MapProj_tion
advertisement

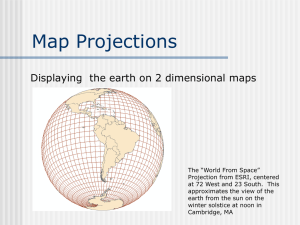
Map Projections April 13, 2015 For Summer School 1 Map Projections Meridians North-South lines (such as Longitude) Parallels East-West lines (such as Latitude) April 13, 2015 2 Map Projections Definition A map projection is a portrayal of the earth’s surface (or portion of the earth’s surface) onto a flat surface. There is no universally perfect projection system, thus there are a number of systems. April 13, 2015 3 Map Projections Why are they so important? Think of trying to trace lines from a globe onto a flat piece of paper. You can’t do it without folding, tearing, or stretching the paper. Map projections give us a controlled method for doing this. April 13, 2015 4 Map Projections April 13, 2015 5 Map Projections Stages of Map Projection Curved Surface (Datum Surface) Projection surface (Intermediate Surface) Plane Surface April 13, 2015 (Map Surface) 6 Map Projections Visualize a light shining through the transparent Earth onto a surface (Latitudes and longitudes Projected onto a Paper) April 13, 2015 7 Map Projections How projections are classified: 1. (a) By the distortions of Shape / Area / Distance / Direction • Shape • Area • Distance • Direction April 13, 2015 8 Map Projections How projections are classified:… (b) By properties • Conformal -maintains angles at which lines intersect • Equal-area -maintains area • Equidistant -maintains distances • Direction -maintains directions April 13, 2015 9 Map Projections How projections are classified:… 2. By the shape they are projected onto • Azimuthal: Projection of a sphere onto a plane. • Conical: Projection of a sphere onto a cone • Cylindrical: Projection of a sphere onto a cylinder. • Miscellaneous: Unprojected and other projections. April 13, 2015 10 Map Projections Aspect • Normal - equatorial / East-West • Transverse - North-South regions • Oblique - other angles April 13, 2015 11 Map Projections Cases ►Tangent – projection surface touches sphere ►Secant – surface cuts through sphere ►No distortion at contact points ►Distortion increases away from contact points April 13, 2015 12 Map Projections Tangent Cases April 13, 2015 13 Map Projections Secant cases April 13, 2015 14 Map Projections • Cones, Cylinders, Planes can be flattened without distortion • A point or line of contact is created when surface is combined with a sphere April 13, 2015 15 Map Projections Azimuthal Projections • Straight or curved meridians, curved parallels • Meridians radiate from poles • Parallels may be equally spaced April 13, 2015 16 Map Projections Azimuthal Projections Azimuthal Equidistant Used to show air-route distances. Distances from the centre are true, distortion radiates out from the center of the map. April 13, 2015 17 Map Projections Conic Projections • Straight meridians, curved parallels • Meridians radiate from poles • Parallels may be equally spaced April 13, 2015 Common Conic Projections • Albers • Lambert • Polyconic 18 Map Projections Conic Projections Albers Equal Area Conic Direction, area, and shape distorted away from the standard parallels. Areas and directions are true only in limited portions of a map. Used in regions with longer E-W orientation than N-S orientation. April 13, 2015 19 Map Projections Conic Projections Equidistant Conic Direction, area, and shape distorted away from the standard parallels. Areas and directions are true only in limited portions of a map. Used in regions near the equator. April 13, 2015 20 Map Projections Conic Projections Polyconic Scale is true along each parallel and along the central meridian. April 13, 2015 21 Map Projections Polyconic Properties - Scale is exact along each parallel and central meridian - Parallels are of circle but are not concentric - It is neither conformal nor equal area - Central meridian and equator are straight lines; all other meridians are complex curves - Free of distortion only along central meridian - It has rolling fit with adjacent sheet in E-W direction - Used in USA up to 1950 only - Used in India for topographical maps April 13, 2015 22 Map Projections Polyconic • Drawbacks - The main disadvantage is that it has rolling fit only. When two individual adjacent sheets are kept side by side with graticule showing N-S direction, we find there will be a gap. To avoid this gap the adjacent sheet is rolled and made fit. Thus if we take sixteen 15’ x 15’ quadrangle and try to fit them in one 10 x 10 quadrangle these will not fit exactly. April 13, 2015 23 Map Projections Conic Projections Lambert Conic Direction, area, and shape distorted away from the standard parallels. Areas and directions are true only in limited portions of a map. April 13, 2015 24 Map Projections Lambert Conformal Conic Projection: This projection is used in geographic maps of India and also in the gridded topographical maps. Its main features are : (i) It is conical and conformal i.e. shapes are preserved. (ii) Meridians and parallel cut at right angles everywhere i.e. at any point the scale is same in all directions, so that there is no local distortion. (iii) The projection can be with one or two standard parallels. The scale is true along the standard parallels. It is always better to adopt the projection with two standard parallels to limit distortions in scale over large area. (iv) The standard parallels are selected at 1/6th of the extent in NS directions i.e. Latitudinal extent. (v) Parallels are projected as unequally spaced arcs of concentric circles, more closely spaced near the center of the map. (vi) Meridians are equally spaced radii of the same circles, thereby cutting parallels at right angles. (vii) This projection is mainly used for the countries and regions with predominant east-west extent. April 13, 2015 25 Map projections Conformal Property - Angles on the surface of the datum are preserved on the map. - Shapes of small areas are preserved. - Meridians and parallels cut each other at right angles. April 13, 2015 26 Map Projections Standard Parallels -The projection can be with one or two standard parallels. -The scale is true along standard parallels. -Always better to adopt projection with two standard parallels to limit distortion in scale over large areas. -To design projection, limiting parallels & meridians are prescribed which cover the entire area to be projected. - Standard parallels are selected at 1/6th of the extent in N-S direction. - Central meridian is chosen midway between limiting meridians. - Value of central parallel is calculated mathematically. April 13, 2015 27 Map Projections Origin of Co-ordinate system is taken as point of intersection of central parallel and central meridian. To avoid negative values of co-ordinates assumed values are given to the origin. The assumed co-ordinates are Easting or x = 500,000 metres Nothing or y = 500,000 metres This results in an assumed origin which has coordinates x = 0 and y = 0 with respect to the system of rectangular co-ordinates. This is also known as False Origin. April 13, 2015 28 Map Projections Lambert Conformal Conic (With Two Standard parallels) April 13, 2015 29 Map Projections 76º 00 20º 80º 30 85º 00 20º Limiting Parallel 00 00 k>1 18º k=1 18º Standard Parallel 2 45 16º 15 19 45 k<1 ko=0.9990540231 O x = 5,00,000 m y = 5,00,000 m 13º 45 k=1 16º Central Parallel 15 19 13º Standard Parallel 1 45 k>1 12º 30 76º 00 April 13, 2015 80º 30 12º 30 85º 00 Limiting Parallel 30 Map Projections Cylindrical Projections • Straight meridians and parallels • Meridians equally spaced • Parallels unequally spaced April 13, 2015 Common Cylindrical Projections • Peters • Mercator • Universal Trnsverse Mercator 31 Map Projections Cylindrical Projections Peters De-emphasizes exaggerations in the high latitudes April 13, 2015 32 Map Projections Cylindrical Projections Mercator Emphasizes exaggerations in the high latitudes April 13, 2015 33 Map Projections Cylindrical Projections Transverse Mercator Projection • • • • • • • • Main features :It is a Transverse application of Cylindrical projection. Conformal i.e. shapes are preserved Central meridian, Equator and each meridian 90 degree from Central meridian are projected as straight lines. Other meridians and parallels are complex curves. Scale is true along central meridian and along two straight lines equidistant from and parallel to central meridian Scale becomes infinite 90 degree from central meridian Used extensively for quadrangle maps from 1:25,000 to 1:250,000 Not used in India, but extensively used in USA, Great Britain. April 13, 2015 34 Map Projections Cylindrical Projections Universal Transverse Mercator Grid (UTM): UTM is a particular case of Transverse Mercator Projection. It is a world wide projection system brought out by US army in 1947 for designating rectangular coordinates on large scale military maps of the entire world. Its specifications are given below :(i) The world is divided into 60 E-W equal parts from 180º W through 0º to 180º E and called 1 to 60. (ii) The N-S subdivision is from 80º S to 84º N being all 8º spread except the last one, which is 72º N to 84º N. The identification starts with ‘C’ from 80º S to 72º S, ‘D’ for 72º S to 64º S ……... and so on till 64º N to 72º N, and ‘X’ for 72º N to 84º N - remembering that alphabets ‘I’ and ‘O’are not used. April 13, 2015 35 Map Projections Cylindrical Projections Universal Transverse Mercator Defines horizontal positions into 6 zones. Each zone has a central meridian. Is actually 60 projections! April 13, 2015 36 Map Projections Cylindrical Projections Universal Transverse Mercator Defines horizontal positions into 6 zones. Each zone has a central meridian. April 13, 2015 37 Map Projections Illustration of Various Projections with same origin April 13, 2015 Difference in distance between Polyconic and LCC Found to be approximately 4 mm on scale 1:50,000, i.e 200 m. on ground. 38 Map Projections Choice of Projections:• There can be number of projections. It is purpose specific. However when one purpose is well served, other qualities need to be preserved as far as possible. A map can be of equal area type but then the conformality is certainly lost. When the area covered on map is rather small, all properties can be preserved within a small allowance, by almost all the projections. But when the portion of the globe that comes as a map is much, choice of projections becomes important. Again the choice of the projections will be influenced by location on the globe. If it is the whole globe, or only a hemisphere or a continent or two – the projection can vary. • Rhumb lines and great circles on globe are important for navigation and Mercator or Gnomonic projections are good respectively. In azimuthal maps, straight lines through center of projection are great circles on globe. April 13, 2015 39 Map Projections Projections used for different regions on Earth Polar Regions - Azimuthal Projections. Tropical Regions Conical Projections. (Mid-latitude Regions) Equatorial Regions - April 13, 2015 Cylindrical Projections. 40 Map Projections Some Examples of Projections & Maps • Topographical maps Polyconic Projection,LCC, Stereographic Azimuthal, Transverse Mercator, UTM etc.. • Geographical maps Lambert Conformal Conic ( large extent in N-S direction) (LCC) Projections * Cadastral Maps Cassini projection, LCC (small extent in E-W direction) * Air & Sea Navigation maps - i) Mercator Projection (Equatorial regions ) ii) Gnomonic projection ( Polar regions ) * World Maps in one piece Lambert’s Azimuthal Equal area, Mercator Projection, Gall’s Stereographic Cylindrical * Continents and Atlases Simple Conic, Bonne’s Equal area, Lambert Azimuthal Equal area, LCC April 13, 2015 41 Map Projections Comparision of Transverse Mercator projection with Lambert Conformal Conic projection * Both are excellent conformal map projections, used worldwide and can be used to map any area on any scale and for most of the applications. * Transverse Mercator projection is more suitable for areas predominant in North-South extent, whereas LCC projection is more suitable for areas predominant in East-West extent. * Closed formulae are available in respect of LCC making calculations easy, whereas in Transverse Mercator projection lengthy series formulae are used which are difficult to handle. April 13, 2015 42