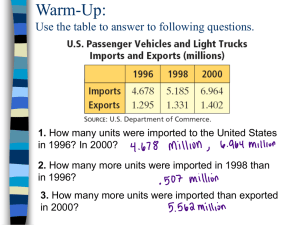
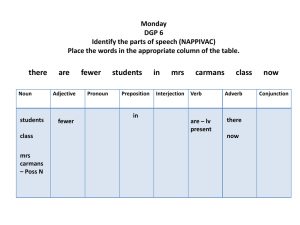
Matrices The Basics
advertisement

Matrices The Basics Vocabulary and basic concepts A matrix is an array of numbers For example Three classes are split into boys and girls. A: 15 boys and 17 girls. B: 18 boys and 14 girls. C: 10 boys and 19 girls. This data could be arranged as a 2 X 3 MATRIX. 15 18 10 17 14 19 Mrs. S Richards A matrix with R rows and C columns is called an R X C Matrix. This is called the ORDER of the matrix. Each entry in the matrix is called an ELEMENT. Mrs. S Richards The CO-ORDINATE (2,3) has ONE ROW and TWO COLUMMS. It is a 1X2 matrix A matrix with only one row is called a ROW VECTOR. 6 The vector 2 represents a TRANSLATION or shift 6 units to the right and 2 units down. A matrix with only one column and any number of rows is called a COLUMN VECTOR. A Matrix with the same number of ROWS as COLUMNS is called a SQUARE MATRIX. Mrs. S Richards 1 2 6 6 3 7 3 0 10 Addition and Subtraction of Matrices We may add or subtract two matrices ONLY if they have the SAME ORDER. Adding or subtracting matrices is carried out by adding or subtracting their corresponding elements. 2 1 6 5 8 4 3 4 1 7 4 11 2 3 4 1 6 2 1 3 2 1 3 6 0 5 4 1 2 2 5 7 0 2 5 3 3 2 3 If two matrices A and B are of UNEQUAL ORDER then A + BMrs.does not exist. S Richards Addition and Subtraction of Matrices If two matrices A and B are of EQUAL ORDER then A+B=B+A Addition of Matrices (where allowed) is COMMUTATIVE 2 1 6 5 6 5 2 1 3 4 1 7 1 7 3 4 8 4 4 1 1 Mrs. S Richards EQUAL MATRICES Two matrices A and B are equal if EVERY element in A is equal to EVERY element in B. Two matrices may be the SAME ORDER but NOT EQUAL. 4 3 4 3 1 0 1 0 Mrs. S Richards CAN YOU SEE WHY? Multiplication by a Scalar If k is a constant scalar, the matrix kA is such that EACH OF ITS ENTRIES ARE MULTIPLIED by k 4 3 A 1 0 8 6 2A 2 0 4k 3k kA 1k 0k Mrs. S Richards 1 5 54 53 A 1 5 0 The ZERO or NULL Matrix Has every element ZERO. 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Adding or subtracting the NULL Matrix will have no effect. MULTIPLYING by the NULL Matrix will create another NULL MATRIX. Mrs. S Richards The UNIT or IDENTITY MATRIX I 1 0 A VERY IMPORTANT MATRIX. (Later work!) 1 0 0 These are always SQUARE 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 MATRICES This is denoted by the letter I and has zero entries except for 1’s on the diagonal. MULTIPLYING by the IDENTITY Matrix will create the SAME MATRIX. In a similar way to Multiplying a number by 1 Mrs. S Richards The TRANSPOSE OF A MATRIX The rows are written as columns and the columns as rows. 1 2 A= 0 5 3 1 2 B 1 2 0 4 5 7 1 0 A 2 5 t 3 1 4 Bt 1 2 5 2 0 7 Mrs. S Richards