ppt - eweb.furman.edu
advertisement

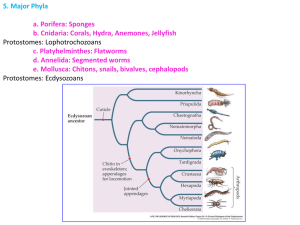
5. Major Phyla Deuterostomes: l. Chordata Vertebrata Gnathostomes - Tetrapods 350 mya Devonian 417 mya Radiation of the “stem tetrapods” !!! Carboniferous Old friends a fish 5. Major Phyla Deuterostomes: l. Chordata Vertebrata Gnathostomes - Tetrapods Caecilians Salamanders Frogs 5. Major Phyla Deuterostomes: l. Chordata Vertebrata Gnathostomes Tetrapods - Amniotes The amniotic egg was a big advance Resist desiccation - amnion protects the embryo - yolk sac provides nourishment - allantoic sac holds waste produced by embryo Provision embryo allows for colonization of dry habitats 5. Major Phyla Deuterostomes: l. Chordata Vertebrata Gnathostomes Tetrapods - Amniotes SYNAPSID Amniote ancestor ANAPSID (turtles?) Hylonomus Casineria DIAPSID 5. Major Phyla Deuterostomes: l. Chordata Vertebrata Gnathostomes Tetrapods - Amniotes The Permian Formation of Pangaea dries the landscape; amniotes dominate like the gymnosperms. shelled egg and the seed Dimetrodon – a Pelycosaur 5. Major Phyla Deuterostomes: l. Chordata Vertebrata Gnathostomes Tetrapods - Amniotes The Permian Pelycosaurs The synapsids radiate and dominate Dicynodonts Gorgonopsids Therapsids Cynodonts A cynodont Mammals 5. Major Phyla Deuterostomes: l. Chordata Vertebrata Gnathostomes Tetrapods - Amniotes Mammals - excellent transitional sequences from cynodont ‘reptiles’ - first fossils with all mammalian features (jaw, ear, dentition, fur) date to ~200 mya - Morganucodontids Radiations of Mammals They diversify during the Mesozoic, but the modern groups radiate and dominate in the Cenozoic 5. Major Phyla Deuterostomes: l. Chordata Vertebrata Gnathostomes Tetrapods - Amniotes Mammals - Monotremes: lay eggs, “sweat” milk 5. Major Phyla Deuterostomes: l. Chordata Vertebrata Gnathostomes Tetrapods - Amniotes Mammals - Monotremes: egg laying, “sweat” milk - Marsupials: live birth to embryo – attaches to nipple to complete development. Mother does not need to abandon the nest/young to feed. Pygmy possum – Australia (opossums in Western Hemisphere) 5. Major Phyla Deuterostomes: l. Chordata Vertebrata Gnathostomes Tetrapods - Amniotes Mammals - Monotremes: egg laying, “sweat” milk - Placentals: Longer internal development allows for precocial behavior (independence on birth); placental allows for direct, energyefficient transfer of nutrients between blood systems of mother and offspring. Each energy transformation is less than 100% efficient Milk production in mammary glands DIGESTION Nutrients in bloodstream of mother Placenta - Marsupials: live birth to embryo – attaches to nipple to complete development. Mother does not need to abandon the nest/young to feed. FOOD FOOD for OFFSPRING DIGESTION Nutrients in bloodstream of offspring 5. Major Phyla Deuterostomes: l. Chordata Vertebrata Gnathostomes Tetrapods - Amniotes Mammals - Monotremes: egg laying, “sweat” milk - Marsupials: live birth to embryo – attaches to nipple to complete development. Mother does not need to abandon the nest/young to feed. - Placentals: Longer internal development allows for precocial behavior (independence on birth); placental allows for more direct and energy-efficient nutrient transfer precocial altricial 5. Major Phyla Deuterostomes: l. Chordata Vertebrata Gnathostomes Tetrapods - Amniotes In the Mesozoic, the synapsids are replaced by the great diapsid radiations of Ichthyosaurs, Pterosaurs, and Dinosaurs Archosaurs: Dinosaurs, Pterosaurs, Crocodilians, Birds Lepidosaurs: Lizards, Snakes, Sphenodonts) Diapsida Ichthyosaurs Younginiformes 5. Major Phyla Deuterostomes: l. Chordata Vertebrata Gnathostomes Tetrapods - Amniotes - Archosaurs Crocodilians Pterosaurs Ornithiscians Dinosaurs Saurischians Sauropods Theropods Carnosaurs Birds 5. Major Phyla Deuterostomes: l. Chordata Vertebrata Gnathostomes Tetrapods - Amniotes Birds: (derived traits) No teeth Feathers and endothermy flight feathers keeled breastbone Clavicles united into wishbone Pneumatic skeleton (houses air sacs from respiratory system) Unidirectional respiration 5. Major Phyla Deuterostomes: l. Chordata Vertebrata Gnathostomes Tetrapods - Amniotes In the Mesozoic, the synapsids are replaced by the great diapsid radiations of Ichthyosaurs, Pterosaurs, and Dinosaurs Archosaurs: Dinosaurs, Pterosaurs, Crocodilians, Birds Lepidosaurs: Lizards, Snakes, Sphenodonts) Diapsida Ichthyosaurs Younginiformes 5. Major Phyla Deuterostomes: l. Chordata Vertebrata Gnathostomes Tetrapods - Amniotes - Lepidosaurs Keuhniosaurs Squamates Scales, moveable quadrate (double hinged jaw), hinged skull Rhynchocephalians (Tuatara) 5. Major Phyla Deuterostomes: l. Chordata Vertebrata Gnathostomes Tetrapods - Amniotes - Lepidosaurs - Squamates