6_GTAW
advertisement

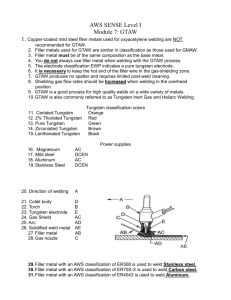
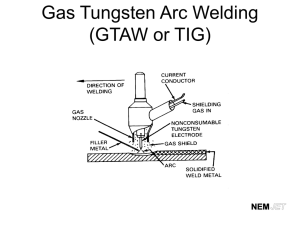
GTAW (TIG) Definition Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) is an arc welding process that uses a non consumable tungsten electrode to establish the arc and gas from a cylinder to provide shielding. The filler metal is supplied by a manual rod. Also called Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding. 2 Machine Functions 1 2 3 4 5 Store and provide shielding gas at the correct rate Provide desired welding current Variable current control Store and circulate water through the torch (watered cooled) Semiautomatic control Machine Nomenclature A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. L. M. N. O. P. Q. R. Torch Power switch AC balance control Mode switch Digital Amp meter Output (Amp) control Cylinder Flow meter Roto meter Flow control valve Regulator Post flow timer Pulse frequency control Polarity switch Output connector Remote pedal Ground clamp Remote receptacle Explain the function(s) of each one of these controls/parts. Torch Nomenclature A. B. C. D. E. F. G. Cap Collet Torch body Collet body Gas orifice Cup Electrode What is the function of each part? How are GTAW torches cooled? Introduction How does the GTAW process meet the three requirements of arc welding? Heat GTAW Shielding Filler metal Hazards Associated with GTAW Hot metal Harmful rays Fumes High frequency RF Flying objects Loud Noise What is the best management practices for these hazards? Heat The heat produced by an electric arc between the nonconsumable tungsten and the metal is sufficient to melt the base metal and the filler rod. What determines the amount of heat produced by the electric arc? For the TIG welding process, is the current adjusted by changing the amperage or the voltage? Heat – Currents Three common currents: DCDC+ AC--HF Note: many power supplies have the option of pulsed current for better puddle control. Why is HF (high frequency) used with AC? Heat – Current - Polarity For the best welds, and ease of welding, the correct current must be used for the metal being welded. Heat - Tungsten The tungsten electrode is nonconsumable and is used to form the arc between the torch and the metal. Different alloys of tungsten are available. ID % Alloy Color Characteristic EWP 100 % Tungsten Green Good arc stability with AC EWTh-2 2 % Thorium Red Better Arc with DC EWZr-1 1 % Zirconium Brown AC when high weld quality is required EWCe-2 2 % Cerium Orange Better starting, higher current EWLa-2 2 % Lanthanum Black 50% greater current capacity with AC Which alloy/color should be used when welding thicker aluminum with AC? Heat – Tungsten - Preparation The shape of the tungsten electrode end must be appropriate for the current being used. AC Hemispheric or balled end no more than 1.5 times the electrode diameter. Grinder lines parallel with electrode. DC- Needle point for very thin metal, blunt point for thicker metal. Taper = 2 to 2-1/2 times the diameter. What does it mean if the end of the electrode appears dull? What does it mean if the end of the electrode is blue or blackened? How long should the the shielding gas flow after the welding has stopped? Heat – Tungsten - Size Diameter (in) Gas Cup Inside Dia. DC(Ce, Th % La) AC (Pure) AC (Ce, Th % La) 0.040 #5 (3/8 in) 15 – 80 20 – 60 15 - 80 0.060 (1/16 in) #5 (3/8 in) 70 - 150 50 – 100 70 – 150 0.093 (3/16 in) #8 (1/2 in) 150 – 250 100 - 160 140 – 235 0.125 (1/8 in) #8 (1/2 in) 250 – 400 150 – 200 225 - 325 Shielding In the GTAW process shielding is supplied from a cylinder. How is the flow of the shielding gas controlled? For best results the shielding gas must be appropriate for the type and thickness of metal. How much gas (ft3) will each gallon of liquid argon produce? Filler Metal A welding rod is used to fill in the joint. Most common type is 36 inch rods that are fed into the weld pool by hand. What are three important characteristics of GTAW rods? AWS GTAW Aluminum Filler Rods Aluminum Alloy Filler Rod 1100 2014-T6 2219-T81 3003 5005 ER1100 ER4043 ER2319 ER1100 ER5356 Process Preparation for Welding Three (3) steps in preparing to weld: 1 Safety check 2 Metal preparation 3 Set up machine Preparation - Safety 1 2 3 Check the machine, cables, torch and ground clamp. Insure the helmet is in good condition and the correct shade of lens. Cover all exposed skin. Preparation – Metal – Aluminum • Contamination is the biggest problem when welding aluminum with the GTAW process. • The metal must be cleaned with a stainless steel wire brush. The brush can only be used to clean aluminum. Must clean the adjoining faces and the back edge • Insure the filler rod is clean also. Preparation - Machine • • • • Attach the GTAW torch to the output connector. Attach the remote control pedal to the remote receptacle. Position the polarity switch on AC. Turn on the machine. Insure the torch is not grounded • • Set the mode switch to TIG Set the amperage. 150 amp maximum for air cooled torch. • • • Set the AC balance control. Set the pulse control. Set the postflow timer. Preparation – Machine - Torch • • • • If the torch has been used to weld carbon steel or stainless steel then the cup and electrode must be replaced. The tungsten electrode must be clean and the correct shape. The torch cup must be clean The electrode must be set with the correct stickout. Welding aluminum Setting Amperage Aluminum is a good conductor of heat. Aluminum melts at a lower temperature that steel. Aluminum Amperage ACHF Tungsten electrode diameter Filler rod diameter Amperage Butt 3/32 – 1/8 in 3/32 in Lap 3/32 – 1/8 in Corner Type CFH 125 - 150 Argon 20 3/32 in 130 - 160 Argon 20 3/32 – 1/8 in 3/32 in 120 - 140 Argon 20 Fillet 3/32 – 1/8 in 3/32 in 130 - 160 Argon 20 Butt 1/8 – 5/32 in 1/8 in 180 - 225 Argon 20 Lap 1/8 – 5/32 in 1/8 in 190 - 240 Argon 20 Corner 1/8 – 5/32 in 1/8 in 180 - 225 Argon 20 Fillet 1/8 – 5/32 in 1/8 in 190 – 240 Argon 20 Butt 5/32 – 3/16 in 3/16 in 240 - 280 Argon 25 Lap 5/32 – 3/16 in 3/16 in 250 – 320 Argon 25 Corner 5/32 – 3/16 in 3/16 in 240 - 280 Argon 25 Thickness 1/8 in 3/16 in Gas Joint 1/4 in Troubleshooting GTAW • • • Troubleshooting is the process of determining the cause of a problem. Assumes the welder is in proper working order. Requires gathering information and a logical thought process. Troubleshooting - 1 Problem Cause Excessive electrode consumption Inadequate gas flow DCEP electrode Excessive current density Tungsten oxidation during cooling What would you do to remedy these causes? Troubleshooting - 2 Problem Cause Aluminum contamination of electrode Electrode contacting filler rod Electrode contacting metal What would you do to remedy these causes? Troubleshooting - 3 Problem Weld porosity and dark color Cause Condensation in system Atmospheric contamination Contaminated filler metal What should be done to remedy these causes? Contaminated base metal Troubleshooting - 4 Problem Yellow powder or smoke on cup Cause Insufficient gas flow Atmospheric contamination Inadequate post flow What should be done to remedy these causes? Incorrect shielding gas Incorrect tungsten size or cup size References http://www.millerwelds.com/resources/TIGhandbook/