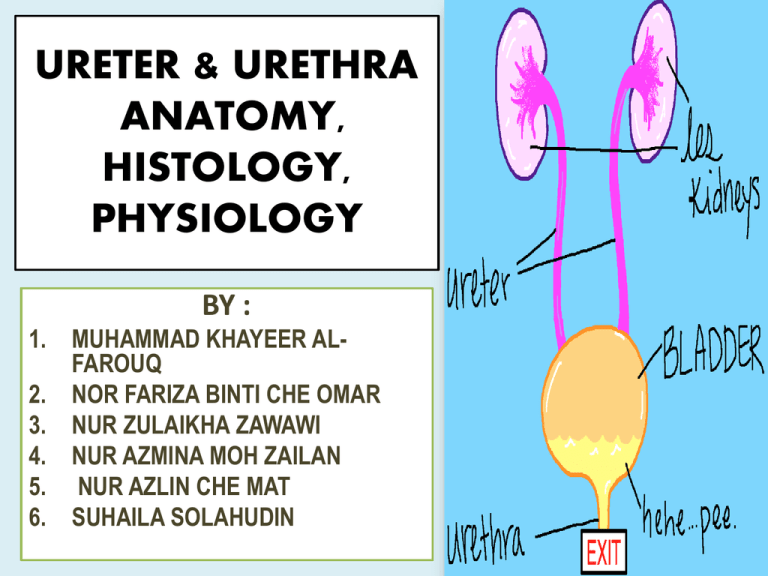
URETER & URETHRA
ANATOMY,
HISTOLOGY,
PHYSIOLOGY
BY :
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
MUHAMMAD KHAYEER ALFAROUQ
NOR FARIZA BINTI CHE OMAR
NUR ZULAIKHA ZAWAWI
NUR AZMINA MOH ZAILAN
NUR AZLIN CHE MAT
SUHAILA SOLAHUDIN
ANATOMY OF THE URETER
BY : MUHAMMAD KHAYEER AL- FAROUQ
D11B040
• The ureter is a muscular tube, which passes
caudally In the retroperitoneal along the dorsal
body wall.
• Reaching the pelvic cavity, it turns medially to
enter the broad uterine ligament in the female,
and yto the mesoductus deferens in the male.
• Ureter ends by inserting into the dorsolateral
surface of the urinary bladder within the lateral
ligament of the bladder.
URETER
Urogenital system of cat
Ventral aspect
ANATOMY OF URETHRA
BY : NOR FARIZA BINTI CHE OMAR
D11B041
Female urethra
• Female urethra extends
caudally on the pelvic
floor ventral to the
reproductive tract. It
passes obliquely through
the wall of the vagina and
opens with the external
urethral opening (ostium
urethrae externum)
ventrally at the junction
between vagina and
vestibule.
• The length and diameter of
the urethra varies
considerably between the
domestic mammals.
• Horse : short and wide and
comparatively long in the
dog were it opens on a
small elevation flanked by
two grooves.
• Cow and sow : urethralis
muscle encloses the
suburethral diverticulum
which opens together with
the urethra into the
vagina.
Ureteral
orifice
Urethral crest
Urethral m.
Suburethral
diverticulum
External urethral
orifices
Male urethra
• Extends from an
internal opening at the
bladder neck to an
external opening at
the end of the penis.
• It is divisible into a:
– Pelvis part
• Preprostatic portion
• Prostatic portion
– Penile part
Pelvic part
• Begins at the internal
opening at the bladder
neck.
• Preprostatic portion
– extends from the internal
opening to the seminal
hillock, an oval
enlargement of the urethra
crest which protrudes into
the lumen of the urethra.
• Prostatic portion
– joined by the deferent and
vesicular ducts and passes
through the prostate gland
Penile part
• Begins at the ischial
arch and is described
with the penis
Differentiate between male and
female
Female
– Short
– Wide
– Elastic
Male
–
–
–
–
Tortuous
Long
Narrow
Less elastic
HISTOLOGY OF URETER
BY : NUR ZULAIKHA BINTI MAT
ZAWAWI
D11A028
Histology Of Ureter
Magnification
25x
100x
Key
1. Lumen
2. Transitional epithelium
3. Mucous glands in lamina propria
4. Muscularis
Microscopic structure of ureter
• Histology of the Mucosa
- inner layer of the ureter
- consists of
-epithelium
- lamina propria.
• Epithelium
-The ureter is lined by
transitional epithelium.
- The epithelial layer is
avascular.
-does not contain lymphatics.
• Lamina Propria
- composed of areolar
connective tissue.
- contains blood vessels and
nerves.
• Histology of the Muscularis
-The middle layer, the muscular coat
-consists of smooth muscle.
-consist of
- Circular muscular layer (smooth
pink layer)
- Longitudinal muscular layer
(bumpy purple layer)
.
-The main function of the muscularis
is peristalsis which propels the urine.
• Adventitia/Serosa
-The outer layer, the fibrous coat, is a
supporting layer of fibrous connective
tissue.
-Adipose tissue is present in the
adventitia.
-A portion of the ureter has serosa
covering it.
URETER
Stained with haematoxylin and
eosin
1 - tunica mucosa
2 - tunica submucosa
3 - tunica muscularis propria
4 - tunica adventitia
5 - transitional epithelium
(urothelium) of the mucosa
6 - tunica propria of the mucosa
URETER
transitional epithelium of the mucosa
Stained with haematoxylin and eosin
1 - transitional epithelium
2 - lamina propria of the mucosa
HISTOLOGY OF URETHRA
BY : NUR AZMINA BT MOHD
ZAILAN
D11A025
HISTOLOGY OF FEMALE URETHRA
-The urethra in females is short. It is only about 1.5 inches.
-The lining epithelium of the female urethra is pseudostratified columnar
epithelium and stratified squomous epithelium.
HISTOLOGY OF FEMALE URETHRA
HISTOLOGY OF MALE URETHRA
-The urethra in the male is longer than the urethra of females.
-The male urethra is 7 to 8 inches.
-The male urethra functions as a conduit for urine and semen.
-The male urethra can be divided into 3 sections : prostatic urethra,membranous
urethra, and spongy urethra.
HISTOLOGY OF MALE URETHRA
Male urethra is lined by stratified columnar epithelium.
HISTOLOGY OF PROSTATIC URETHRA
(MALE)
Stained with haematoxylin and eosin
1- transitional epithelium
2- tunica propria of the mucosa of prostatic part of the urethra
HISTOLOGY OF MEMBRANOUS
URETHRA( MALE)
• The second part of the male urethra.
• This is a short segment.
• The lining epithelium of the membranous
urethra is pseudostratified columnar
epithelium.
HISTOLOGY OF SPONGY URETHRA
• The third part of the urethra.
• Spongy urethra is also called the penile
urethra.
• The longest section of the male urethra.
• The lining epithelium of the spongy urethra is
pseudostratified columnr epithelium which
then transitions to stratified squamous
epithelium distally.
PHYSIOLOGY OF URETER
BY : NURAZLIN BINTI CHE MAT
D11A029
Flow Of Urine In Ureter
• Myogenic = Controlled by the longitudinal and
circular muscle of ureter wall
• Peristaltic movement = waves of active muscular
contraction, that move at near-constant speed
along the ureter towards the bladder . This
causes urine to flow from the ureter lumen to the
urinary bladder
• Unaffected by drugs that block the sympathetic
and parasympathetic nervous system .
• muscular wall constricts & becomes thinner
during luminal enlargement ( urine present )
Very low volume of
urine at certain part of
ureter or no urine at all
Volume of urine at certain part of
ureter increases
High volume of urine at
certain part of ureter
Diagram showing the different stages of ureter opening during urine flow in it
1a, 2a, 3a, 4a
Pictures of cross section
of ureter showing stages
of ureter opening upon
urine flow in it
( light micrograph)
1b,2b,3b,4b
Photograph of cross
section of ureter showing
various stages of ureter
opening upon urine flow
in it
No urine present at certain part of ureter
=At the end of a peristaltic movement or at
rest between movements
= The lumen is collapsed with its epithelial
surfaces in contact with each other . The
lumen has a stellate form
• There are junctional complexes, comprising
a zonula occludens, zonula adherens , and
macula adhaerens or desmosome,
between the lateral borders of the
squamous cells . It is suggested that this
complex is t h e major obstacle to the
free flow of water from the extracellular
spaces into the hypertonic urine
( in lumen of ureter )
PHYSIOLOGY URETHRA
BY : SUHAILA BINTI SOLAHUDIN
D11A035
Function of urethra both in
male and female :
Transport urine from the
urinary bladder to the
exterior of the body
Special function in male :
• Carries semen from the
ejaculatory duct outwards
through the penis.
How the urine flow out of the
body?
• When the sphincter muscle is
relaxed.
• Urethral sphincter muscle is at
the base of the bladder
• It controls the release of urine
from the bladder into the
urethra
• Then flows out of the meatus
(opening at the end of the
urethra) when urinating.
BLUE GLAUCUS
• THANK YOU (^^,)