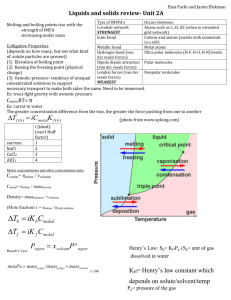
Unit Cells - Employees Csbsju
advertisement
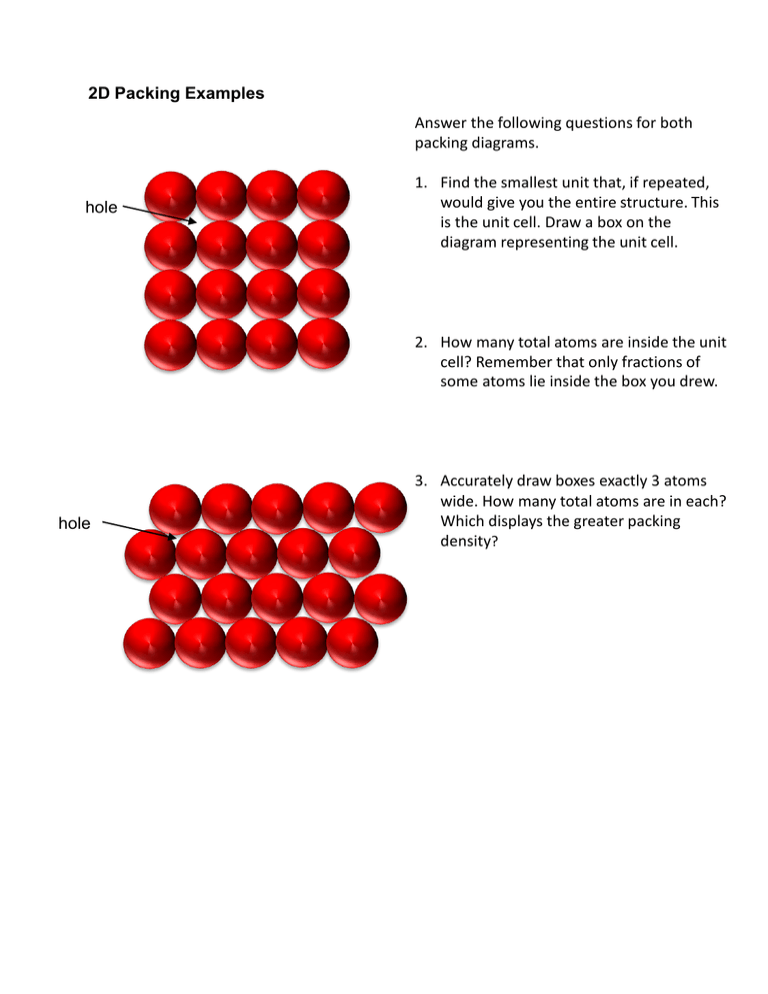
2D Packing Examples Answer the following questions for both packing diagrams. hole 1. Find the smallest unit that, if repeated, would give you the entire structure. This is the unit cell. Draw a box on the diagram representing the unit cell. 2. How many total atoms are inside the unit cell? Remember that only fractions of some atoms lie inside the box you drew. hole 3. Accurately draw boxes exactly 3 atoms wide. How many total atoms are in each? Which displays the greater packing density? SIMPLE CUBIC PACKING A TOP VIEW AA SCP 1 | Flash Anim | Jmol 1 A unit cell: simple cubic BODY CENTERED CUBIC PACKING - ABAB A B Unit cell: body centered cubic Do not touch BCP 1 | Flash Anim | Jmol 1 HEXAGONAL CLOSEST PACKING - ABAB B A 1200 Unit cell: hexagonal CUBIC CLOSEST PACKING B A C A 7 6 A 8 4 3 5 C B 1 2 B A C Unit cell: face centered cubic 6 7 8 A 4 3 5 CUBIC CLOSEST PACKING FCC = CCP: Jmol CCP (FCC) 1 | Flash Anim | Jmol 1 2 1 Counting atoms in a unit cell 1. What fraction of the white colored sphere is part of a unit cell in each of the lattices shown below. A face atom? ________ An edge atom? ________ A corner atom? ________ 2. From your answers above, how many spheres below to the unit cell shown. Simple Cubic ________ Face centered cubic ________ Body centered cubic ________ Now to some real structures. How do we know the arrangement of ions and atoms? X-Ray Crystallography: • Na – bcc – what’s up with it’s 3s1 electron • NaCl • Bragg’s Law and diffraction • Xray diffraction (Laue transmission) from simple cubic, bcc and fcc lattices How do you describe salts with more than one atom type? By unit cells and holes NaCl Space fill Types of Holes 109.50 3 atoms e clouds in plane Tetrahedron – 4 identical equilateral triangles 5 atoms/ e clouds in plane •What's a tetrahedron •What's an octahedron •Holes: Cubic, tetrahedral, and Octahedral •CCP and holes SF6 Octahedron – 8 identical triangles Determining the empirical formula from unit cell data: A salt must be electrically neutral. If you know the charge on the cations and anions, you can determine MxNy. Alternatively, you can use crystal data to determine the structure of the unit cell and hence the empirical formula. Determine the number of each different ion in the following unit cells. Does it correspond to the formula from charge balance? 1. Copper (I) chloride Cl Cu 4. Based on Clalone, what type of unit cell is this? What type of “hole” is occupied by Cu+? 2. Barium Chloride 5. Based on just Clalone, what type of unit cell is NaCl? What type of “hole” is occupied by Na+? 3. Rhenium oxide Calculation of the atomic radius of a polonium atom, which forms a simple cubic cell, from macroscopic parameters. How many P atoms are in the unit cell? Given Polonium Data • density 9.23 g/cm3 macroscopic meas. • molar mass: 208.98 g • Avogadro’s #: 6.022 x 1023 atoms/mol r Top Side views 2r Use 2 simple equations Solve for the following: Vatom/Veff = 2r Veff (from density data) and dimensional analysis Veff = Vatom = rPo = Body-Centered Cubic Unit Cell unit cell a 4r a √2 a a x2 = a2 + a2 x = √2 a 2 ( 2 a) a a 2 ( 4r ) 4r 3 Vunitc ell ( 4r 3 ) 3 2 Edge sphere Do how many unit cells does the yellow sphere belong? Corner sphere Do how many unit cells does the yellow sphere belong? Face sphere Do how many unit cells does the yellow sphere belong? CUBIC CLOSEST PACKING ABC ABC B A C A C B A