6-2 Properties of Parallelograms
advertisement

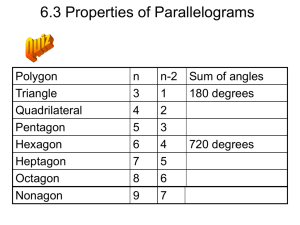
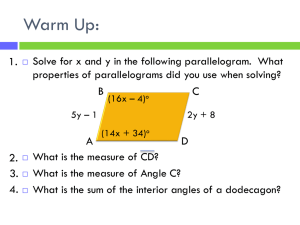
Welcome Parallelogram Experts! Take out the following: (1) Whiteboard and Whiteboard Pen (2) “Discovering Properties of Parallelograms” from Friday Tonight’s Homework Pg. 395 #1-14, 22,24, 33-43 odd Remember: Quiz on Tuesday: 6.1, 6.2, 1.6 and 3.5 of your textbook There is no parent signature sheet for the short week. Tomorrow’s Quiz Topics: 6.1 – Classifying Polygons / Sum of Interior and Exterior Angles 1.6 – Midpoint and Distance Formula 3.5 – Slope formula 6.2 – Properties of Parallelograms 3 Things Lets’ Warm-Up! On Friday’s Exploration worksheet, write a summary of what you learned after completing this packet. Pretend a first grader wants to know about all the properties of a parallelogram. How would you respond? Be ready to share out! Lets’ Warm-Up! In class on Friday, we discussed #1-3. For #4(c), discuss your answer with someone sitting horizontal to you. Then write your solution on a whiteboard. Lets’ Warm-Up! For #5(e), discuss your answer with someone sitting vertical to you. Then write your solution on a whiteboard. Lets’ Warm-Up! For #6(d), discuss your answer with someone horizontal to you. Then write your solution on a whiteboard. Let’s Warm Up On your whiteboard, draw a parallelogram that includes all necessary tick marks and arch marks. 6-2 Properties of Parallelograms Learning Objective: o SWBAT prove and apply properties of parallelograms to solve problems 6-2 Properties of Parallelograms Parallelogram o A quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides. o To write the name of a parallelogram, you use the symbol . Example/Non-Ex of Parallelograms Example Non-Example 6-2 Properties of Parallelograms What question number does this correlate to on your Exploration Worksheet? 6-2 Properties of Parallelograms On your notes, write down the question number from your Exploration Packet that best matches each theorem. Example 1: Properties of Parallelograms In CDEF, DE = 74 mm, DG = 31 mm, and mFCD = 42°. Justify each solution. (a) Find CF. (a) Find mEFC. (b) Find CF. Whiteboards In KLMN, LM = 28 in., LN = 26 in., and mLKN = 74°. Justify each response. a) Find KN. b) Find mNML. c) Find LO. Example 2: Using Properties of Parallelograms to Find Measures WXYZ is a parallelogram. (a) Find YZ. (b) Find mZ. Whiteboards EFGH is a parallelogram. (a ) Find JG (b) Find FH. Whiteboards 1. Opposite sides of a parallelogram are ____________ and congruent. 2. What do the slopes have to be if two lines are parallel to each other? Example 3: Parallelograms in the Coordinate Plane Three vertices of JKLM are J(3, –8), K(–2, 2), and L(2, 6). Find the coordinates of vertex M. Remember: When you are drawing a figure in the coordinate plane, the name gives the order of the vertices. Example 3: Parallelograms in the Coordinate Plane • Step 1: Graph the points. • Step 2: Find the slope of KL by counting the units from K to L. • Step 3: Start at J and count the same number of units. • Step 4: Use the slope formula to verify that Graphing Whiteboard Three vertices of PQRS are P(–3, –2), Q(–1, 4), and S(5, 0). Find the coordinates of vertex R. Math Joke of the Day • What do you call an urgent message sent across a parallel network? • A parallelogram! Example 4: Properties of Parallelograms in a Proof Given: ABCD is a parallelogram. Prove: ∆AEB ∆CED Proof: Statements 1. ABCD is a parallelogram Reasons 1. Given 2. 3. opp. sides diags. bisect each other 4. SSS Steps 2, 3 Whiteboards QRST is a parallelogram. Find each measure. Justify your reasoning. (a) TQ (b) mT Whiteboards In PNWL, NW = 12, PM = 9, and mWLP = 144°. Find each measure (a) PW (b) mPNW Exit Ticket Take out a half sheet of binder paper. Title it: 6.2 Exit Ticket Write your name in the upper right hand corner. 1. List the key ideas from todays lesson. 2. Draw and label every side and angle with the given information for PQRS : a. b. c. PQ= 10 QR=5 mS = 110°