Non-Arc Welding Processes
advertisement
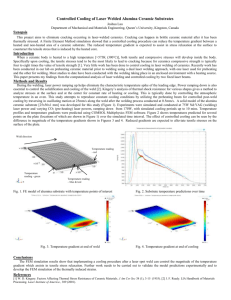
Introduction Non-Arc Welding Processes • Resistive heating, chemical reactions, focused light and electrons, sound waves, and friction can also be used to join materials – – – – – – – Resistance welding Oxy-Fuel Welding Friction welding (&Solid State) Laser and electron beam welding Brazing and soldering Plastics joining Adhesive bonding High Energy Density Processes High Energy Density Processes • Focus energy onto a small area • Laser – CO2 gas: fixed position – Nd-YAG crystal: fiber-optic delivery • Electron Beam High Energy Density Processes • These processes focus the energy onto a small area Examples • Laser - 0.004 inch weld on 1-inch thick stainless steel sheet • Electron Beam - 0.030-inch weld width on 0.5 inch thick steel plate 0.1.1.2.1.T2.95.12 Laser Beam Welding (LBW) Laser 0.1.1.2.1.T3.95.12 High Energy Density Processes Laser Beam Welding (LBW) shielding gas nozzle (optional) Laser beam Plasma plume Plasma keyhole Molten material workpiece motion Keyhole welding High Energy Density Processes Focusing the Beam Heat treatment Surface modification Welding Cutting Advantages Weld penetration, mm 12 6 kW CO2 10 2 kW Nd:YAG 8 6 4 2 0 1 3 5 7 Welding speed, m/min • Single pass weld penetration up to 3/4” in steel • High Travel speed • Materials need not be conductive • No filler metal required • Low heat input produces low distortion • Does not require a vacuum 0.1.1.2.1.T4.95.12 High Energy Density Processes Limitations • High initial start-up costs • Part fit-up and joint tracking are critical • Not portable • Metals such as copper and aluminum have high reflectivity and are difficult to laser weld • High cooling rates may lead to materials problems Electron Beam Welding (EBW) EB Applications 0.1.1.2.1.T6.95.12 High Energy Density Processes Electron Beam Welding (EBW) Advantages • Deepest single pass weld penetration of the fusion processes – 14-inch-thick steel • Fast travel speeds • Low heat input welds produce low distortion High Energy Density Processes Limitations • High initial start-up cost • Not portable • Part size limited by size of vacuum chamber • Produces x-rays • Part fit-up is critical • High cooling rates may lead to materials problems