problemsolving
advertisement

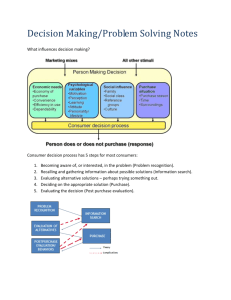
COGNITION Area of psychology that refers broadly to mental processes or thinking Problem Solving Refers to the active efforts to discover what must be done to achieve a goal that is not readily attainable Must go beyond given information to overcome obstacles to reach goal/solution Types of Problems Problems of Inducing Structure – Must discover relations among parts of problem • Analogy Merchant:Sell::Customer: ___ • Series Completion +-XX++-X++--X++-??X Problems of Arrangement – Arrange parts in a way that satisfies some criterion – Often solved w/burst of insight • Anagrams: elsnsmea = salesmen • String Problem p. Problems of Transformation – Must carry out a sequence of transformations in order to reach a goal • Hobbits & Orcs • Water Jar Problem Barriers to Problem Solving Irrelevant Information: trying to use all info. to solve a problem/numerical Functional Fixedness: a tendency to perceive only a limited number of uses for an object, thus interfering with the process of problem solving Mental Set: the tendency to perceive and to approach problems in certain ways--especially ones that worked in the past Try to figure this out… What is the pattern of the following numbers: •8 5 4 1 7 6 3 2 0 More barriers… Unnecessary Constraints: perceiving barriers that don’t exist – People usually make assumptions that impose unnecessary constraints on problem-solving • Nine-dot problem Producing Strategies & Evaluating Progress Trial & Error: works best with limited choices Algorithm: step-by-step problem-solving method that guarantees a solution Heuristics: short cuts to problem solving; called “rule of thumb” used to simplify problem – Forming subgoals – Analogy – Changing representation of problem-good to use when your initial attempts were unsuccessful Unscramble the following letters… G S P L O Y O C H Y – Algorithm • All 90, 208 combinations – Heuristic • Throw out all YY combinations Decision Making Involves evaluating alternatives and making choices among them Simon’s theory of bounded rationality: asserts people frequently make irrational decisions that are less than optimal – We tend to use simple strategies that only give us a few options where more are available Making Choices Additive Strategy: list/weigh options (p. 231) Elimination by Aspects: alternatives are eliminated by evaluating attributes We tend to use additive more often, however, as more options/factors are added we switch to elimination by aspects. Decision Making Heuristics Availability: easily retrieved information from LTM sways decision • KLNRV: Do these letters appear more often in the 1st or 3rd letter position? • Is flying more dangerous than driving? » People tend to overestimate the likelihood of improbable events Representativeness: resemblance to a stereotypic model used to judge a new situation • Steven is articulate, outgoing, artistic, and politically liberal. Is it more likely that he: – A) is an engineering major, or – B) started out as an engineering major and switched to journalism? » Illustrates conjunction fallacy Confirmation Bias: seeking evidence in support of our beliefs; ignoring evidence that is not Overconfidence Effect: people put too much faith in their estimates, beliefs, and decisions – We tend to be more confident than accurate! – The more confident we are about our predictions, the more likely we are overconfident. (p. 237)