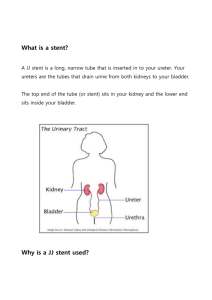
Review the components of urinary
system and how abnormalities cause
urologic problems
Discuss the surgical management of
common urologic problems
Management of the inpatient urology
patient
Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction
Vesicoureteral Reflux
Kidney stones
Hypospadias
Testicular Torsion
Circumcision complications
Narrowing of the ureter that cause dilation of the kidney
Hydronephrosis
* prenatal ultrasound
*evaluation for recurrent UTI
Evaluation of abdominal or flank pain of
unknown origin
Ultrasound reveals hydronephrosis
VCUG is negative for vesicoureteral
reflux
Renogram is the use of IV tracer to
determine how long it takes for kidney to
clear tracer (Nuclear Med Test)
Surgical correction of UPJ obstruction
Flank incision
Removal of obstructed portion and
reanastomosis of the ureter
What to expect?
IV, penrose drain, flank incision, IV, foley
and abdominal binder
23-48 hour admission
Postop day 1: suppository in am,
advance diet if bowel sounds present,
walk the hall, discontinue foley
Backflow of urine from the bladder back
to the kidney
Concern with UTI that may cause a
pyelonephritis
Reflux is caused by the way ureter enters
the bladder wall
Prophylactic antibiotics when patient
has had recurrent UTI especially
associated with fever
Improve voiding habits
Surgical intervention after age of 3 or 4
Deflux injection in grades 2 and
sometimes 3
Extravesical reimplantation in grade 3 or
higher
Type: s
JPG
Ureters are detached from the bladder
and reimplanted into a stronger portion
of the bladder
Pfannenstiel incision (c-section
Foley catheter remains in place 1 week
NPO Post op day 0
Post Op Day 1: suppository in am, bowel
sounds present advance diet as
tolerated, up out of bed and walking the
halls
Plan for discharge 23 to 48 hours after
discharge
Patient will present with flank pain, blood
in the urine, may have hydronephrosis
due to blockage of the ureter
NON contrast CT scan to determine
presence of stone
No need for surgical management unless
stone is blocking ureter
Extracorporeal shCockwave lithotripsy
Endoscopic Lithotripsy
Both require placement of ureteral stent
to allow drainage of urine
Can be a two to three step process
Normal to have blood in the urine
23 hour admission after stent placement
and stone removal due to high rate of
return due to pain
Require medication for bladder spasms
(ditropan) and antibiotic while stent in
place
Congenital birth defect where urethral
opening is on the underside of penis
rather than the tip
Surgical correction after 6 months of age
Blue dressing in place. DO NOT REMOVE!
Urethral stent stays in place 5-7 days
Keep penis pointed to the nose not the
toes!
Patient will require ditropan for bladder
spasms and septra while stent in place
Tylenol with codeine for pain
Follow up in office for dressing removal
A true urologic emergency
Testicle twists in the scrotal sac cutting off
blood supply
Extreme scrotal pain
Orchiopexy bilaterally
Bleeding
Plastibell is displaced to shaft of the penis
Each of your patients is the absolute
center of their parent’s universe
Listen to parents and be patient
Compassion starts when you imagine
your own child in the same situation
Please remember that every
patient is someone’s child!