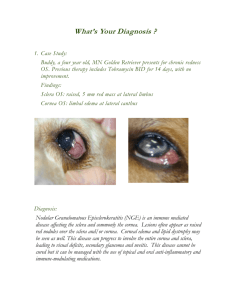
Sclera and cornea
advertisement

Sclera and Cornea Sclera cornea Sclera It forms the posterior portion of the globe It is perforated posteriorly by the optic nerve. Parts of sclera Episclera - Sclera proper Lamina fusca - fibrous tissue containing fine capillaries collagen fibres of the stroma located adjacent of the stroma Blood and nerve supply Choroidal vessels is supplying blood to Episcleral part Anterior insertion of Recti muscles, the anterior ciliary arteries form a dense episcleral plexes. These vessels becomes congestion of ciliary congestion. Nerve supply Short ciliary nerves posteriorly, Long ciliary nerves anteriorly provide sensory innervation. Inflammation of episclera Simple Nodular Diffuse Necrotizing with inflammation without inflammation Types of scleritis Anterior scleritis Posterior scleritis Cornea It is transparent part of the eye with circular wrist watch shape It is 10-11mm diameter It is the most important refractive state of the eye The junction of cornea and sclera is called limbus and also important angle structure of the eye. Part of cornea It has 5 layers in the anatomic structure Epithelium - Bowman’s membrane - Stroma Decemet’s membrane - Endothelium corneal epithelium rests on a basement of membrane secreted by the basal cells. condensation of substania propria - collagen fibrils arranged inset of lamellae, lying parallel to the surface. homogenous, very resistant membrane - single layer of flattened polygonal endothelial cells Blood supply and nerve supply Blood supply : Cornea is avascular structure. Nerve Supply : The cornea nerve, are derived from the long and short ciliary nerves of the ophthalmic division of trigeminal nerve. Types of ulcers Bacterial ulcer Fungal ulcer Viral ulcer Parasitic ulcer Degenerative condition Corneal dystrophies Bacterial ulcer It is defined as a break in the corneal epithelium with added infection Investigations Lacrimal sac syringing Diabetic status Corneal scrapping Gram and Giemsa stains for bacteria Culture on blood agar for aerobic organisms 10% KOH wet preparation for fungus Culture on Sabouraud’s dextrose agar for fungus Viral Ulcer with a branched appearance caused by herpies simplex virus. Investigations Sensation of cornea Fluorescent stain Enlarged and tender pre auricular lymph nodes Keratoconus Bilateral conical protrusion of central part of the cornea due to thinning is called Keratoconus In this condition we have to check keratometry to know the astigmatism Corneal dystrophies Cornea loses its clarity due to deposition of materials in various layers of the cornea it can be seen by Childhood Types of dystrophies Epithelial dystrophy - Map dot finger print Stromal dystrophy - Endothelial dystrophy - Granular or macular or lattice Fuch’s Don’ts in a case of corneal ulcer No Bandage No steroid drop ( except viral) No schiotz tonometer