Substitution Rxns-b-Sn1-12-ques
advertisement

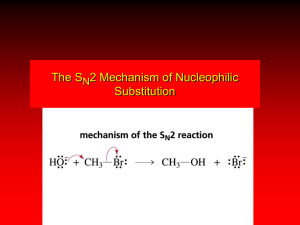
Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions: SN1 Mechanism Two Step Mechanism Which step is rate determining? A) Step #1 B) Step #2 Solvolysis Reactions Tertiary alkyl halides are very unreactive in substitutions that proceed by the SN2 mechanism. But they are highly reactive in solvolysis reactions where the solvent is generally one of the reactants. Hydrolysis of tert-butyl bromide. CH3 CH3 C H .. Br : .. + CH3 : O: H + O: C H CH3 CH3 H CH3 + CH3 CH3 C CH3 .. OH .. + H .. Br : .. .. – : Br : .. Hydrolysis of tert-butyl bromide. CH3 CH3 C CH3 H .. Br : .. + : O: CH3 CH3 H + O: C H H CH3 + This is the nucleophilic substitution stage of the reaction; the one with which we are concerned. .. – : Br : .. Hydrolysis of tert-butyl bromide. CH3 CH3 C CH3 H .. Br : .. + CH3 : O: CH3 H + O: C H H CH3 + The reaction rate is independent of the concentration of the nucleophile and follows a first-order rate law. rate = k[(CH3)3CBr] .. – : Br : .. Hydrolysis of tert-butyl bromide. CH3 CH3 C CH3 H .. Br : .. + CH3 : O: CH3 H + O: C H H CH3 + The mechanism of this step is not SN2. It is called SN1 and begins with ionization of (CH3)3CBr. .. – : Br : .. Kinetics and Mechanism rate = k[alkyl halide] First-order kinetics implies a unimolecular rate-determining step. Proposed mechanism is called SN1, which stands for substitution nucleophilic unimolecular CH3 CH3 Mechanism .. Br : .. C CH3 unimolecular slow H3C + C CH3 CH3 + .. – : Br : .. Mechanism H3C CH3 + C H : O: CH3 H bimolecular fast CH3 CH3 H + C CH3 O: H carbocation formation R+ carbocation capture proton transfer RX + ROH2 ROH Characteristics of the SN1 mechanism first order kinetics: rate = k[RX] unimolecular rate-determining step carbocation intermediate rate follows carbocation stability rearrangements sometimes observed reaction is not stereospecific racemization occurs in reactions of optically active alkyl halides Question What is the rate-determining step in the reaction of cyclobutanol with HCl? A) protonation of the OH group B) attack of the bromide on the carbocation C) simultaneous formation of the C-Br bond and the breaking of the C-OH bond D) carbocation formation Question The species shown below represents _____ of the reaction between isopropyl alcohol and hydrogen bromide. A) the alkyloxonium ion intermediate B) the transition step of the bimolecular proton transfer C) the transition state of the attack of the nucleophile on the carbocation D) the transition state of the unimolecular dissociation Carbocation Stability and SN1 Reaction Rates Electronic Effects Govern SN1 Rates The rate of nucleophilic substitution by the SN1 mechanism is governed by electronic effects. Carbocation formation is rate-determining. The more stable the carbocation, the faster its rate of formation, and the greater the rate of unimolecular nucleophilic substitution. Reactivity toward substitution by the SN1 mechanism RBr solvolysis in aqueous formic acid Alkyl bromide Class Relative rate CH3Br Methyl 1 CH3CH2Br Primary 2 (CH3)2CHBr Secondary (CH3)3CBr Tertiary 43 100,000,000 Decreasing SN1 Reactivity (CH3)3CBr (CH3)2CHBr CH3CH2Br CH3Br Question Select the most stable carbocation. A) B) C) D) Question Which one of the following reacts with HBr at the fastest rate? A) C) B) D) Stereochemistry of SN1 Reactions Generalization Nucleophilic substitutions that exhibit first-order kinetic behavior are not stereospecific. Stereochemistry of an SN1 Reaction CH3 H C R-(–)-2-Bromooctane Br CH3(CH2)5 H HO CH3 C (CH2)5CH3 (S)-(+)-2-Octanol (83%) CH3 H2O H C OH CH3(CH2)5 (R)-(–)-2-Octanol (17%) Figure Ionization step gives carbocation; three bonds to chirality center become coplanar + Leaving group shields one face of carbocation; nucleophile attacks faster at opposite face. Structure of tert-Butyl Cation CH3 + H3C C CH3 Positively charged carbon is sp2 hybridized. All four carbons lie in same plane. Unhybridized p orbital is perpendicular to plane of four carbons. + More than 50% Less than 50% Carbocation Capture + H3C CH3 C+ Cl – CH3 Lewis acid Lewis base Electrophile Nucleophile H3C CH3 C H3C Cl Carbocation Rearrangements in SN1 Reactions Because... carbocations are intermediates in SN1 reactions, rearrangements are possible. Example CH3 CH3 CH3 H2O C CHCH3 H Br CH3 C CH2CH3 OH (93%) H2O CH3 CH3 C H CH3 CHCH3 + CH3 C + CHCH3 H Effect of Solvent on the Rate of Nucleophilic Substitution In general... SN1 Reaction Rates Increase in Polar Solvents SN1 Reactivity versus Solvent Polarity Solvent Dielectric Relative constant rate acetic acid methanol formic acid water Most polar Fastest rate transition state stabilized by polar solvent R X R+ energy of RX not much affected by polarity of solvent RX transition state stabilized by polar solvent R X R+ energy of RX not much affected by polarity of solvent RX activation energy decreases; rate increases In general... SN2 Reaction Rates Increase in Polar Aprotic Solvents An aprotic solvent is one that does not have an —OH group. SN2 Reactivity versus Type of Solvent CH3CH2CH2CH2Br + N3– Solvent Type Relative Rate CH3OH polar protic 1 H2O polar protic 7 DMSO polar aprotic 1300 DMF Acetonitrile p polar aprotic 5000 Mechanism Summary SN1 and SN2 When... primary alkyl halides undergo nucleophilic substitution, they always react by the SN2 mechanism tertiary alkyl halides undergo nucleophilic substitution, they always react by the SN1 mechanism secondary alkyl halides undergo nucleophilic substitution, they react by the SN1 mechanism in the presence of a weak nucleophile (solvolysis) SN2 mechanism in the presence of a good nucleophile SN1 vs. SN2 – The Leaving Group The most commonly used leaving groups are halides and sulfonate ions. CONCEPTUAL CHECKPOINT 7.28. SN2 vs. SN1 – Solvent SN2 reaction, use a polar, aprotic solvent To promote an SN1 reaction, use a polar, protic solvent: The protic solvent will hydrogen bond with the nucleophile, stabilizing it, while the leaving group leaves first. Various Functions from Substitution Reactions Calibrated Peer Review / Lab Experimentation http://chemconnections.org/organic/chem226/calendar-f-12