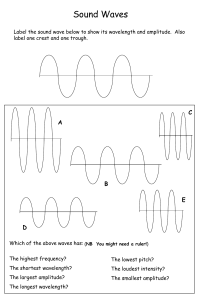
PARCC Packet part 1
advertisement
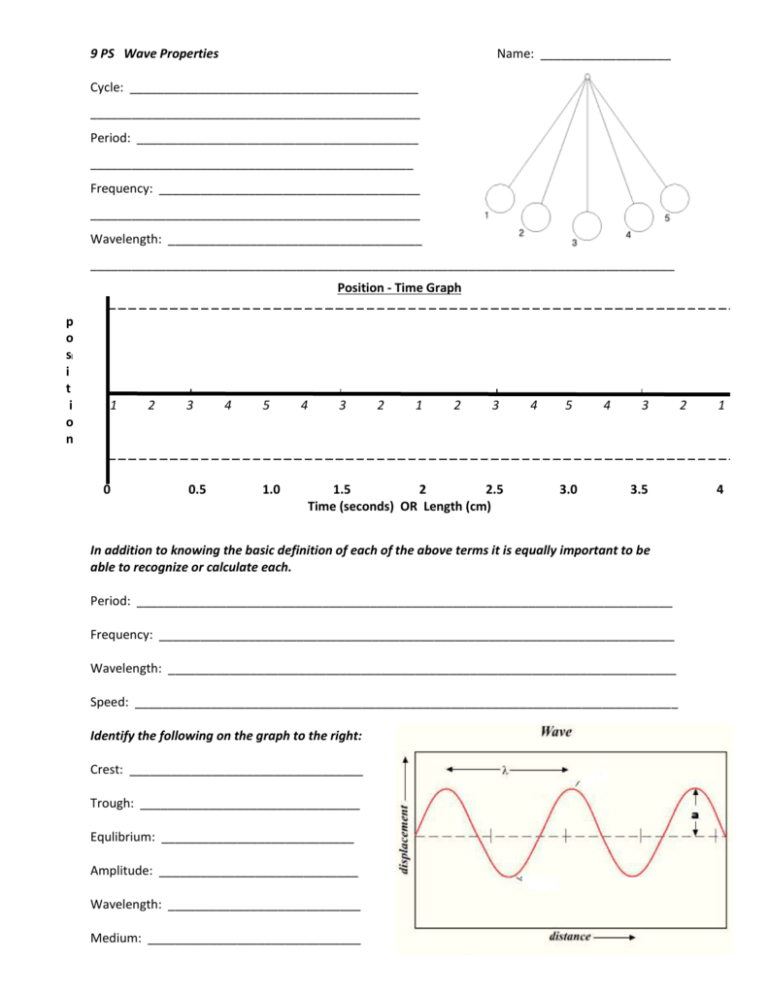
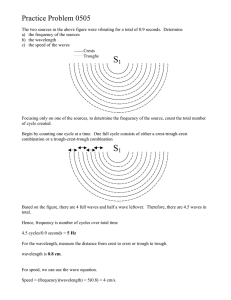
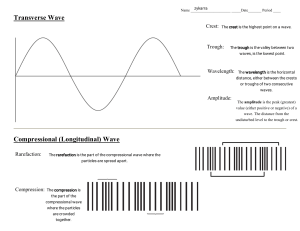
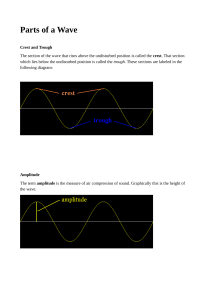
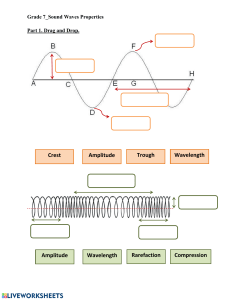
9 PS Wave Properties Name: ___________________ Cycle: __________________________________________ ________________________________________________ Period: _________________________________________ _______________________________________________ Frequency: ______________________________________ ________________________________________________ Wavelength: _____________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Position - Time Graph _____________ p o s i t i o n 1 0 2 3 0.5 4 5 1.0 4 3 2 1 2 3 1.5 2 2.5 Time (seconds) OR Length (cm) 4 5 3.0 4 3 3.5 In addition to knowing the basic definition of each of the above terms it is equally important to be able to recognize or calculate each. Period: ______________________________________________________________________________ Frequency: ___________________________________________________________________________ Wavelength: __________________________________________________________________________ Speed: _______________________________________________________________________________ Identify the following on the graph to the right: Crest: __________________________________ Trough: ________________________________ Equlibrium: ____________________________ Amplitude: _____________________________ Wavelength: ____________________________ Medium: _______________________________ 2 1 4 Period and Frequency Solve the following problems - use 3 step math. 1. A dog's tail wags 50.0 times in 40 seconds. a. what is the frequency? b. the period? 2. A computer screen refreshes 150 times in 2 seconds. a. what is the frequency? b. the period? 3. Tarzan is swinging back and forth on a vine. Each complete swing takes 4.0 seconds. a. what is the period? b. the frequency? 4. A certain tuning fork makes 7,680 vibrations in 30 seconds. a. what is the frequency? b. the period? Complete each sentence by circling the correct answers and crossing out the incorrect answer. 1. The amplitude of a wave can be measured from the (medium, crest) or the (trough, wavelength) to the equilibrium (rest position) of the wave’s medium. 2. Waves with greater amplitudes carry (more, less) energy than waves with smaller amplitudes. 3. The wavelength of a transverse wave is often measured from (crest to crest, crest to trough). 4. The number of waves that pass a point in one (second, minute) is the wave’s (amplitude, frequency). 5. Waves with longer wavelengths have a (lower, higher) frequency and waves with shorter wavelengths have a (lower, higher) frequency. Label the appropriate parts of the diagram below. Be careful - not all letters can be identified with a term. F