Parallelogram Properties & Conditions Geometry Presentation
advertisement
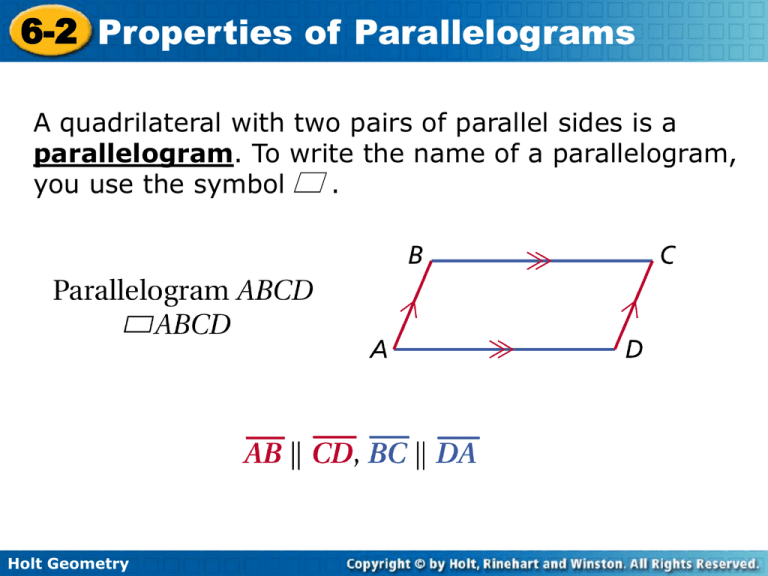
6-2 Properties of Parallelograms A quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides is a parallelogram. To write the name of a parallelogram, you use the symbol . Holt Geometry 6-2 Properties of Parallelograms Holt Geometry 6-2 Properties of Parallelograms Holt Geometry 6-2 Properties of Parallelograms Go to the following videos to see how to work the next problems. http://my.hrw.com/math06_07/nsmedia/lesson_videos/geo/player.h tml?contentSrc=6551/6551.xml http://my.hrw.com/math06_07/nsmedia/lesson_videos/geo/player.h tml?contentSrc=6754/6754.xml http://my.hrw.com/math06_07/nsmedia/lesson_videos/geo/player.h tml?contentSrc=6755/6755.xml Holt Geometry 6-2 Properties of Parallelograms Example 1A: Properties of Parallelograms In CDEF, DE = 74 mm, DG = 31 mm, and mFCD = 42°. Find CF. opp. sides CF = DE Def. of segs. CF = 74 mm Substitute 74 for DE. Holt Geometry 6-2 Properties of Parallelograms Example 1B: Properties of Parallelograms In CDEF, DE = 74 mm, DG = 31 mm, and mFCD = 42°. Find mEFC. mEFC + mFCD = 180° mEFC + 42 = 180 mEFC = 138° Holt Geometry cons. s supp. Substitute 42 for mFCD. Subtract 42 from both sides. 6-2 Properties of Parallelograms Example 1C: Properties of Parallelograms In CDEF, DE = 74 mm, DG = 31 mm, and mFCD = 42°. Find DF. DF = 2DG diags. bisect each other. DF = 2(31) Substitute 31 for DG. DF = 62 Simplify. Holt Geometry 6-2 Properties of Parallelograms Watch this video. It will help with your homework worksheet. http://my.hrw.com/math06_07/nsmedia/lesson_videos /geo/player.html?contentSrc=6754/6754.xml Holt Geometry 6-2 Properties of Parallelograms Check It Out! Example 2a EFGH is a parallelogram. Find JG. diags. bisect each other. EJ = JG Def. of segs. 3w = w + 8 Substitute. 2w = 8 Simplify. w=4 Divide both sides by 2. JG = w + 8 = 4 + 8 = 12 Holt Geometry 6-2 Properties of Parallelograms Check It Out! Example 2b EFGH is a parallelogram. Find FH. diags. bisect each other. FJ = JH 4z – 9 = 2z 2z = 9 z = 4.5 Def. of segs. Substitute. Simplify. Divide both sides by 2. FH = (4z – 9) + (2z) = 4(4.5) – 9 + 2(4.5) = 18 Holt Geometry 6-3 Conditions for Parallelograms Holt Geometry 6-3 Conditions for Parallelograms The two theorems below can also be used to show that a given quadrilateral is a parallelogram. Holt Geometry 6-3 Conditions for Parallelograms http://my.hrw.com/math06_07/nsmedia/lesson_videos/geo/player .html?contentSrc=6552/6552.xml Holt Geometry 6-3 Conditions for Parallelograms Example 1A: Verifying Figures are Parallelograms Show that JKLM is a parallelogram for a = 3 and b = 9. Step 1 Find JK and LM. JK = 15a – 11 Given LM = 10a + 4 Substitute JK = 15(3) – 11 = 34 and simplify. LM = 10(3)+ 4 = 34 Holt Geometry 6-3 Conditions for Parallelograms Example 1A Continued Step 2 Find KL and JM. KL = 5b + 6 KL = 5(9) + 6 = 51 Given JM = 8b – 21 Substitute and simplify. JM = 8(9) – 21 = 51 Since JK = LM and KL = JM, JKLM is a parallelogram by Theorem 6-3-2. Holt Geometry 6-3 Conditions for Parallelograms Example 1B: Verifying Figures are Parallelograms Show that PQRS is a parallelogram for x = 10 and y = 6.5. mQ = (6y + 7)° mQ = [(6(6.5) + 7)]° = 46° Given Substitute 6.5 for y and simplify. mS = (8y – 6)° Given Substitute 6.5 for y and simplify. mR = (15x – 16)° Given Substitute 10 for x mR = [(15(10) – 16)]° = 134° and simplify. mS = [(8(6.5) – 6)]° = 46° Holt Geometry 6-3 Conditions for Parallelograms Example 1B Continued Since 46° + 134° = 180°, R is supplementary to both Q and S. PQRS is a parallelogram by Theorem 6-3-4. Holt Geometry 6-3 Conditions for Parallelograms http://my.hrw.com/math06_07/nsmedia/lesson_videos/geo /player.html?contentSrc=6757/6757.xml Holt Geometry 6-3 Conditions for Parallelograms Example 2A: Applying Conditions for Parallelograms Determine if the quadrilateral must be a parallelogram. Justify your answer. Yes. The 73° angle is supplementary to both its corresponding angles. By Theorem 6-3-4, the quadrilateral is a parallelogram. Holt Geometry 6-3 Conditions for Parallelograms You have learned several ways to determine whether a quadrilateral is a parallelogram. You can use the given information about a figure to decide which condition is best to apply. Holt Geometry