File
advertisement

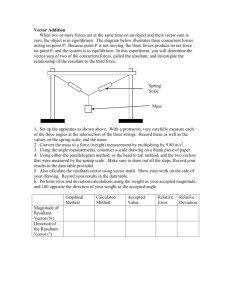
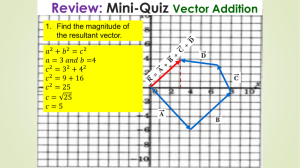
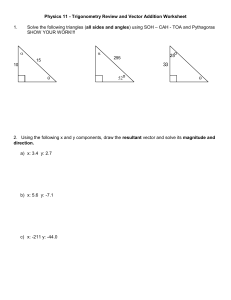
Keswick School Physics Department Summer unit Year 11 into Year 12 2015 During the summer holidays, you are required to complete this preparation unit which will be used during the first lessons of your Year 12 course. The work is divided into three sections. 1. Recap of GCSE 2. Electricity 3. Mechanics Each section of this task will be taken in by the teacher who will be teaching the relevant section of the specification. Please bring this work to the first lesson in September. Section 1 Recap of GCSE. You have been issued with a book “Headstart to A-Level Physics” Your task is to read each page of the book and answer the questions at the bottom of the page. You must then mark the work in a different colour pen to that which you used to answer the questions. You will be expected to hand this work in during the first lesson in September. Section 2 Electricity You are a brand new physics teacher in training and your first job in your new school is to teach the new Year 12 AS class about electricity. The specification for this section of work is shown below Your task is to produce a set of notes for your students. In the notes you need to: Explain the terms VOLTAGE, POTENTIAL DIFFERENCE, CHARGE, CURRENT, and RESISTANCE, including the differences between them; Include any relevant definitions and units; Explain how current flows through a wire; Explain how energy is transferred to the components in the circuit; Explain the difference between SERIES & PARALLEL circuits Explain how the current knows which way to split at a junction These notes are to be handed in to the teacher who is taking you for this unit of work. Section 3 Mechanics Name .................................................... The specification for the first part of the mechanics section of work is shown below Start to learn about this section by looking at the following links. (There is lots of other material on the internet.) http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/A-level_Physics/Forces_and_Motion/Scalars_and_vectors https://www.khanacademy.org/test-prep/mcat/physical-processes/vectors-andscalars/v/introduction-to-vectors-and-scalars http://www.cyberphysics.co.uk/topics/forces/vectors.htm Then, answer the following questions 1. Which of the following are vector quantities? Speed, acceleration, velocity, distance, mass, friction, density, upthrust, 2. Explain why 5N + 4N does not always mean a resultant force of 9N 3. What is the resultant force in a tug of war competition when one team pulls right with 240N and the other team pulls with 320N in the opposite direction? 4. Draw a scale vector diagram showing the resultant force of 3N and 5N pushing a mass west. 5. Draw a scale vector diagram showing the resultant force of 4N and 2N pulling a mass west. 6. Calculate the resultant forces on the masses below 2N 4N 2N 4N 3N 2N 4N 6N 4N 6N 3N 6N 4N 2N 7. William and Adam are both trying to pull a horse out of a horsebox. William stands straight in front of the horse and pulls with a force of 120N. Adam stands slightly to the side at angle of 30o to the direction in which the horse will move and pulls with a force of 150N. a. Whose force causes the greater effect of the horse? b. Draw a scale vector diagram to show the resultant force. c. If the horse is not moving, what force must it be exerting? 8. This is a question from an AS standard paper (a) State the difference between vector and scalar quantities. (1) (b) State one example of a vector quantity (other than force) and one example of a scalar quantity. (2) (c) A 12.0 N force and a 8.0 N force act on a body of mass 6.5 kg at the same time. For this body, calculate (i) the maximum resultant acceleration that it could experience, (ii) the minimum resultant acceleration that it could experience. (4) (Total 7 marks)