pptx
advertisement

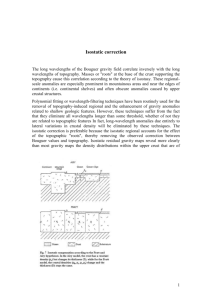
Isostasy: The Concept of Floating Blocks • Isostasy = the concept that large topographic features effectively float on the asthenosphere – Iso = same – stasis = standstill – Involves a state of constant pressure at any point • Pressure: P = ρ g h – If g were measured from a balloon at constant elevation you would expect a mass excess (i.e. larger g) above mountains. • We commonly observe considerably less g over large mountains – Consistent with low density roots beneath large mountains Isostasy: The Initial Discovery • The hypothesis that large mountains have low density roots was first proposed during topographic surveys of India and the Himalayan Mountains Questions: • How does this low density root form? • As a mountain range becomes eroded why are there not large negative anomalies due to the low density roots? Explanation: • Large topographic features effectively ‘float’ on the asthenosphere • Follows Archimedes principle Archimedes’ Principle • Supposedly, Archimedes was taking a bath one day and noticed that the tub overflowed when he got in. – He realized that displaced water could be used to • Detect volumes of odd shaped objects • Detect density differences (helped determine that a crown wasn’t 100% gold) Archimedes Principle: • As an object is partially submerged in a fluid, the weight of fluid that is displaced = the weight reduction of the object • When the displaced fluid = the weight of the object – It floats Isostatic Compensation • Take the case of a layered block floating in a fluid – Remove two layers and… • The bottom is now less deep below the surface of the liquid • The top is less elevated above the surface of the fluid – Thus, floating blocks will seek isostatic equilibrium and are said to be isostatically compensated – In the case of the continental crust, density differences are small, so any significant topography in isostatic equilibrium must be balanced by a thick crustal root • E.g. the Himalayas are < 9 km above sea level, but have roots > 70 km • So, mountains in isostatic equilibrium are like the tip of an iceberg Isostasy and Gravity If blocks are in isostatic equilibrium… • Gravity measurements made at some constant elevation above the blocks would detect (almost) no variation in g – There would be small variations at the edges of blocks due to the nearby topography Isostatic Calculations • Take the simple example of two floating blocks A and B – Each has different layers of varying thickness and density • Includes an asthenospheric layer and an air layer – If A and B are in isostatic equilibrium • Their total weights are the same 1 g h1 2 g h2 3 g h3 air g hair Weight g h asth g hasth BlockA 1 g h1 2 g h 2 air g h air asth g h asth BlockB g 1 h1 2 h2 3 h3 asth hasth BlockA g 1 h1 2 h 2 asth hasth BlockB 1 h1 2 h2 3 h3 asth hasth BlockA These are referred to as the weight equation n i hi i 1 Block A n i hi i 1 Block B 1 h1 2 h 2 asth h asth BlockB Isostatic Calculations • If A and B are in isostatic equilibrium – Their total heights are the same h1 h2 h3 hair h asth BlockA h1 h 2 hair h asth BlockB – This is referred to as the height equation n hi i 1 Block n hi i 1 Block In practice… • Choose the top to be the highest elevation of rock (or water/ice) • Choose the bottom to be the lowest elevation of lithosphere A B Example Isostatic Calculation #1 • Take the case of adding a 2 km thick glacier on top of a continent – The weight of the ice causes the block to sink deeper until isostatic equilibrium is reached – Treat the before and after as two separate blocks that are both in equilibrium and use weight equation (3 x 2.0) + (30 x 2.7) + (70 x 3.1) + (ha x 3.2) = (2 x 0.9) + (3 x 2.0) + (30 x 2.7) + (70 x 3.1) ha = 0.56 km So what does this mean? • • Adding 2 km of ice on top of this continent caused 0.56 km of isostatic subsidence The elevation of the top of the ice sheet after isostatic equilibrium is reached will be only 1.44 km above the original block (from height equation) hair + 3 + 30 + 70 + 0.56 = 2 + 3 + 30 +70 hair = 2 – 0.56 = 1.44 km Example Isostatic Calculation #2 • Suppose that there was a large 2 km deep lake (in equilibrium) • Gradually, sediments are brought in by rivers that eventually replace the water and fill the lake up to its current water level – How thick would the sediments be? (why not 2 km?) (2 x 1.0) + (3 x 2.0) + (30 x 2.7) + (90 x 3.1) + (ha x 3.2) = (hs x 1.8) + (3 x 2.0) + (30 x 2.7) + (90 x 3.1) Two unknowns! Need another equation. Use the height equation. 2 + 3 + 30 + 90 + ha = hs + 3 + 30 + 90 hs = ha + 2 Substitute hs = ha + 2 into weight equation 2 + ha x 3.2 = hs x 1.8 2+ ha x 3.2 = (ha + 2) x 1.8 3.2 ha + 2 = 1.8 ha + 3.6 3.2 ha = 1.8 ha + 1.6 1.4 ha = 1.6 ha = 1.142857142 km ha = 1.1 km Use Height equation to figure out hs hs = ha + 2 = 3.1 km Example Isostatic Calculation #2 • So, ha = 1.1 km and hs = 3.1 km – It took 3.1 km of sediment to completely fill up to the previous lake level – This 3.1 km of sediment added weight and caused an isostatic compensation of -1.1 km (subsidence) – Likewise, removing material would cause isostatic uplift • But the overall elevation would decrease even after isostatic adjustment Airy and Pratt Models of Isostasy • Two end member models have been proposed to account for isostasy. • Airy Model: All blocks have the same density but different thicknesses • Pratt Model: All blocks float to the same depth but have different densities Airy Model of Isostasy • Airy Model: All blocks have the same density but different thicknesses – Thicker blocks have higher elevation and much thicker roots – Higher ground is where the lithosphere is thicker – The weight equation becomes: hlith lith hasth asth A hlith lith h asth asth B Pratt Model of Isostasy • Pratt Model: All blocks float at the same depth, but have differing density – higher elevations indicate less dense rocks – Higher ground is where the lithosphere is thicker – The weight equation becomes: hlith lith A hlith lith B – The height equation is the same for both Airy and Pratt models Airy vs. Pratt: Which is Correct? • The Airy and Pratt are not the only possible models – They are end member models – A combination of density changes and lithosphere thickness may occur But, in general, most data supports… • The Airy model for continental mountain ranges – Continental mountain ranges have thick crustal roots • The Pratt model for mid-ocean ridges – Mid ocean ridges have topography that is supported by density changes • Increased temperature at ridges ---> rocks expand ---> lower density The Isostatic Anomaly • Recall that earlier we learned that floating blocks (in equilibrium) should produce no anomaly. • Gravity measurements at B and D will yield the same values if the free-air correction is applied. – When only the latitude and free-air corrections have been made the result is called the free-air anomaly • If the Bouguer correction is made, the extra mass above B is removed and results in a negative Bouguer anomaly The Isostatic Anomaly • If a region is not isostatically compensated – The free-air anomaly will be positive – The Bouguer anomaly will be zero • Partially compensated regions are common – free-air anomaly > 0 – Bouguer anomaly < 0