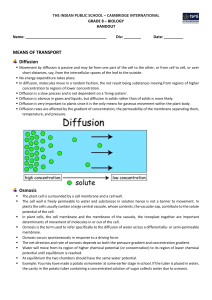
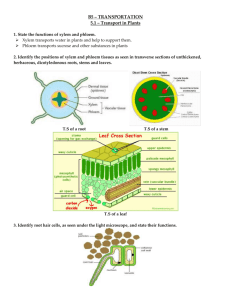
Stomata_and_Transpiration
advertisement

Root Hair Cells Look at the following pictures. What adaptations do roots have to allow for absorption of water? Root Hair Cells Transpiration Water Movement Mass flow of water in xylem vessels – pressure lowered as water leaves vessels. Water moves up from the roots where the pressure is higher. Diffusion of water through cells from xylem. Water vapour diffuses through leaf air spaces. If the concentration of water vapour in the leaf is higher than outside, water vapour will diffuse out of the leaf through the stomata. Capillary action (water molecules attracted to polar molecules in xylem walls (adhesion)). Cohesion – tension theory. Cohesion-Tension Theory Water molecules have dipoles which cause an attraction between them. Water is ‘pulled’ up the xylem vessels by transpiration. When this happens, the pull is transmitted all the way down the water column, pulling all of the water molecules up the vessel. For this to work, the xylem vessel must be a continuous column of water i.e. contain no bubbles. Cross Section of A Leaf Opening/ Closing Stomata Stomata can be closed to prevent water loss. Guard cells curve apart when turgid. When flaccid, the edges of the cells lie close together. However, this drastically slows transpiration and means that no carbon dioxide can enter the leaf (= no photosynthesis). Stomata Diagrams Animation link Factors Affecting Water Loss Diffusion rate is affected by: Surface area (the higher the surface area, the greater the rate of diffusion). Difference in concentration (the greater the concentration gradient, the higher the rate of diffusion). Length of the diffusion path (the greater the length, the lower the rate of diffusion). http://www.sciencemag.org/site/feature/mi sc/webfeat/vis2005/show/transpiration.swf Preventing Excess Water Loss Cuticle (waxy layer) on leaf which is impermeable to water. Most stomata found on underside of leaf as it is cooler in dicotyledons. Thick leaves = reduced water loss. Spines/ hairs increasing boundary layer (undisturbed layer of air). Stomata closed at certain times of the day. Stomata may be sunken and found in pits. Xerophytes – Marram Grass • Found on sand dunes. • When dry, leaves roll up, so stomata open to an enclosed space. • Water vapour accumulates in this space = reduced diffusion gradiant. • Spines increase width of boundary layer. Xerophytes Cont. Some xerophytes may have large numbers of stomata. Xerophytes cells may have extra support to prevent cells collapsing when they dry out. Extensive root system. Leaves may have evolved to become spines, with water being stored in the stem e.g. cacti.