Geography Tools
advertisement
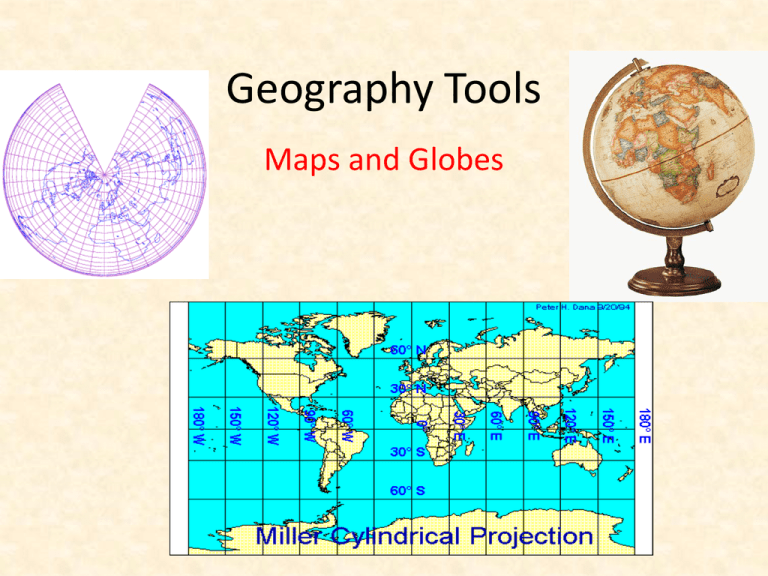
Geography Tools Maps and Globes Globes • Advantages: They are an exact representation of the Earth as it exists traveling through space. • Disadvantages: – Not easily portable – Can only see one half at a time since it is a sphere Maps – 2 Dimensional, graphic representations of the Earth’s surface • Advantages: – Can be drawn to any scale – Easily Portable • Disadvantages: – Distortion occurs because you are trying to put a round figure onto a flat surface Dealing With Distortion • To deal with distortion Cartographers use different types of map projections. • Cartographer – map maker • Map Projection – way to draw a map that reduces distortion 3 Types of Map Projections • Planar Projections • Conical Projections • Cylindrical Projections Planar Projection • Also known as Azimuthal • The details of the globe are projected onto a plane (a flat surface) yielding a rectangular-shaped map. • It distorts size and shape • A line drawn through the center to any point is the shortest possible line Conical Projection • Shows fairly accurate shapes, but its distorts along the edges…good for displaying large land masses Cylindrical Projections • 3 types of Cylindrical Projections: – Mercator – Homolosine – Robinson Mercator • Shapes of continents are distorted at poles, and somewhat compressed near the equator Homolosine • Shows accurate size and shapes of landmasses, but distances between these points are not correct (sometimes called interrupted maps) Robinson • Shows the entire Earth, with almost true sizes and shapes, but the shapes of the land near the poles are flat 3 Types of Maps • General Reference – usually topographic, showing natural and man made features of the earth • Thematic – emphasize specific types of information, such as climate, population, etc. • Navigation – used by sailors, pilots, etc Surveying • Surveying is the first step in the map making process • Types of surveying: – Remote Sensing – satellites or aerial photography (most modern surveying is done this way) – Out dated methods – exploring by sea and land Satellites and Geography • Landsat – a series of satellites that orbit more than 100 miles above the earth, they scan a path of land 115 miles wide while making their orbit, and can scan the entire earth in 16 days • GOES – Geostationary Operational Environment Satellite – most often a weather satellite; it orbits at the same speed as the earth’s rotation, in order to constantly update information about that exact spot on earth (Satellites continued) • GIS – Geographical Information System – collects and analyzes many different types of information; layers the information to draw conclusions – Ex. A map that shows population density, cities, natural landforms, and land use patterns (Satellites continued) • GPS – Global Positioning System – originally developed for the military; uses 24 satellites called NavStars to give an exact position (latitude, longitude, elevation, and time)