RESPIRATION - Plantsbrook School
advertisement

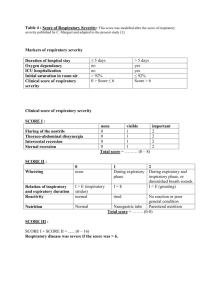
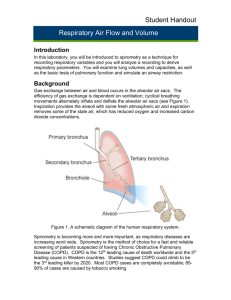
RESPIRATION ACTIVITY 1 Write down as many terms as you can that are used to describe the respiratory system •Bullet point your answers The air continues into many branching airways known as the bronchial tree The trachea and bronchi have supporting cartilage to keep the airways open Bronchiole walls contain more smooth muscle. The air is moistened, warmed and filtered as it flows through these passageways The airways from the nasal cavity through the terminal bronchioles are called the conducting zone The air then reaches the respiratory zone The respiratory zone The respiratory zone contains alveoli, tiny thin walled sacs where gas exchanges occurs. Terminal bronchi Alveoli Lets now look at the actual site of diffusion, the respiratory membrane ACTIVITY 2 Complete the following worksheets: 1. WS.1 2. Worksheet 5.1 3. Worksheet 5.2 ACTIVITY 3 Highlight the key words within the following text on IS 1 MECHANICS OF RESPIRATION DURING EXERCISE • What muscles are involved? • Inspiration – SCOM (sternocleidomastoid), scalenes & pectoralis minor • Expiration – internal intercostals & rectus abdominals / obliques Sternocleidomastoid (SCOM) Scalenes ABDOMINALS ACTIVITY 4 Highlight the key words on IS 2 Respiratory system – 3 main processes • Pulmonary respiration – The breathing of air into and out of the lungs • External respiration – Exchange of O2 and CO2 between the lungs and the blood • Internal respiration – Exchange of O2 and CO2 between the blood and muscle tissues RESPIRATORY VOLUMES AT REST • Tidal volume (TV) – Amount of air inhaled and exhaled with each breath (approx 500ml) • Frequency (F) – Rate of breathing • Minute Ventilation (VE) – VE = TV X f • Residual volume (RV) – Volume of air remaining in the lungs (1200ml) RESPIRATORY VOLUMES AT REST (Cont’d) • Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV) The additional air that can be inhaled after a normal tidal breath in. The maximum volume of air that can be inspired in addition to the tidal volume. • Expiratory reserve volume (ERV) The amount of additional air that can be pushed out after the end expiratory level of normal breathing *see IS 3 LUNG CAPACITIES • Inspiratory capacity = IRV + TV • Expiratory capacity = ERV + TV • Vital capacity –Maximal volume of air that can be expired after maximal inspiration • Total lung capacity –Maximal volume of air contained in the lungs after a maximal inspiration –TLC = TV + IRV + ERV + RV Control of breathing • Respiratory Control Centre (RCC) regulates breathing. • Located in the medulla oblongata • Respiratory muscles – involuntary neural control • RCC – 2 areas –Inspiratory centre –Expiratory centre Important terminology 1. Chemoreceptors from within the carotid arteries send information to the inspiratory centre on chemical changes 2. Proprioceptors – muscle movements 3. Thermoreceptors – blood temperature 4. Baroreceptors – stretch receptors NEURAL CONTROL DURING EXERCISE • Associated muscles (inspiratory centre): – Sternocleidomastoid – Scalenes – Pectoralis minor • Associated muscles (expiratory centre): – Internal intercostals – Rectus abdominus – Obliques This is summarised on IS 4 Complete WS2