Recent Advances in IOP measurements
advertisement

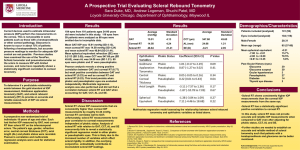
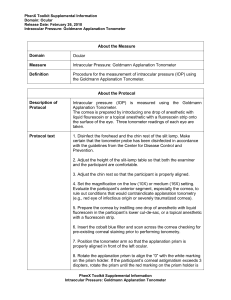
Recent Advances in IOP measurements Dr Deepak Megur Cataract and Glaucoma services Megur Eye Care Centre Bidar Karnataka Tonometry Why…? • Because…. – “IOP is the only modifiable risk factor in Glaucoma” – Most frequently examined parameter in the follow up of a glaucoma pt. What to use…? • Goldmann Applanation Tonometry • Gold Standard TonoPen: Acceptable (SEAGIG Asia Pacific Glaucoma guidelines) Factors affecting measured IOP. • Central Corneal Thickness: – Thicker Corneas: Artificially elevated IOP – Thinner Cornea: Artificially decreased IOP – Correction nomogram: • 525 Micron • 1 -3 mm hg per 40 micron deviation. ( SEAGIG Asia Pacific Guidelines 2004) Central Corneal Thickness • Measurement – Ultrasonic Pachymeter – Measured along / Before GAT – Time of measurement, waking hours • CCT – Predicting Risk factor – Prognostic significance – Response to drugs CCT independent IOP Measurements: • Pascal’s Dynamic Contour Tonometry • Contour Matching • Ocular Response Analyzer: – Corneal Hysteresis – Less influenced by • Corneal thickness and resistance Pascal’s Dynamic Contour Tonometry. • Slitlamp-mounted.. • Direct measurement of pressure - no systematic errors from force-to-pressure conversion. • Numerical display of result. • No mechanical calibration required; self-calibrating. • Convenient disposable tip prevents contamination and potential infection • Battery operated - no cabling. • Visual control of eye/tip interface through transparent SensorTip. • Single button operation. Pascal’s Dynamic Contour Tonometry • Dynamic contour tonometry (DCT) is a novel method which uses principle of contour matching instead of applanation. • This is designed to reduce the influence of biomechanical properties of the cornea on measurement. • These include corneal thickness, rigidity, curvature, and elastic properties. • It is less influenced by corneal thickness but more influenced by corneal curvature than the Goldmann tonometer DCT -Principles • It uses a miniature pressure sensor embedded within a tonometer tip contour-matched to the shape of the cornea. • The tonometer tip rests on the cornea with a constant appositional force of one gram. • When the sensor is subjected to a change in pressure, the electrical resistance is altered and the PASCAL's computer calculates a change in pressure in concordance with the change in resistance • The contour matched tip has a concave surface of radius 10.5 mm, which approximates to the shape of a normal cornea when the pressure on both sides is equal. • The probe is placed adjacent to the central cornea. • The integrated piezoresistive pressure sensor automatically begins to acquire data, measuring IOP 100 times per second. • A complete measurement cycle requires about 8 seconds of contact time. • The device also measures the variation in pressure that occurs with the cardiac cycle. (Ocular pulse Amplitude) I-Care Rebound Tonometer • • • • Contact tonometer Rebound principle Digital reading Probes changed for every patient Rebound Tonometers Principle • Determine IOP by bouncing a small plastic tipped metal probe against the cornea. • The device uses an induction coil to magnetise the probe and fire it against the cornea. • As the probe bounces against the cornea and back in to the device it creates an induction current from which the intraocular pressure is calculated. I-Care Rebound Tonometer • Advantages: – Fast – No Anaesthetic required – Pt friendly – children • Affected by corneal properties. – Thickness – Hysteresis Transpalpebral tonometry Diaton tonometer (BiCOM, Inc) • measuring intraocular pressure through the Eyelid. • Transpalpebral tonometry does not involve contact with the cornea and does not require sterilization of the device or topical anesthetic during routine use. • only moderate correlation with those provided by applanation tonometry • More affected by the corneal thickness than Goldmann tonometry. Diaton tonometer Principle… • The Diaton tonometer calculates pressure by measuring the response of a free falling rod • the principle is based on Newton's second law, as it rebounds against the tarsal plate of the eyelid. • The patient is positioned so that the tip of the device and lid are overlying sclera. Non-contact tonometry or airpuff tonometry • Non-contact tonometry: • It uses a rapid air pulse to applanate the cornea. • Corneal applanation is detected via an electro-optical system. • Intraocular pressure is estimated by detecting the force of the air jet at the instance of applanation. • Non-contact tonometry or airpuff tonometry • A fast and simple way to screen for high IOP. • However, modern non-contact tonometers have been shown to correlate well with Goldmann tonomtery measurements • Particularly useful – in children and other non-compliant patient groups. • non-contact tonometry – which reduces the potential for disease transmission…?