Frankish Art PowerPoint 4
advertisement

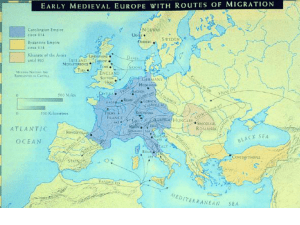
Frankish Art Who were the Franks? • One of many Germanic nomads pushing into Roman Empire • Most influential barbarian tribe because they convert to Roman Catholic Christianity during Merovingian Dynasty (5th to 8th century CE) • Height during Carolingian Dynasty (8th to 10th century CE) • Charlemagne revives title of Holy Roman Emperor = Roman Empire = Frankish federation = Salian Franks 358 = Conquests to 460 = Conquests to 482 = Frankish Kingdom 482 = Conquests to 496 = Conquests to 507 = Frankish Kingdom 511 = Conquests to 537 = Vassal states = Frankish Kingdom 768 = Conquests to 814 = Loosely held territories = Losses 798 Ring with a Cross, 6th century CE, Gold filigree, cloisonné cells inset with garnet; • Worn by high ranking men and women • Sometimes used as seals but mostly decorative • Sophistication of Frankish metalwork Pair of Bird-Shaped Brooches, 550–600 CE Gold sheet, cloisonné cells Brooch with a runic inscription on back Merovingian, 6th century CE Length: 7.4 cm Glass drinking-horn Frankish/Merovingian, 5th century CE Animal head from Oseberg ship burial, ca. 825 CE, wood, about five feet tall Germanic animal style Belt Buckle, 675–725 CE; Found in Germany; Iron with silver inlays. Iron and silver buckle Merovingian, 7th century CE Iron axe-head inlaid with silver Merovingian, 7th century CE From Germany Length: 17.5 cm •A ceremonial or battle axe •The throwing axe was the favorite weapon of the Franks •Silver in-lay shows the status/military rank of original owner Frankish "Claw" Beaker, 400–600 CE Fragment of a Sarcophagus, 700s CE •Monogram of Christ (Chi and Ro) along with alpha and omega – common motifs •Non-Greek speaking sculptor Equestrian statuette of Charlemagne 9th Century Bronze, Maximum height of horse: 21 cm •Artists took up the Gallo-Roman tradition of casting and based their works on examples from antiquity