DWT Based Beat Rate Detection in ECG Analysis
advertisement
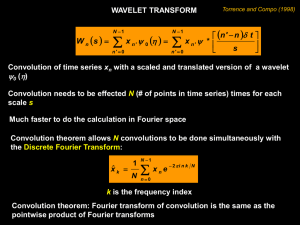
Applications of The Discrete Wavelet Transform in Beat Rate Detection Advisor:Jian-Jiun Ding Speaker:Jian-Hwu Wang Date:11/25/2010 DISP Lab, GICE, NTU 1 Outline • Introduction to Wavelet Transform • Applications of the Discrete Wavelet Transform in Beat Rate Detection – DWT Based Beat Rate Detection in ECG Analysis. – Improved ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet and Feature. • Conclusion • Reference DISP Lab, GICE, NTU 2 /22 Introduction to wavelet transform • Fourier transform is the well-known tool for signal processing. X ( f ) x(t )e j 2ft dt • One limitation is that a Fourier transform can’t deal effectively with non-stationary signal. • Short time Fourier transform X (t , f ) w(t )x( )e j 2f d where w(t ) is mask function DISP Lab, GICE, NTU 3 /22 Introduction to wavelet transform • Gabor Transform – The mask function is satisfied with Gaussian distribution. • Uncertainly principle t f 1 4 t x(t ) dt , x(t ) dt 2 2 where 2 t 2 f X ( f ) df X ( f ) df 2 2 2 f 2 • We expected to occur a high resolution in time domain, and then adjust t2 or 2f . DISP Lab, GICE, NTU 4 /22 Introduction to wavelet transform • The principle of wavelet transform is based on the concept of STFT and Uncertainly principle. – A mother wavelet (t ) . 1 t ( ) and translating (t b) . – Scaling a a • Sub-wavelets a ,b (t ) • Fourier transform 1 t b ( ) a a (t ) F[ (t )] a,b (t ) F[ a,b (t )] DISP Lab, GICE, NTU 5 /22 Introduction to wavelet transform • Continuous wavelet transform(CWT) wa ,b 1 a ,b , x(t ) a x(t ) a ,b ( t b )dt a • ICWT 1 x(t ) C dadb wa,b a,b (t ) a 2 where C 0 ( w) w dw and DISP Lab, GICE, NTU ( w) dw 6 /22 Introduction to wavelet transform • Discrete wavelet transform(DWT) wm,n x(t ), m,n a0m / 2 f (t ) (a0m (t ) nb0 )dt – Sub-wavelets m,n (t ) a0m/ 2 (a0m (t ) nb0 ) • IDWT m, n Z x(t ) wm,n m,n (t ) m n DISP Lab, GICE, NTU 7 /22 DWT applications for beat rate detection • DWT Based Beat Rate Detection in ECG Analysis – The purpose of this paper is to detect heart beat rate by the concept of discrete wavelet transform, which is suitable for the non stationary ECG signals as it has adeuate scale values and shifting in time. DISP Lab, GICE, NTU 8 /22 DWT Based Beat Rate Detection in ECG Analysis • ECG(Electrocardiogram) signal DISP Lab, GICE, NTU 9 /22 DWT Based Beat Rate Detection in ECG Analysis • Preprocessing – Denoise • Baseline wandering • Moving average method and subtraction procedure. DISP Lab, GICE, NTU 10 /22 DWT Based Beat Rate Detection in ECG Analysis • Preprocessing – Denoising : The wavelet transform is used prefiltering step for subsequent R spike detection by thresholding of the coefficients. • Decomposition. • Thresholding detail coefficients. • Reconstruction. DISP Lab, GICE, NTU 11 /22 DWT Based Beat Rate Detection in ECG Analysis • Feature extraction using DWT – Detect R-waves. – Thresholding. • Positive threshold. • Negative threshold. DISP Lab, GICE, NTU 12 /22 DWT applications for beat rate detection • Improved ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet and Feature. – This paper introduced wavelet to extract features and then distinguish several heart beat condition, such as normal beats, atrial premature beats, and premature ventricular contractions. DISP Lab, GICE, NTU 13 /22 Improved ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet and Feature. • Some kinds of ECG signal: Atrial premature beat Normal beat Premature ventricular contractions DISP Lab, GICE, NTU 14 /22 Improved ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet and Feature. • ECG signal analysis flow DISP Lab, GICE, NTU 15 /22 Improved ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet and Feature. • Feature Extraction – Matlab : wpdec function, the wavelet ‘bior5.5’. DISP Lab, GICE, NTU 16 /22 Improved ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet and Feature. • Feature Extraction – Energy 1 N 2 E( j)n ( x m ) i N 1 i 1 – Normal Energy E( j )norm_ n E( j)n E( j )12 E( j ) 22 E( j ) 2n – Entorpy N Ent( j )log_ n log(xi2 ) i 1 DISP Lab, GICE, NTU 17 /22 Improved ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet and Feature. • Feature Extraction – Clustering DISP Lab, GICE, NTU 18 /22 Improved ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet and Feature. • Method 1 wavelet: bior5.5, decomposition level: 1 and 3 with Method 1(●: normal beats, □: atrial premature beats, ○ : premature ventricular contractions) DISP Lab, GICE, NTU 19 /22 Improved ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet and Feature. • Method 2 wavelet: bior5.5, decomposition level: 1 and 3 with Method 2(●: normal beats, □: atrial premature beats, ○ : premature ventricular contractions) DISP Lab, GICE, NTU 20 /22 Conclusion • Wavelet analysis is widely used in many application. Because it provides both time and frequency information, can overcome the limitation of Fourier transform. • We can learn about the wavelet transform which is able to detect beat rate of signals and to classify the difference of signals. • We also use the wavelet transform on the other beat rate detection. DISP Lab, GICE, NTU 21 /22 Reference • Chui, C.K. (1992). An Introduction to Wavelets. Academic Press, San Diego, CA. • S.S. Joshi, C.V. Ghule, "DWT Based Beat Rate Detection in ECG Analysis," Proc. of IEEE International Conference and Workshop on Emerging Trends in Technology(ICWET 2010), pp. 765-769, 2010. • A. Matsuyama, M. Jonkman, F. de Boer, ”Improved ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet and Feature Extraction”, Methods Inf. Med.,vol. 46, pp.227-230, 2007 DISP Lab, GICE, NTU 22 /22 Q&A DISP Lab, GICE, NTU