Phylum Chordata
Phylum:
Chordata
4 Characteristics of Chordates
1
2
3
4
Defining Characteristics
Notochord. Found under the nerve chord. Runs down the
dorsal side of an organism
4 Characteristics of Chordates
1
2
3
4
Defining Characteristics
Notochord. Found under the nerve chord. Runs down the
dorsal side of an organism
Dorsal Tubular nerve cord. Nerves arranged as a pipe filled
with fliud
4 Characteristics of Chordates
1
2
3
4
Defining Characteristics
Notochord. Found under the nerve chord. Runs down the
dorsal side of an organism
Dorsal Tubular nerve cord. Nerves arranged as a pipe filled
with fliud
Pharyngeal gill pouches (develop into gills in fish and
amphibians and various other parts in reptiles to mammals
(eg. Inner ear))
4 Characteristics of Chordates
1
2
3
4
Defining Characteristics
Notochord. Found under the nerve chord. Runs down the
dorsal side of an organism
Dorsal Tubular nerve cord. Nerves arranged as a pipe filled
with fliud
Pharyngeal gill pouches (develop into gills in fish and
amphibians and various other parts in reptiles to mammals
(eg. Inner ear))
Muscular Postanal Tail (post = after anal = anus)
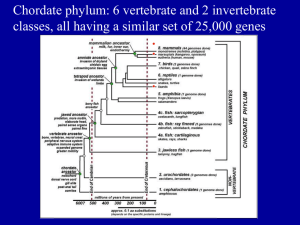
Subphylums of Chordata
Subphylum
Urochordata
Cephalochordata
Vertebrata
Characteristics
Larvae: Has all 4 characteristics of chordates
Adult: Sessile, Lacks chordate characteristics
with the exception of the pharyngeal pouches
Subphylums of Chordata
Subphylum
Urochordata
Cephalochordata
Vertebrata
Characteristics
Larvae: Has all 4 characteristics of chordates
Adult: Sessile, Lacks chordate characteristics
with the exception of the pharyngeal pouches
Aquatic organisms containing all 4 characteristics
of chordates as an adult
Subphylums of Chordata
Subphylum
Urochordata
Characteristics
Larvae: Has all 4 characteristics of chordates
Adult: Sessile, Lacks chordate characteristics
with the exception of the pharyngeal pouches
Cephalochordata
Aquatic organisms containing all 4 characteristics
of chordates as an adult
Vertebrata
Contain all 4 characteristics of chordates. The
notochord, however, is replaced by vertebral
column
Trends in Evolution of Chordates
Trends in Evolution of Chordates
Trends in Evolution of Chordates
Trends in Evolution of Chordates
Trends in Evolution of Chordates
Trends in Evolution of Chordates
Subphylum Vertebrata
Class Osteicthyes: Most diverse class of vertebrate
Fins
Uses: Balance and Movement
Two types of fins
Subphylum Vertebrata
Class Osteicthyes: Most diverse class of vertebrate
Fins
Uses: Balance and Movement
Two types of fins
1) Ray-finned fishes: Thin fins
supported by rigid ray structures
2) Lobe-finned fishes: fins are made of fleshy
appendages. Later evolved into legs.
Characteristics of Ray-Finned Fish
1) Bony Skeleton and scales
2) Swim bladder (Air sac allows fish to hover in
the water column)
3) 2 chambered heart
Characteristics of Ray-Finned Fish
1) Bony Skeleton and scales
2) Swim bladder (Air sac allows fish to hover in
the water column)
3) 2 chambered heart
4) Paired fins
5) Jaws
6) Gills
Class: Amphibia
Amphibian: Live in land and water (Larval stage
is aquatic, Adult stage is terrestrial)
Common Examples: Frogs, Toads, Newts,
Salamanders, Caecilians,
Major Evolutionary Change:
Class: Amphibia
Amphibian: Live in land and water (Larval stage
is aquatic, Adult stage is terrestrial)
Common Examples: Frogs, Toads, Newts,
Salamanders, Caecilians,
Major Evolutionary Change: Jointed Limbs that
allowed the move to land
Characteristics of Amphibians
1)
2)
3)
4)
5)
Tetrapods (four legs)
Undergo metamorphosis
Three chambered heart
Lungs in adults
Smooth moist skin (Capable of gas exchange)