PowerPoint-Präsentation
advertisement
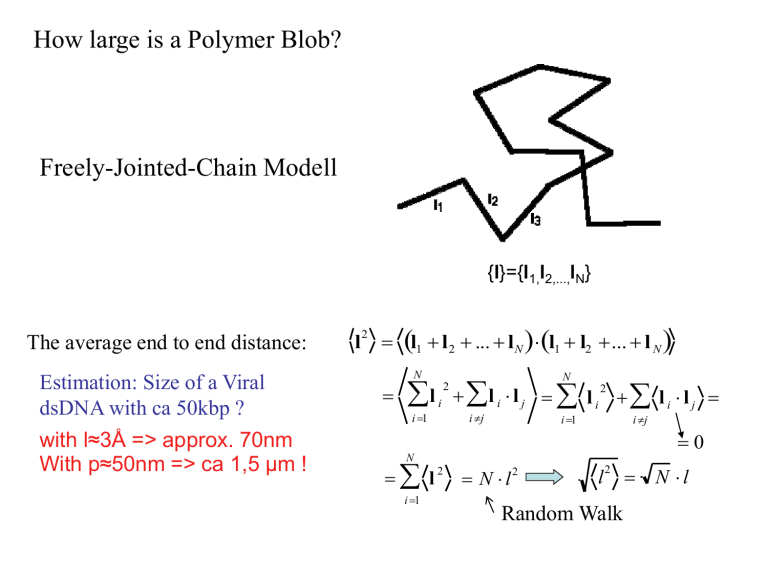
How large is a Polymer Blob?
Freely-Jointed-Chain Modell
{l}={l1,l2,...,lN}
The average end to end distance:
Estimation: Size of a Viral
dsDNA with ca 50kbp ?
with l≈3Å => approx. 70nm
With p≈50nm => ca 1,5 µm !
l
2
l1 l 2 ... l N l1 l2 ... l N
N
l
i 1
2
i
N
l i l j l i 2 l i l j
i j
i 1
i j
0
N
l 2 N l2
i 1
l
2
Random Walk
N l
The excluded Volume
• The simple model of a random walk resulted
for the end to end distance oft the polymer blob:
r2 N l2
• Problem: The polymer cannot occupy the same space. Thus the average quadratic
end to end distance should be bigger.
• Flory solved the problem with a simple heuristic argument:
If two monomers overlap, they repell each other. The Probability that 2 monomers
occupy the same space increases with the concentration squared
Energy Density:
W vkBT cm
W vkBT
N
2
r2
E Ausschluß W
Gaub/WS 2006
cm
2
N
r
2
3
The average end to end
distance is used as measure
for the radius of the
polymers.
6
r2
3
vkB T
BPM §1.4.2
N2
r
2
3
2
• The energy for the excluded volume drives the polymer blob apart. This force has
to be balanced by an entropic force which wants to keep the blob together:
EA usschluß W
FAusschluß
E Ausschluß
Fentr
3kT
2
Nl
1
2
l
Gaub/WS 2006
r
2
r
r
2
3
vkB T
r
2
r
r
2
5
v N
3
5
3
2
N2
r
2
4
(von FJC Model)
N2
vkBT 3
2
r
vkB T 3
3kT
2
N l
2
N2
r2
!
4
0
3
BPM
N §1.4.2
In contrast to the FJC Model
r
2
N
0.5
3
Java-Simulation Self-avoiding Random Walk
http://polymer.bu.edu/java/java/saw/sawapplet.html
The Worm-Like-Chain Model for semiflexible Polymers
s
s
A measure for the stiffness of a polymer is the persistence length Lp, which measures
at which length s=Lp the orientation and s are not correlated any more.
A measure for the correlation of the orientation oBdA
is the following average value:
f(s) cos (s) (0)
cos (s)
1
1
cos( ) d 2 O(d 4 ) sin( ) d cos( ) d 2
2
2
1
1
2
2
f (s) d
sin( ) d cos( ) d
2
2
df sin( ) d
=0
Gaub/WS 2006
d 2
df
1
BPM
f(s)§1.4.2
ds
ds
ds
2
5
Calculation: Energy change of a beam of length
s, if it is bent by the angle
Local Bending Radius
dU M d
E
mit M I
R
EI 1
dU
d s
R R
U
0
d 1
ds R
R
EI 1
d s
R R
1
R0
R s
d 2
1 EI
EI 1
1
d s
EI s
2 s
ds
2 R0
R R
2
s
d 2 2 U
ds EI s
d 2
df
1
f(s) ds
ds
ds
2
d 2 2 U
ds EI s
df
1
kT
f(s)
Äquipartition Theorem
ds
2
EI
in 2-D
f(s) f (0)e
U
df
f (s)
ds
EI
Bending is a thermodynamic
degree of freedom
kT
s
2EI
in 3-D two angles can fluctuate, each containing the average energy kT/2.
in 3-D
f(s) f (0)e
s
Lp
f(s) f (0)e
Lp
EI
kT
kT
s
EI
DNA Lp=53 nm
Aktin Lp = 10 µm
Mikrotubuli Lp =1 mm
Persistence length
Connection between FJC und WLC-Modell
s
r
t ds
L
L
r r r t(s) ds t(s) ds
0
0
2
L
2
L
t(s) t( s) ds ds
2
s0 s s
L
2
L
f ( s s) ds ds 2
s0 s s
Comparison with FJC
2
2
r N l N ll L l
Gaub/WS 2006
L
L
s0 s s
L
L
e
s0 s s
s s
Lp
L L
t(s) t( s) ds ds
0 0
cos ( s) (s) ds ds
L Lp
L
L
2 Lp
2 L L
2
L
e
1
ds ds
p
p
L
p
Both models yield the same average
end to end distance when the chain
of FJC coincides with twice the
l 2
L
BPMp§1.4.2persistence length
8
l=2Lp
Force Extension Curves: Comparison of Models
Freely Jointed Chain (FJC)
F l kT
F l
: N l L
r N lcoth
k T
k T F l
kT 1 r For negligible
F
L
N l fluctuations
l
Worm-like Chain Model (WLC)
With Stretch Modulus K0 of Monomer
(e.g. stretching of DNA)
Force Extension Curve of dsDNA