Lecture 9
advertisement

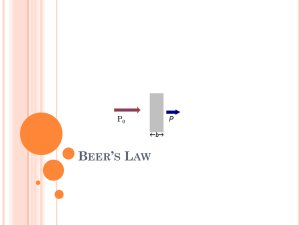
UV/VISIBLE SPECTROSCOPY UV/VIS Spectroscopy What does a UV/Vis Spectrometer Measure? UV/VIS Spectroscopy Transmittance (T) is defined as the amount of light passing through the sample solution (P) divided by the amount of incident radiation (Po) T = P/Po In practice Po is estimated by a “blank” which accounts for reflection and scattering losses. UV/VIS Spectroscopy As the radiation is absorbed in the sample, the total intensity of radiation is reduced as it travels through the sample. This results in a non-linear relationship between transmittance and concentration. UV/VIS Spectroscopy Absorbance (A) is based on the amount of light absorbed by the solution and is defined as the log of the inverse of the transmittance. A = log10(1/T) UV/VIS Spectroscopy Within limits, the relationship between absorbance and concentration is linear. UV/VIS Spectroscopy Beer’s law or the Beer-Lambert law A = bc is the molar absorptivity with units of (L/mol-cm) b is the path length of the sample ie. the inside cross section of the sample cuvette (cm) c is the concentration of the compound in solution in (mol/L) UV/VIS Spectroscopy Increased interaction between the molecules can affect absorbance at high concentrations. Electrolytes can also alter the molar absorptivity of the analyte by electostatic interactions. Molar absorptivity is also altered by the refractive index of the solution. UV/VIS Spectroscopy When an analyte associates or dissociates in solution producing products with different absorption spectra, deviations from Beer’s law can be observed if the equilibrium shifts at different concentrations. Hindicator H+ + Indicator- UV/VIS Spectroscopy Other causes of deviation from Beer’s law: Radiation is not monochromatic Stray radiation Absorbance readings less than 0.10 and higher than 1.5 can contain significant error and should be avoided. UV/VIS Spectroscopy Absorbance Quantification of Two Compounds Spectra of Compound 1 Spectra of Compound 2 Wavelength UV/VIS Spectroscopy Quantification of Two Compounds The method to determine the concentrations of two compounds (a & b) in a mixture involves the simultaneously solution of the following two equations: At wavelength 1 A1 = ea1ca + eb1cb At wavelength 2 A2 = ea2ca + eb2cb UV/VIS Spectroscopy A = bc Quantification of Two Compounds At wavelength 1 A1 = ea1ca + eb1cb At wavelength 2 A2 = ea2ca + eb2cb Where ea1, eb1, ea2, eb2 are the molar absorptivities for the two compounds at the two wavelengths which are determined from standard solutions and ca and cb are the concentrations of the two unknown compounds. UV/VIS Spectroscopy Quantification of Two Compounds EXAMPLE Sample Compound a Compound b Absorptivity at λ465 11636 17949 Absorptivity at λ540 26579 2667 Absorbance of the mixture at λ465 = 0.870 at λ540 = 0.362 UV/VIS Spectroscopy Quantification of two compounds Set up equations: (1) (2) 0.870 = 11636ca + 17949cb 0.362 = 26579ca + 2667cb multiply equation (2) by 6.73, giving equation (4): (3) (4) 0.870 = 11636ca + 17949cb 2.436 = 178877ca + 17949cb UV/VIS Spectroscopy Quantification of two compounds Set up equations: (3) (4) 0.870 = 11,636ca + 17,949cb 2.436 = 178,877ca + 17,949cb Subtract (3) from (4), giving equation (5): (5) 1.566 = 167,240ca UV/VIS Spectroscopy Quantification of Two Compounds (5) 1.566 = 16724ca Solve for ca: (6) ca = 9.36 x 10-6 moles/L = concentration of compound a Substitute value from (6) into equation (1) and solve for cb: 0.870 = 11636(9.36 x 10-6) + 17949cb 0.870 = 0.109 + 17949cb 0.760 = 17949cb cb = 4.24 x 10-5 moles/L = concentration of compound b