File
advertisement

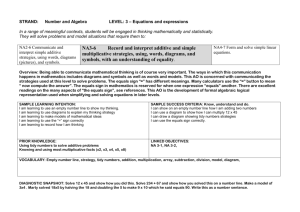
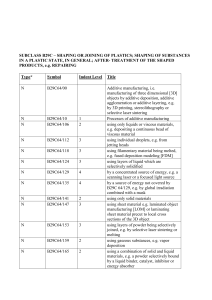
idtech S. Y. 2 0 1 1 - 2 0 1 2 Principles of Design Essentials of the Structure • INVISIBLE STRCUTURE the plan is the beginning of the structure. From within to without VISIBLE STRUCTURE FORM -direction -shape SURFACE -texture -tone -color • FORM – the primary identifying characteristic of a volume, it is determined by the shapes and interrelationships of the plans that describe the boundaries of the volume. “general to the particular” , mass to detail • MASS - a shape or three-dimensional volume that has or gives the illusion of having weight, density, and bulk. • VOLUME - The amount of space occupied by a three-dimensional object or region of space, expressed in cubic units. VISIBLE STRUCUTRE -direction Vertical Dominant vertical with horizontals Horizontal Major & two minor horizontals VISUAL PROPERTIES OF FORM The principal identifying characteristic of form Shape The real dimension of form Size The hue, intensity and total value Color The surface characteristic of form Texture The form’s location relative to its Position environment or visual field The form’s position relative to the Orientation ground plane. Compass point The degree of concentration Visual Inertial and stability of form • VISUAL PROPERTIES OF FORM a. Shape – the principal identifying characteristic of form. circle – is centralized, introverted figure that is normally stable and self centering in its environment. triangle – signifies stability when resting on one of its sides but tends to fall over onto one of its sides. square – represents the pure and national. It is static and neutral figure having no preferred direction PLATONIC SOLIDS SPHERE Rak Convention and Exhibition Center, UAE By: Ras Al Khaimah By: C Ledoux PLATONIC SOLIDS CYLINDER Rotonda de la Villette, Paris by: Arch. C. Ledoux Chapel of MIT by: Arch Eero Saarimen PLATONIC SOLIDS CONICAL Museum of Glass Metropolitan Cathedral, Rio, Brazil TRANSFORMATION OF FORMS DIMENSIONAL TRANSFORMATION ADDITIVE TRANSFORMATION SUBTRACTIVE TRANSFORMATION • ADDITIVE FORMS by SPATIAL TENSION – two forms relatively close to each other, or share a common visual traits such as shape, material of color • ADDITIVE FORMS by EDGE TO EDGE CONTACT – to forms share a common edge, and can pivot about an edge Claude-Nicolas-Ledoux-Architecture • ADDITIVE FORMS by FACE TO FACE CONTACT – two forms to have flat, planar surface that are parallel to each other. • ADDITIVE FORMS by INTERLOCKING VOLUMES – two forms interpenetrate each other’s space • FIVE DIAGRAMS OF FORMS CENTRALIZED FORMS – a number of secondary forms clustered about dominant, central, parent forms. • FIVE DIAGRAMS OF FORMS LINEAR FORMS – consist of forms arranged sequentially in a row. • FIVE DIAGRAMS OF FORMS RADIAL FORMS – composition of linear forms that extend outward from central forms in radial manner. • FIVE DIAGRAMS OF FORMS CLUSTERED FORMS – consist of forms that are grouped together by proximity or sharing of a common visual trait. Same Shape Same Shape different sizes same size • FIVE DIAGRAMS OF FORMS GRID FORMS – modular forms whose relationship are regulated by three dimensional grids.