adrenal and parathyroid
advertisement

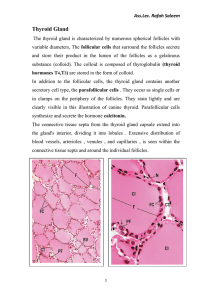
ENDOCRINE GLANDS Dr Iram Tassaduq ADRENAL (SUPRARENAL ) GLAND • Lies on upper pole of each kidney • Comprised of two zones outer cortex inner medulla • Develops from intermediate mesoderm and neural crest cells INTRODUCTION • The adrenal gland is encased in a connective tissue capsule that extends septae into the substance of the gland. The organ is richly vascularized and capsular blood vessels, nerves and lymphatics penetrate along with the connective tissue septae. CORTEX • zona glomerulosa - thin, outermost zone • zona fasiculata - thick, middle zone • zona reticularis - thin, inner zone ZONA GLOMERULOSA • Composed of columnar or pyramidal cells arranged as rounded or arched cords • Occupy 15% of gland volume ZONA GLOMERULOSA ZONA FASICULATA • Cells are arranged in straight cords. 1-2 cells thick • Cords run at right angles to the surface of organ and have capillaries between them • Occupy 65% of gland volume ZONA FASICULATA ZONA RETICULARIS • Polyhedral cells with lipid droplets • Form 7% of gland • Appears vacuolated in histological preparations • Cells are smallest in size ZONA RETICULARIS ADRENAL MEDULLA • Composed of cords or clumps of cells called chromaffin cells. These can acquire brown colour which is due to oxidation of catecholamines • Modified postganglionic sympathetic neurons ADRENAL MEDULLA FUNCTIONS OF ADRENAL GLAND THYROID GLAND • C.T. sheath formed by deep cervical fascia • Extremely labile gland & varies in size & structure Three dimensional view of thyroid follicles DEVELOPMENT OF THYROID GLAND • Begins to develop during 4th week of gestation from a primordium originating as an endodermal thickening of floor of primitive pharynx STRUCTURAL UNIT OF THYROID GLAND ----- THYROID FOLLICLE FOLLICULAR EPITHELIUM Follicular cells Para follicular cells FOLLICULAR CELLS PRINCIPAL/ CHIEF CELLS • Responsible for the production of T3 & T4 • Vary in size & shape • Slightly basophilic in H & E stained slides • Lipid droplets COLLOID • Inactive storage form of thyroid hormone • Constituents • Principal component is thyroglobulin (large iodinated glycoprotein) • Enzymes • Glycoproteins • Staining with both acidic & basic dyes. Strongly with PAS PARAFOLLICULAR CELLS C CELLS/ CALCITONIN CELLS Located in periphery of follicular epithelium No exposure to lumen In H & E stained slides appear as pale staining cells Secrete calcitonin FUNCTION OF THYROID GLAND PARATHYROID GLAND • Two pairs in mammals • Embedded within thyroid gland substance • C.T. capsule is thin PRINCIPAL CELLS/ CHIEF CELLS • More numerous of parenchymal cells • Small, polyhedral cells, of 7-10 um in diameter • Rounded, vesicular nuclei • Responsible for secretion of PTH chief cells OXYPHILL CELLS • Constitute a minor portion of parenchyma • Found singly or in clusters • More rounded & larger than principal cells • Distinctly acidophilic cytoplasm • No secretory activity