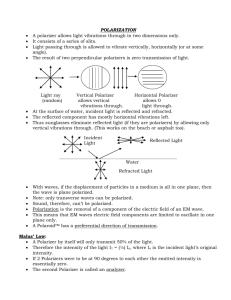
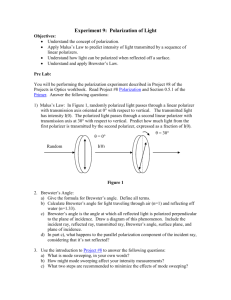
24.Polarizers

Through the Looking Glass and What We Found There
n
c j
k
Reduced phase velocity:
Absorption: n
TE TM
Brewster’s Angle
At Brewster’s Angle, the Transverse Magnetic mode is not reflected, leaving only a Transverse Electric polarized reflection.
TE + TM
TE
“glare”
Physical Interpretation
An oscillating charge radiates strongest perpendicular to the oscillation, and zero along the oscillation.
At Brewster’s angle, the refracted beam causes dipoles to oscillate along the reflected direction.
Homogeneous - same properties at all points.
opposite: inhomogeneous
Isotropic - same properties in all directions.
opposite: anisotropic
Polarizers, phase retarders, and rotators: based on anisotropy in n+j
Linear Polarizer
“dichroism”
1. The effect of causing white light to be split into colors.
2.
absorbed by different amounts (anisotropy in ) .
Linear Polarizer polarizer analyzer transmission axis (TA)
The effect of a polarizing element is described by its Jones Matrix, which multiplies the light’s Jones Vector.
0
0
0
1
TA vertical
1
0
0
0
TA horizontal
sin cos
2
cos
sin
sin
2 cos
TA at