in terms of the angle of kinetic friction, = atan (). Solution: F x. 0 N P sin W cos 0 F y. 0 P cos W sin tan W cos P sin 0 P N W cos P sin W sin tan cos cos tan sin Namas Chandra Introduction to Mechanical engineering Hibbler Chapter 2-12 EML 3004C Problem 4-110 (continued) P W cos cos P W sin cos d d sin sin cos cos sin sin P W sin sin cos 2 W sin sin sin 0 P W sin cos Namas Chandra Introduction to Mechanical engineering 0 W sin 0 0 0 P W sin Hibbler Chapter 2-13