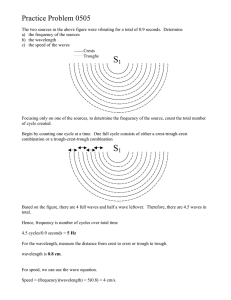
Name _______________________________________ Hour ____________________________ Chapter 5 Test Review ● These are just a few examples for you to practice with. Other resources to use will be your chapter 5 packet, past assignments, notes from class and your BOOK! Directions: Define and use the following terms or vocabulary words. ● Electromagnetic radiation ● wavelength, amplitude, frequency, crest, trough ● Electromagnetic spectrum ● Temperature ● quantum/quanta ● Photoelectric effect ● Photons ● Atomic emission spectra ● Ground state electron configuration ● Aufbau Principle ● Pauli Exclusion Principle ● Hund’s Rule ● Electron Orbital Diagram ● Noble Gas Notation ● Valence Electrons ● Electron Dot Diagram ● Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom ● Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle ● Energy sublevels (s, p, d, f) Equations: Know how and when to use the following equations and constants. C = λν Equantum = hν Ephoton = hν C = 3.00 x 108 m/s h = 6.626 x 10-34 Js Directions: Use the equations and constants to answer the following questions. 1. What wavelength of light is needed to eject a photoelectron from atoms of platinum, which require at least 9.8 x 10-19 J/photon? (2 steps) 00000000000000000098 2. What is the frequency of a wave with a wavelength of 3.2 nm? What type of electromagnetic wave is this? f= c λ 3. Fill in the following chart. Energy Level 1 2 3 4 Sublevels (s, p,d, or f) # electrons S P D F 2 6 10 4. Draw the shapes of the following orbitals and indicate where you are most likely to find electrons. 1 orbitals S 3 orbitals P 6 orbitals d 5. Label the wavelength, amplitude, trough and crest. The bumps are the wave the space in the bumps are amplitude the bottom is the trough and the crest is the top 6. What is the frequency of the wave above? Hz 7. Use this electromagnetic spectrum to answer the following questions: a) Which type of radiation has the longest wavelength? Radio waves b) Which type of radiation has a frequency of about 106 Hz? c) What is the relationship between wavelength and frequency? Wavelength is directly proportional d) Which type of radiation has the longest wavelength and shortest frequency? Gamma 8. Write the ground state electron configurations for the following elements: a. Copper (Cu) 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d b. Silicon (Si) 1s22s22p63s23p2 c. Bromine (Br) [Ar]4s²3d¹⁰4p⁵ 9. Write the noble gas configuration for the following elements: a. Nobelium (No) Rn 5f14 7s2 b. Bismuth (Bi) 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p3 c. Ytterbium (Y) Xe 4f14 6s2 10. Draw the orbital diagram for the following elements: a. Neon (Ne) Cant do b. Potassium (K) Cant do 11. Which element ends in the configuration 4d6? Rhodium 12. Which element ends in the configuration 6s1? xenon 13. Which element ends in the configuration 5d2? 14. Which element ends in the configuration 5p2? chlorine 15. Which element ends in the configuration 2p5? Silicon 16. Draw the electron dot diagrams for a. Sodium b. Carbon c. Oxygen d. Krypton