Time-Chainage Diagram: Construction Project Management
advertisement

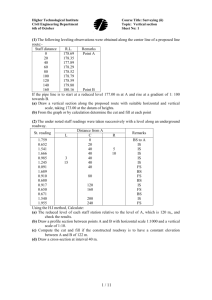
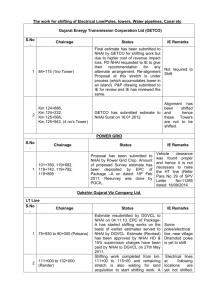
TIME-CHAINAGE DIAGRAM Sewon Kim, Kevin Tran, Mary Svennerborg Contents What is the Time-Chainage Diagram? What is the principal benefit? History Advantage of Time-Chainage chart Example Think about References 1.What is the Time-Chainage Diagram? TIME CHAINAGE 1.What is the Time-Chainage Diagram? It is an extension of the Bar Chart (Gantt Chart). enables the time dependencies between activities to be shown, together with their order and direction of progress along the job. 2.What is the principal benefit? The principal benefit is the management of work in confined spaces where typically only one operation can be performed at a time. Description of Diagram 3.History Widely applied roadwork projects and in the development of the motorway system in UK for many years used for the planning of the tunnelling and fixed equipment installation on the channel tunnel project Discussed in proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers Applicable only for limited types of project not as widely appreciated in the industry as bar charts and network techniques. 4. Advantage of Time-Chainage chart When Constructing Roads Railways Pipelines Tunnels Transmission Lines Bridges 4. Advantage of Time-Chainage chart Easy to know The order of activities or operations Where activities are happening locationally How activities must progress in relation to direction and distance Time, key dates and holidays, etc. 5.Example Business of constructing the road The length of road = 3.5 Km Starting point of construction = 0+000 Finishing point of construction = 3+500 6 Activities on construction plan 6 Steps to draw Time-Chainage Diagram 6 Activities Fencing Drainage Bulk Earthworks Footbridge Retaining wall Road Surfacing 6 Steps 6 Steps to draw diagram Step 1 Draw the diagram layout Decide the intervals of chainage 1000m 6 Steps to draw diagram Step 2 0 26 H … 28 40 3… Chainage 2… 0 Select either the horizontal or vertical format Draw an outline with time and distance (chainage) Add main holiday periods allowing 2 weeks me(… 6 Steps to draw diagram Step 3 Make the main program activities or operations OPERATION EXAMPLE Set up site Offices for contractor and engineer Activity 1 Fencing Activity 2 Drainage Activity 3 Bulk Earthworks Activity 4 Foot Bridge Activity 5 Retaining Wall Activity 6 Road Surfacing Holiday Christmas Shut down 6 Steps to draw diagram Step 4 Fill in the ‘site set-up’ and ‘clear site’ activities 6 Steps to draw diagram Step 5 Decide in turn where and when each activity will take place 12 15 20 25 Act2 Act1 -16 Act3 -16 Act4 Act5 15 16 -24 -25 30 35 Project Completion Act6 6 Steps to draw diagram Step 6 Complete all activities on the list 6.Think about Advantage of Horizontal axis -Easy to notice that has to be constructed. Advantage of Vertical axis -More easier to read by those familiar with bar charts. The choice is a matter of personal preference. References ICE(1992) Proceeding of the Institution of Civil Engineers. The Channel Tunnel Part 1: Tunnels. Thomas Telford. http://www.noweco.com/qei/qeie08.htm Cormican,D.(1985) Construction Management: Planning and Finance. Construction Press http://pclarke.co.uk/html/time_chainage.html