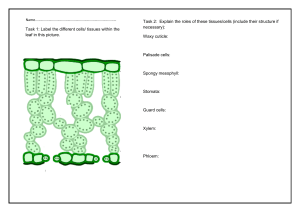
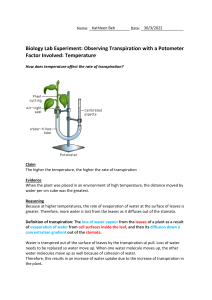
Y10 Biology Unit 8_Transport in plants Translocation Translocation is the movement of sucrose and amino acids in phloem from sources to sinks. • The source is the region of production (usually the leaves). • The sink is the region they are transported to. • This may be for storage (i.e. in the roots or developing parts of the plants – new leaves, fruits, seeds), respiration or growth. Q: Phloem is used to transport sucrose and amino acids in plants. Sucrose is a carbohydrate. Describe the uses of carbohydrates and amino acids in plants. [4] Carbohydrates are: used to make cellulose cell walls converted into starch to store as energy used during respiration of plants used to attract insects to flowers // used to make nectar/fruits Amino acids are: used to make enzymes used for the plant growth Transpiration Transpiration is the loss of water vapour from leaves by evaporation of water at the surfaces of mesophyll cells, followed by diffusion of water vapour through the stomata. Loss of water vapour is related to: The large internal surface area provided by the interconnecting air spaces The size and number of stomata Factors that affect the rate of transpiration: Factor Effect on transpiration rate Increase in temperature Increases transpiration rate • because increase in temperature increases the kinetic energy of the water molecules, so they diffuse faster. • Transpiration is likely to be faster on a hot day. Increase in humidity Decreases transpiration rate • because increase in humidity increases the concentration of water molecules outside the leaf. This reduces the concentration gradient for diffusion. Less diffusion of water vapour. Increase in wind speed Increases transpiration rate • because the wind removes water vapour from the surfaces of the leaves so there is a greater diffusion of water from the leaves. 1 Y10 Biology Unit 8_Transport in plants Mechanism of water movement through the xylem Water leaves the xylem into the mesophyll cells by osmosis. The water on the cell walls of the mesophyll cells evaporates into the air spaces. Water vapour diffuses out of the leaf through the stomata by diffusion into the surrounding air. Water molecules are held together by cohesion. Water moves by the pull from the leaves caused by transpiration. Xylem vessels are very thin, so they act like a capillary tube helping to draw water upwards. Pathway taken by water through the root, stem and leaf Root hair cells root cortex cells xylem spongy mesophyll cells stomata 1. Root hair cells absorb water by osmosis, and ions by diffusion or by active transport. 2. Water passes through root hair cells to the root cortex cells by osmosis and then into the xylem vessels. 3. In the xylem vessels, water and ions travels up through the stem to the leaves due to transpiration pull. Xylem vessels act like tiny tubes, drawing water up the stem by capillary action. 4. In the leaves, water and ions passes out of the xylem vessels into the mesophyll cells. 5. Water in mesophyll cells form a layer on their surfaces. 6. The water evaporates into the air spaces in the spongy mesophyll. 7. The water diffuses out of the leaf through the stomata by diffusion into the surrounding air. Wilting Environmental factors that can cause plants to wilt: 1. Lack of water Cells become flaccid and will no longer press against each other. Stems and leaves then lose their rigidity and wilt. 2. High temperature Increase the kinetic energy of water molecules. Water diffuses out of stomata faster. If the amount of water lost from the leaves is greater than the amount taken into the roots, the plant will have a water shortage. 3. Low humidity/dry air Concentration of water molecules outside the leaf decreases. Diffusion of water vapour out of the leaf will more likely occur. 4. Wind Wind removes water vapour from the surfaces of the leaves so there is a greater diffusion of water from the leaves. Advantage of a plant wilting: During wilting, the stomata close to prevent more water loss. Water is conserved for other parts of the plant. Wilting also decreases the surface area that is exposed to the sun. 2