ppt - eweb.furman.edu
advertisement
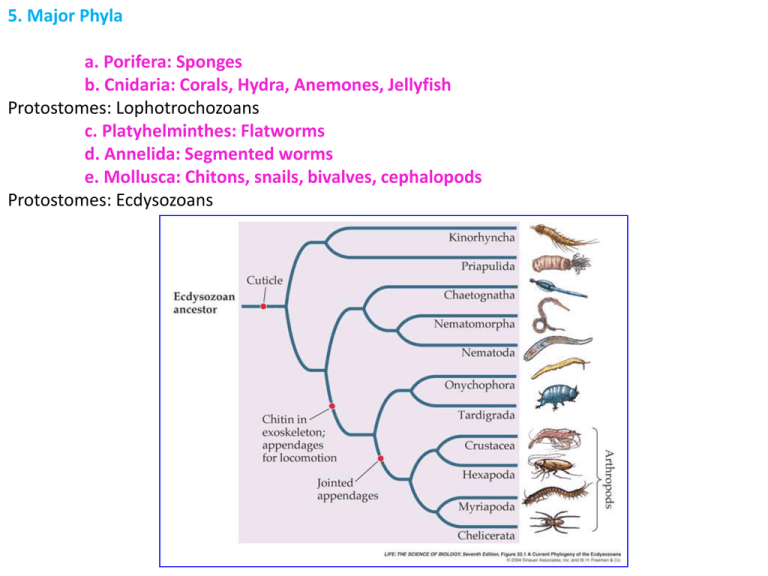
5. Major Phyla a. Porifera: Sponges b. Cnidaria: Corals, Hydra, Anemones, Jellyfish Protostomes: Lophotrochozoans c. Platyhelminthes: Flatworms d. Annelida: Segmented worms e. Mollusca: Chitons, snails, bivalves, cephalopods Protostomes: Ecdysozoans 5. Major Phyla Protostomes: Ecdysozoans f. Nematoda - molt four times, resecreting their cuticle each time - complete digestive tract - some cephalization with anterior neural ganglion - free living and parasitic -human parasites: trichinosis, filariasis, elephantiasis, Ascariasis (two foot intestinal worms) 5. Major Phyla Protostomes: Ecdysozoans f. Nematoda g. Tardigrada Cryptobiotic: can dehydrate to less than 1% of normal and endure for 10 years. Can endure the vaccuum of space and 6000 atmospheres of pressure. Thin exoskeleton, unjointed legs 5. Major Phyla Protostomes: Ecdysozoans f. Nematoda g. Tardigrada h. Onychophora Sister group to the Arthropods; thin exosleleton and unjointed legs, like tardigrades Predatory; immobilize prey by shooting glue 5. Major Phyla Protostomes: Ecdysozoans f. Nematoda g. Tardigrada h. Onychophora i. Arthropoda Myriapoda Vericrustacea Mandibulata Exoskeleton Jointed legs Crustacea Remipedes Hexapods Trilobita Arachnomorpha Xiphosura Chelicerata From Regier et al. (2010) Arachnids 5. Major Phyla Protostomes: Ecdysozoans f. Nematoda g. Tardigrada h. Onychophora i. Arthropoda Arachnomorpha clade: Includes trilobites and Chelicerates. The chelicerates have two body regions, the cephalothorax and abdomen. They also have only one pair of appendages before the mouth – usually pincers. In spiders, these are fangs that inject poison. 5. Major Phyla Protostomes: Ecdysozoans f. Nematoda g. Tardigrada h. Onychophora i. Arthropoda The Mandibulata clade: Includes the myriapods (centipedes and millipedes) and crustaceans and their descendants (the hexapods). So, insects are the terrestrial descendants of crustaceans. 5. Major Phyla Protostomes: Ecdysozoans f. Nematoda g. Tardigrada h. Onychophora i. Arthropoda So in the mandibulata clade, we see duplication (myriapods), specialization (crustaceans), and reduction/fusion (insects) 5. Major Phyla Protostomes: Deuterostomes: j. Echinodermata Internal skeleton composed of interlocking plates of calcium carbonate. A system of internal canals fills and empties tube feet. 5. Major Phyla Protostomes: Deuterostomes: j. Echinodermata k. Hemichordata Hollow dorsal nerve cord Pharygeal gill slits All marine – some reach 8 ft in length 5. Major Phyla Protostomes: Deuterostomes: j. Echinodermata k. Hemichordata l. Chordata 4 characteristics: - hollow dorsal nerve chord - notochord - pharygeal gill slits - post-anal tail 5. Major Phyla Protostomes: Deuterostomes: j. Echinodermata k. Hemichordata l. Chordata subphyla: Urochordata Cephalochordata Vertebrata “Tunicates”: Mobile larvae, sessile filterfeeding adults - filter with the pharynx and gill slits. 5. Major Phyla Protostomes: Deuterostomes: j. Echinodermata k. Hemichordata l. Chordata subphyla: Urochordata Cephalochordata Vertebrata Mobile larvae, sessile filterfeeding adults - filter with the pharynx and gill slits. 5. Major Phyla Protostomes: Deuterostomes: j. Echinodermata k. Hemichordata l. Chordata subphyla: Urochordata Cephalochordata Vertebrata Pikaia – the earliest Chordate – dates from the Cambrian period 5. Major Phyla Protostomes: Deuterostomes: j. Echinodermata k. Hemichordata l. Chordata subphyla: Urochordata Cephalochordata Vertebrata “Jointed spine” – vertebrae. Although Hagfish lack this, so sometimes the group is called Craniata (has a skull) Patterns in evolution: Innovation, radiation, competitive contraction 5. Major Phyla Deuterostomes: l. Chordata Vertebrata Hyperoartia: “Jawless fishes” Lampreys and Hagfish Lamprey larvae look very much like cephalochordates 5. Major Phyla Deuterostomes: I. Chordata Vertebrata Hyperoartia: “Jawless fishes” Evolve in late Cambrian, radiate in the Ordovician 5. Major Phyla Deuterostomes: l. Chordata Vertebrata Gnathostomes – Jawed Vertebrates Move from detritivores to predators 5. Major Phyla Deuterostomes: l. Chordata Vertebrata Gnathostomes – Jawed Vertebrates The Devonian was the “Age of Fishes” – a radiation of the first jawed vertebrates, dominated first by the Placoderms and then by Cartilaginous and bony fishes Arthrodires Placoderms Antiarchs Chondrichthyes (Sharks, rays) Acanthodians Teleosts Ray-finned Fishes Bony Fish Lobe-finned Fishes 5. Major Phyla Deuterostomes: l. Chordata Vertebrata Gnathostomes – Jawed Vertebrates The Devonian was the “Age of Fishes” – a radiation of the first jawed vertebrates, dominated first by the Placoderms and then by cartilaginous and bony fishes 5. Major Phyla Deuterostomes: l. Chordata Vertebrata Gnathostomes – Jawed Vertebrates Bony fishes dominate today: lighter skeleton and swim bladder Ray-finned Fishes Lobe-finned Fishes 5. Major Phyla Deuterostomes: l. Chordata Vertebrata Gnathostomes – Jawed Vertebrates Bony Fishes (Osteichthyes) comprise 40% of living vertebrate species