Functional Groups, etc.

Organic Chemistry I
The study of carbon-containing compounds
Unit 1
A little bit of everything…
Oops!
We are not starting at the beginning of Chapter 1…
because you need a little more time with the concepts from the following sections:
2.12, 1.10, 1.11, 2.13, 2.14
Hydrocarbons
Compounds that contain only H and C atoms.
alkanes (contain all single bonds)
alkenes (contain C=C)
alkynes (contain C ≡ C)
aromatics (contain a benzene ring)
Alkanes
Each C atom is bonded to 4 other atoms...why?
methane ethane propane butane pentane hexane heptane octane
CH
4
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
CH
2
CH
3
CH
3
(CH
2
)
2
CH
3
CH
3
(CH
2
)
3
CH
3
CH
3
(CH
2
)
4
CH
3
CH
3
(CH
2
)
5
CH
3
CH
3
(CH
2
)
6
CH
3 nonane decane
CH
3
(CH
2
)
7
CH
3
CH
3
(CH
2
)
8
CH
3
Alkanes
The most significant reaction of alkanes is combustion.
This is because alkanes do not have any functional groups.
Functional groups are where reactions occur.
CH
3
(CH
2
)
8
CH
3
+ 15.5 O
2
(g) 10CO
2
(g) + 11H
2
O(l)
Showing the Structure of an
Organic Molecule
You must be able to read and interpret drawings of molecules from the start!
structural formula = Lewis structure
condensed (structural) formula
line-angle formula
3-dimensional formula
(The molecular formula does not show structure. It just gives numbers and types of atoms.)
Molecular Formula, Lewis Structure, and Condensed Structural Formula
The Lewis structure shows all bonds and unbonded valence electrons. Please view the Lewis structures
PowerPoint on the 2114 web page if you need a refresher.
These are all the same compound: cis-hex-3-en-2-one
Condensed Structural Formula
• The atoms following the C are bonded to the C: CHCl
2
CH
3
• Sometimes the atoms bonded to the leading C are shown on the left:
H
3
CCH
2
CH
3 or CH
3
CH
2
CH
3
• The C is bonded to the C immediately before it and the C atom immediately after it…all C atoms in molecules have 4 bonds.
Condensed Structural Formula
• A group bonded to a C is shown in parentheses, except on the last C.
CH
3
CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
OH is 1-propanol
CH(OH)CH
3 is 2-propanol
• Typically, C=C and C ≡ C are shown, but C=O is not.
CH
3
CH
2
CH=CHCOCH
3
Line-Angle Structure
There is a C at the end of every line segment and enough H atoms to give each neutral C four bonds.
3-D Structure
Solid lines are bonds in the plane of the board or paper.
Wedges show bonds to atoms in front of the plane.
Dashed lines show bonds to atoms behind the plane.
Showing the Structure of an
Organic Molecule
START NOW practicing drawing these different types of structures!
Functional Groups
Functional groups are sites of reactivity in an organic compound.
Is this compound an alkane?
Is it a hydrocarbon?
It contains two functional groups: an alkene and a ketone.
Functional Groups
In hydrocarbons
alkanes (no functional groups)
alkenes (contain C=C)
alkynes (contain C ≡ C)
aromatics (contain an aromatic ring, the most common of which is the benzene ring)
Two representations of a benzene ring…it is NOT classified as an alkene!
Functional Groups
In hydrocarbons
Alkyl Substituents
We look for the longest chain of C atoms in the molecule.
Groups of atoms attached to the C atoms in the chain are called substituents.
Alkyl Substituents
When the substituent is an alkane, it is called an alkyl group.
The letter R is often used to denote an alkyl substituent.
a methyl group any alkyl group
Functional Groups
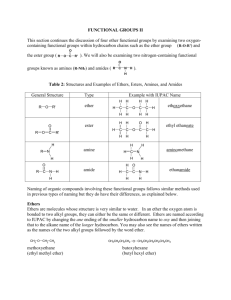
In compounds containing O
alcohols (R-OH)
ethers (R-O-R’)
ketones (contain C=O)
aldehydes (contain HC=O)
carboxylic acids (COOH)
carboxylic acid derivatives
esters (RCOOR’)
amides (RCONH
2
, RCONHR’, RCONR’R”)
acid chlorides (RCOCl)
Functional Groups
In compounds containing N
amines (RNH
2
, RNHR’, RNR’R”)
amides (RCONH
2
RCONR’R”)
, RCONHR’,
nitriles (R-C ≡ N)
In compounds containing X
alkyl halides or haloalkanes
X=halogen
Functional Groups-Alcohols (R-
OH) and Ethers (R-O-R’)
Functional Groups-Aldehydes
(HC=O) and Ketones (RC=OR’)
C=O is a carbonyl group.
C=O on the end of the carbon chain is an aldehyde.
C=O elswhere in the carbon chain is a ketone.
Functional Groups-Carboxylic
Acids and Their Derivatives
COOH is a carboxylic acid group.
COOR is an ester.
COCl is an acid chloride.
Functional Groups-Amines,
Amides, and Nitriles
Amides are like amines, but with an adjacent C=O.
Be careful! Both amines and amides have different forms: primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°).
Nitriles are R-CN.
Primary (1°) Amines and
Amides
A primary (1°) amine has one C atom (one alkyl group R) and two H atoms bonded to the N. The general formula is RNH
2
.
A 1° amide has one acyl group and two H atoms bonded to the N. The general formula is RCONH
2
.
Secondary (2°) Amines and
Amides
A secondary (2°) amine has two C atoms
(two alkyl groups) and one H atom bonded to the N. The general formula is
RNHR’.
A 2° amide has two C atoms (one in the acyl group) and one H atom bonded to the
N.
The general formula is RCONHR’.
Tertiary (3°) Amines and
Amides
A tertiary (3°) amine has three C atoms
(three alkyl groups) and no H atoms bonded to the N. The general formula is
RNR’R”.
A 3° amide has three C atoms (one in the acyl group) and no H atoms bonded to the
N.
The general formula is RCONR’R”.
1°, 2°, 3° Amines and Amides
Classify these.
Functional Groups - Alkyl
Halides
Classify the halides as 1°, 2°, or 3°.
Cycloalkanes are alkanes that have a ring of C atoms.
Functional Groups
Circle and label each functional group.
threonine
γ-butyrolactone
(GBL) fructose acetaminophen vitamin A
(retinol)