Introduction
advertisement

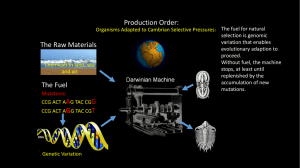
Intro • For a gentleman should know something of invertebrate zoology, call it culture or what you will, just as he ought to know something about painting and music and the weeds in his garden. • Martin Wells, Lower Animals, 1968 Kingdoms of life • Eubacteria, Archaea, Fungi, Plantae • Protista ~ 18 Phyla • Animalia ~ 34 Phyla Diversity of known groups • Kingdom Animalia – 1,000,000+ described species – Vert’s (~50,000) – Invert’s and other Chordates (~ 1 million) – Total species? • 10-30 million • Or 100-200 million Phyla with most spp. • Arthropoda ~ 1.1 million • Mollusca ~ 100,000 • Protista ~ 80,000 Invert origins • Life on earth: after cooling ~ 4.6 billion YA • Eukaryotic cells: ~ 2.7 billion YA • Shared ancestors of plants + animals: ~ 1.6 billion YA • Metazoans: ~ 600 million YA • Evidence? Geological strata • Learn major eras, periods, epochs • (of Phanerozoic eon) • http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/help/timeform.html Cambrian Explosion? • Major phyla first appear and diversify • Precambrian – Cnidaria and Porifera Cambrian explosion • Paleozoic – Mollusca, Brachiopoda, Ctenophora, Priapulida, Onychophora, Arthropoda, Phoronida, Annelida, Echinodermata, Chordata, Hemichordata, Tardigrada, Nematoda, Nemertina Phyla Brachiopoda, Ctenophora, Priapulida Phyla Onychophora, Phoronida, Arthropoda Phyla Annelida, Echinodermata, Hemichordates Phyla Tardigrada, Nemertina, Nematoda Hookworm Cambrian explosion • Mesozoic – Entoprocta, Rotifera, Nematomorpha, Platyhelminthes, Gastrotricha, Acanthocephala Biomes and ecosystems Marine ecosystems • Most of planet is marine • Available habitats: – Littoral, pelagic, benthic (epifauna, infauna), interstitial Estuaries, coastal marshlands • Salt marsh • Estuary Freshwater • Less stable than marine • Requires diapause, hibernation, aestivation Terrestrial • Temperature extremes • Lower diversity (except arthropods) Evolution • Anagenesis = microevolution causes changes w/in species • Macroevolution: – Speciation = birth of a species – Extinction = death of a species Microevolution • Changes caused by: • Random genetic drift, Natural selection, etc. • Changes occur that result in organisms that “fit” their environment Macroevolution • Cladogenesis = origins + radiations of species lineages • Mass extinctions • Rapid speciation and radiation What causes major species radiations? • Flexible architecture of genetic regulation – Developmental pathways undergo major changes with few genetic differences – Results in changes in body plan – Requires flexible architecture of genetic regulation Classification, systematics, phylogeny • Review basic philosophy of systematics Classification • Ordering organisms into groups • By taxa: species, genera, families, etc. How are they grouped? Nomenclature • Rules for naming • 1. Each kind of organism has only one correct name • 2. No 2 kinds of organism have the same name. Binomial nomenclature • Linnaeus’ system • Binomial = Genus + species ICZN • International Code of Zoological Nomenclature: 1758 • Principles: • Scientific names are Latin, valid name based on first usage, names must be based on type specimens ICZN in practice • Author who first describes species has name following species name Wheel bug, Arilus cristatus (Linnaeus) • In parentheses = in different genus than originally placed Systematics • = taxonomy + phylogenetics • Study of kinds and diversity of life on Earth, and of relationships between them Alpha taxonomy • Naming species: • Describing undescribed organisms • Uniting multiple descriptions of same organism Science of systematics • Classical science based on morphology • Currently use embryology, physiology, immunology, behavior, biochemistry, molecular genetics, morphology • Growing science Basic terms • Monophyletic group = includes all descendants • Paraphyletic group = does not include all descendants • Polyphyletic group = some arose from different ancestors Characters • Attributes of organisms used in comparisons • Homology = shared common ancestor has this character