Surveying and Geometry
advertisement
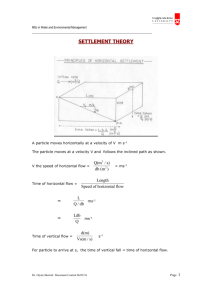
Surveying and Geometry Brittany Crawford-Purcell What is Surveying? ► Science of accurately determining the terrestrial or three-dimensional position of points and the distances and angles between them. Prolong a Straight Line Forward from an Existing Point Prolong a Straight Line Forward from an Existing Point Line Needs to Extending Through an Obstruction ► 1. Find appropriate point C at angle α from AB direction. ► 2. Turn angle -2α at C and locate point D such that CD = BC. ► 3. Turn angle α at D to locate E and extension of original line. The Collinearity of A, B, D and E The line AB extended through B must meet CD say at some point D'. The Collinearity of A, B, D and E In a triangle each exterior angle is equal to the sum of the other two interior angles. Therefore <CBD’ and <CD’B are equal = α The Collinearity of A, B, D and E Becasuse <CBD’ and <CD’B are equal = α CD= BC = CD’, D=D’ A, B, D are collinear Horizontal Distance of a Surface A map is flat and shows all the points on the same level ► But the surface of the earth is rarely flat due to all the local ups and downs ► How do you calculate the distance between two objects of different height? ► Use the distance between two objects (on the slope) and the correction term Ch Horizontal Distance of a Surface Ch= L- d =L - √(L2-h2) Using the Pythagorean Theorem =L - L(1 - (h/L)2)1/2 Newton's binomial expansion (1 -x)1/2 = 1 - x/2 - x2/8 + ... with x = (h/L)2 Ch = h2/2L + h 4/ 8L3 Horizontal Distance of a Surface cos α = d/L d=L* cos α Ch= L- d = L- (L* cos α) Ch= L (1- cos α)