Oxyfuel Gas Welding: Flat Position
advertisement

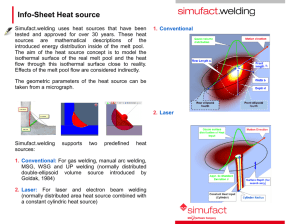
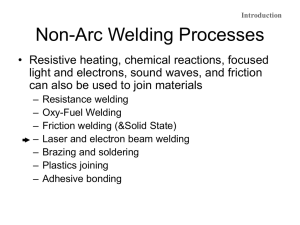
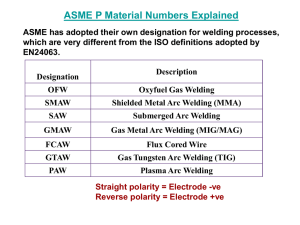
Oxyfuel Gas Welding: Flat Position 4 Basic Positions In Welding • Flat– Also known as “down hand welding” – The easiest and most efficient position • Horizontal • Vertical • Overhead Holding The Torch • Held Like A Pencil • Held Like A Hammer Forehand Welding • Torch tip is held so that the flame is pointing in the direction of travel Backhand Welding • Torch tip is held so that the flame is pointed away from the direction of travel Torch Angles • Travel Angle • Work Angle • Push Angle • Drag Angle Travel Angle • Angle between a line perpendicular (90°) to the weld axis • Proper angle to create a weld pool is (35-45°) Work Angle • Angle between a line perpendicular to the major work piece and a plane determined by the centerline of the torch tip and weld axis Push Angle • Angle used during forehand welding when the welding end of an electrode or a gas flame points in the direction of travel Drag Angle • Angle used during backhand welding when the welding end of an electrode or gas flame points opposite the direction of travel Creating A Continuous Weld Pool • Weld Pool- small pool of molten metal that is formed directly below the welding flame • Penetration is controlled by the width of the weld pool. • The width of the pool should increase as the metal gets thicker. • A wider pool results in deeper penetration Selecting A Welding Rod • A welding rod is added to a weld pool to accomplish: – Fill a groove weld – Form a fillet weld – Fill a weld pool that has a depression in it – Make a completed weld as strong as the base metal Welding Rod Sizes • • • • • • • • 1/16th (16mm) 3/32nd (2.4mm) 1/8th (3.2mm) 5/32nd (4.0mm) 3/16th (4.8mm) 1/4th (6.4mm) 5/16th (7.9mm) 3/8th (9.5mm) Laying A Weld Bead • Adding filler metal to a weld pool • Flat Bead Weld- a flat bead contour used when the bead will be ground down or machines • Convex Bead Weld- a weld bead with a surface that curves outward, away from the root of the weld Your Assignment • Define Technical Terms (Page 271) • Review Question #1-10 (Page 286)