Community Based Newborn Care
advertisement

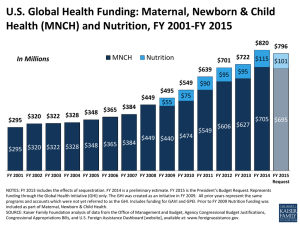
BRAC Community Based Newborn Care PRESENTATION OUTLINE Maternal and Child Health Scenario in Bangladesh BRAC MNCH Programme Service Delivery Service provider Intervention areas ANC, PNC Essential Newborn Care Reduction of NMR Challenges addressed, Lessons learned Maternal and Child Health Scenario in Bangladesh A reduction from 12,000 maternal deaths per year in 2001 to about 7,300 in 2010 An increase in hospital birth from 9.2% to 23% and skilled attendance at delivery from 12.2% to 26.5% in three years Of 250,000 annual under-five deaths, over half die in their first month At least two-thirds of these deaths could be averted by ensuring appropriate care Source : BMMS 2010, BDHS 2007 BRAC MNCH PROGRAMME Rural MNCH Improving Maternal, Neonatal and Child Survival BRAC-GoB-Unicef DFID, AusAID, EKN and BRAC www.brac.net BRAC MNCH PROGRAMME IMPLEMENTATION AREAS 19 million rural populations www.brac.net 5. Linkage between community and p health facilities public/private 4. Timely Referral of emergency cases 2. Community empowerment 1. Capacity development of HR NHW SS SK CSBA Midwife 3. Services rendered at community, households and facilities Staff OPERATIONAL STRATEGIES SERVICE PROVIDER AT COMMUNITY LEVEL Selected from localities Age 25-45 years Married Willingness to work Community acceptability Selected from localities Age 25-45 years Married Willingness to work Community acceptability Shasthya Shebika Selected from localities Age 20-35 years Married Minimum SSC Willingness to work Community acceptability Shasthya Kormi Newborn Health Worker SERVICE DELIVERY Maternal Care Identification of pregnancy Ante, intra & post natal care Referral of maternal complications Family planning Post-abortion care Neonatal Care Essential Newborn care Special care for LBW babies Management of birth asphyxia Detection and referral of Neonatal sepsis Referral of complications Child Care Exclusive breast feeding and complementary feeding Immunization and Vitamin A intake Community case management of ARI and diarrhea Referral of complications REFERRAL SYSTEM Referral Hub UTILIZATION OF ANTENATAL AND POSTNATAL CARE 4 or more ANC 100 83 88 93 60 40 20 3 or more PNC 15 100 0 BDHS 2007 Baseline 2009 2010 2011 (JanSep) 80 80 Percentage Percentage 80 84 86 60 40 20 28 0 Baseline 2009 2010 2011 (Jan-Sep) www.brac.net TREND IN PLACE OF BIRTH Trend in place of birth 100 14 90 22 25 78 75 30 80 70 86 60 70 50 Baseline 2009 Home 2010 2011 (Jan-Sep) Hospital A major shift is observed in place of birth from home to Hospitals www.brac.net 91 94 93 95 2011 (Jan-Sep) 100 2010 ESSENTIAL NEWBORN CARE 87 84 76 Percentage 75 66 68 50 43 26 25 11 Thermal care within 10 minutes BDHS 2007 2011 (Jan-Sep) 2010 2009 BDHS 2007 2011 (Jan-Sep) 2010 2009 BDHS 2007 Trained attandance at home delivery 2009 - 0 Initiation of breast feeding within 1 hour of birth Increasing coverage of essential newborn care LOW BIRTH WEIGHT DETECTION AND SPECIAL CARE Low birth weight detection and special care 100 85 84 80 60 40 20 19 21 15 19 0 2010 Birth weight taken 2011 (Jan-Sep) Low birth weight Spacial care Sick Newborn Case Management Neonatal sepsis diagnosed and referred 2.5 Birth asphyxia diagnosed and managed 4 3.5 2 3 2.5 1.5 2 1 1.5 1 0.5 0.5 0 0 2009 2010 Diagnosed 2011 (Jan-Sep) Referred 2009 2010 Diagnosed 2011 (Jan-Sep) Managed by SS REDUCTION OF NEONATAL MORTALITY 60 52 50 48 The NMR reduction is 29% over four years Per 1,000 Live Births 42 40 30 41 37 31 30 22 28 26 22 20 10 0 National Statistics Intervention Areas * BDHS 2007; BRAC MIS CHALLENGES ADDRESSED Changes in behavior and practices Community health worker’s adoption of new knowledge and practices Lack of competence among health providers to manage neonatal sepsis Lack of services in referral facilities for managing newborn complications LESSONS LEARNED Community health workers can perform if properly trained and supervised Support of skill mix team Postnatal home visit Performance based incentives Community support network Referral support network THE END