ANNISTON ARMY DEPOT COMMANDER`S OFFSITE
advertisement
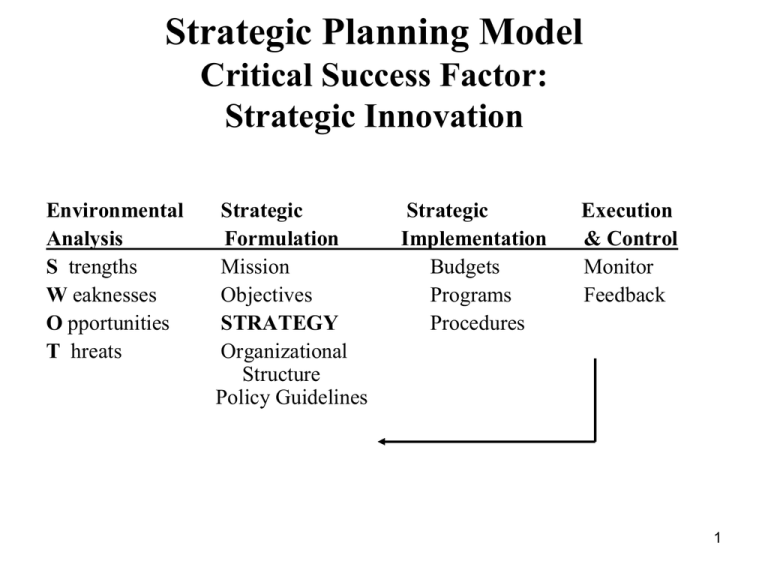
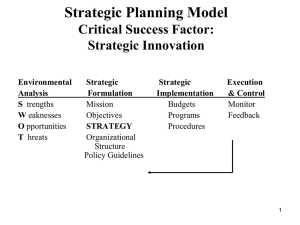
Strategic Planning Model Critical Success Factor: Strategic Innovation Environmental Analysis S trengths W eaknesses O pportunities T hreats Strategic Formulation Mission Objectives STRATEGY Organizational Structure Policy Guidelines Strategic Implementation Budgets Programs Procedures Execution & Control Monitor Feedback 1 Life Cycle and Competitive Advantage Introduction R&D Tech change Attention to quality Design change Process change Growth Improve product Econ of scale Process improve Distribution Value added Forecasting Maturity Decline Focus on Cost Control Standardize Reduce capacity Efficiency Cut products Costs cuts Few changes Optimal capacity Creating a Sustainable Competitive Advantage (David A. Aaker, 1989) Stage of the Product Life Cycle, Business Strategy, and Business Performance (Anderson & Zeithaml, 1984) 2 Competitive Forces Shape Strategy How Competitive Forces Shape Strategy: “By being aware of competitive forces, an organization can position itself to be less vulnerable to attack” (Michael E. Porter, 1979) 3 Competitive Forces Shape Strategy Porter’s 5 Forces Model Threat of New Entrants Bargaining Power of Suppliers Industry Competitive Rivalry Bargaining Power of Customers Threat of Substitutes 4 Strategic Advantage Differentiation (RCA used its R&D strength and its organizational structure to market successfully Color TV) Transformation: From ordinary to revolutionary Low Cost (Southwest Airlines strives to recruit and train the best personnel available, create innovative flight schedules, stress strong customer support, and provide high pay for employees) Transformation: From in-state service to national to? 5 Strategic Advantage Response (FedEx uses a hub-and-spoke system to rapidly respond to request for package shipments worldwide) Transformation: From national letter carrier to global cargo carrier Diversification (Boeing reacts to the maturing airframe market) Transformation: From an airplane builder to a hightech product and service provider 6