Shielded Metal Arc Welding PPT.
advertisement

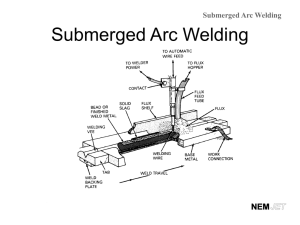
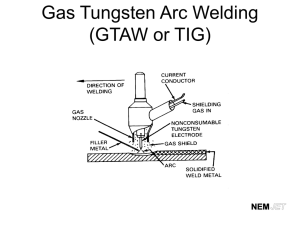
SMAW Shielded Metal Arc Welding OFW/OFC OXY FUEL WELDING OXY FUEL CUTTING Purge To blow or clean out the lines on the Oxy/Acetylene setup Flux Powdered coating around the electrode used in SMAW process. 1) Cleans metal/weld while welding 2) Cools Metal/weld/electrode while welding 3) Stabilizes the arc while welding 4) Keeps out atmospheric gases from the molten puddle Electrode Flux covered conductive rod used as filler in the SMAW process Slag Protective coating over completed weld made up of burnt flux, impurities that have rose to the top of weld which aid in the cooling process. Crater Indentation in the weld (below base metal) usually happens at the end of the weld Arc Length Distance between the tip of the electrode and the base metal. Also known as Arc Gap. Long Arc = large Gap Short Arc = Small Gap Shorter the Gap = Cooler the Arc Longer the Gap = Hotter the Arc Rod Angle Angle the electrode is held from the base metal 1)Base Angle (BA) 2)Direction of Travel Angle (DOTA) Porosity Gas Pocket in/on the weld that is a defect in the weld. Long arc will cause Dirty base metal Broken flux from the rod. Fusion Combining or joining of two materials Penetration Depth of Fusion Ductility Ability of metal to be bent or stretched without breaking 1) Rolled 2) Bent 3) Stretched Alloy What metal is made up of (Elements) 1) Periodic Table Zinc Magnesium Iron Flashback/Backfire 1) 2) 3) Hissing or Popping sound from tip of torch caused by gas and flame going back into the tip. Tip to close Dirty Tip Malfunction of equipment Amps The measure of Electrical Flow 1) electrons traveling 2) Water running out of a garden hose would be compared to Amps 3) Water Flow/Electrical Flow Volts Measure of Electrical Pressure 1) Force of electrons 2) Compared to your finger over a running garden hose to generate more pressure. 3) water pressure/Electrical pressure Puddle Molten metal that follows the electrode, this solidifies to create the weld. Arc Flash/Flash Burn Dangerous lights produced during Arc Welding that damage your eyes/skin if not protected with shaded/filtered lens or protective clothing. Dangerous lights: Ultraviolet/Infrared Arc Flash: Burns unprotected eyes Flash Burn: Burns unprotected skin SMAW <125 amps shade 10 Flash/Arc Burn Ultraviolent/Infrared Light Butt Joint Corner Joint Inside Outside Edge Joint T Joint Lap Joint Electrode #’s Tensile Strength Welding Position Special Characteristics 60 = 60,000 psi 1 = All Positions 0 = Deep/DC + / Fast Freeze 70 = 70,000 psi 2 = Flat/Horizontal 1 = Deep/AC/DC + / Fast Freeze 80 = 80,000 psi 3 = Flat Only 3 = Shallow /AC/DC+/DC- 90 = 90,000 psi 8 = Medium / AC/DC+/Low Hydro X 1000 lbs sq inch Tensile Strength Special Characteristics •Current Type •Flux Characteristics •Metal Type Electrode •Penetration E 60 1 1 Position E 60 11 60,000 psi Special Characteristics •Deep Penetration •Cellulose Potassium flux •Fast Freeze Electrode •AC/DC+ (current) E 60 1 1 All Position E 60 1 0 60,000 psi Special Characteristics •Deep Penetration •Cellulose sodium flux •Fast Freeze Electrode •DC+ (current) E 60 1 0 All Position E 70 1 8 70,000 psi Special Characteristics •Medium Penetration •Iron Powder Low Hydrogen flux •AC/ DC+ (current) Electrode E 70 1 8 All Position E 60 1 3 60,000 psi Special Characteristics •Shallow Penetration •Titania Potassium flux •AC / DC+ / DC - (current) Electrode E 60 1 3 All Position Electrode #’s Quiz Slide E Electrode 80 80,000 psi tensile strength 2 Flat/Horizontal Position 1 Deep Penetration Fast Freeze AC/DC + Tensile Strength Welding Position Special Characteristics 60 = 60,000 psi 1 = All Positions 0 = Deep/DC + / Fast Freeze 70 = 70,000 psi Electrode 80 = 80,000 psi E 90 = 90,000 psi 60 Low + Hydrogen Flux 2 = Flat/Horizontal 1 = Deep/AC/DC / Fast Freeze 60,000 psi tensile Flat Position strength Medium Penetration 3 = Flat Only Only 3 = Shallow /AC/DC+/DC+ 8 = Medium AC/DC / AC/DC+/Low Hydro 3 8 B. Welding Procedures (Cont.) b. A tapping movement is where the electrode is quickly tapped on the surface of the metal to prevent it from sticking to the base metal. 4 Things Required for a Good Weld Amp Setting : Heat and (proper current type) Travel Speed Rod Angle: (Base Angle/Direction of Travel Angle) Arc Length: Gap Should Equal Diameter of Electrode B. Welding Procedures (Cont.) 8. There are two methods used in starting the arc. A striking movement is similar to striking a match. Welding Positions Flat Horizontal Vertical: V Up/V Down (v up Gives deeper penetration) Overhead Flame Types Oxygen Odorless Gas Colorless Gas Line Colors Green Right Handed Threads on Fittings Types of Combustible Gases 3 types commonly Used for Fuel in Oxy/Fuel Welding and Cutting Acetylene Propane Mapp Gas (methylacetylene-propadiene propane) acetylene Colorless Gas Garlic Odor Unstable after 15psi Line Pressure Absorbed into Acetone (cork) to allow higher pressures in Tank Red Colored Hoses w/ Left Handed Threads Duty Cycle The amount of time a welding machine can be operated continuously 70% Duty Cycle= 70% of an hour 70% Duty Cycle = 7 minutes every 10 min Polarity DC+ DCEP Reverse Polarity DCDCEN Straight Polarity