Learning Wavelet Transform by MATLAB Toolbox
advertisement

Learning Wavelet Transform
by MATLAB Toolbox
Professor : R.J. Chang
Student : Chung-Hsien Chao
Date : 2011/12/02
Outline
• Wavelet evolution
• Wavelet transform toolbox in MATLAB
• Wavelet function in MATLAB
Wavelet evolution
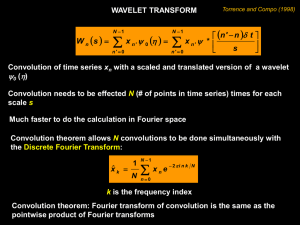
• Fourier transform:
F ( )
i t
f (t ) e
dt
• Time-frequency tile for Fourier transform:
f
t
• Poor time-localization
Wavelet evolution(count.)
• Short-time Fourier transform:
S ( , )
f (t ) w (t ) e
i t
dt
• Time-frequency tile for STFT:
f
f
f
t
t
• w(t-τ) is the window function.
t
f
1 / 2(H eisenberg U ncertainty P rinciple)
t
Wavelet evolution(count.)
• Wavelet transform:
s( t )
C
j,k
j,k ( t ),
k Z j Z
a ,b ( t )
1
a
(
tb
)
a, b Z
a
• Time-frequency tile for wavelet transform:
Translations and Scaling of a Wavelet
f
t
Wavelet evolution(count.)
• Compare these three methods:
Fourier transform
STFT
Wavelet
Resolution in time domain
and frequency domain
No resolution in
time domain
Low resolution in
time domain.
High resolution in
time domain.
Can analyze the nonstationary signal?
No
Yes
Good
Wavelet transform toolbox in MATLAB
• Decomposition and reconstruction :
2
h[n ]
~
h [n]
2
x[n ]
~y [ n ]
H
y H [ n ]
y H [n]
g[n]
~y [ n ]
L
y L [ n ]
y L [n]
2
2
~
x [n]
g~ [ n ]
• This structure contains for J = 3 the terminal nodes of the following tree.
Input signal
Level 1
Level 2
Level 3
Wavelet transform toolbox in MATLAB(count.)
• Step 1:
Type command “wavemenu” at
command window and hit the
Wavelet 1-D button.
• Step 2:
Load signal from “*.mat files”
or “workspace”.
• Step 3:
Select the mother wavelet and
levels, for example: db7, level 5.
• Step 4:
Push “Analyze” button.
Wavelet transform toolbox in MATLAB(count.)
• The signals include approximations(a) and Details(d):
s=a5+d5+d4+d3+d2+d1
d1
d2
d3
d4
a5 d5
Wavelet transform toolbox in MATLAB(count.)
• Step 6:
Push “Statistics” button to show the statistics of signal of each levels.
Wavelet transform toolbox in MATLAB(count.)
• Step 7:
Push “De-noise” button to remove the detail parts.
Wavelet transform toolbox in MATLAB(count.)
Wavelet function in MATLAB
• 1. Single-level discrete 1-D wavelet transform:
[cA,cD] = dwt(X,'wname')
Example:
load noissin
s = noissin(1:1000);
[ca1,cd1] = dwt(s,'haar');
plot(s)
subplot(121),plot(ca1)
subplot(122),plot(cd1)
1.5
1
0.5
0
-0.5
-1
-1.5
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
1000
s
2.5
0.8
2
0.6
1.5
0.4
1
0.2
0.5
0
0
-0.2
-0.5
-0.4
-1
-0.6
-1.5
-2
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
ca1
350
400
450
-0.8
500 0
50
100
150
200
250
cd1
300
350
400
450
500
Wavelet function in MATLAB(count.)
• 2. Single-level inverse discrete 1-D wavelet transform:
X = idwt(cA,cD,'wname')
Example:
load noissin
s = noissin(1:1000);
[ca1,cd1] = dwt(s,'haar');
X = idwt(ca1,cd1,'haar');
plot(X)
2.5
2
1.5
1
0.5
0
-0.5
1.5
1.5
-1
-1.5
1
-2
1
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
500
ca1
+
0.5
0.8
0.5
0
0
0.6
0.4
-0.5
-0.5
0.2
0
-1
-1
-0.2
-0.4
-1.5
-1.5
-0.6
0
100
200
300
400
500
s
600
700
800
900
1000
-0.8
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
cd1
350
400
450
500
0
100
200
300
400
500
X
600
700
800
900
1000
Wavelet function in MATLAB(count.)
• 3. Multilevel 1-D wavelet decomposition:
[C,L] = wavedec(X,N,'wname')
Example:
load sumsin
s = sumsin;
[c,l] = wavedec(s,3, 'db1');
Wavelet function in MATLAB(count.)
• 4. Reconstruct single branch from 1-D wavelet coefficients:
X = wrcoef('type',C,L,'wname',N)
Example:
load sumsin
s = sumsin;
[c,l] = wavedec(s,5, 'sym4');
a5 = wrcoef('a',c,l, 'sym4',5);
Thank you for your attention.