Implementing and
Verifying Basic
EIGRP for the
Enterprise LAN
Architecture
Implementing an EIGRP-Based Solution
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
ROUTE v1.0—2-1
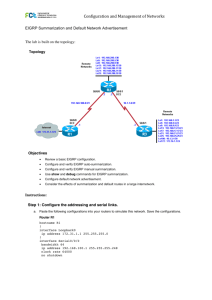
EIGRP Deployment
R1#
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Serial0/0/1
bandwidth 512
ip address 192.168.1.101 255.255.255.224
!
router eigrp 110
network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 192.168.1.0
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
R2#
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 172.17.2.2 255.255.255.0
!
interface Serial0/0/1
bandwidth 512
ip address 192.168.1.102 255.255.255.224
!
router eigrp 110
network 172.17.2.0 0.0.0.255
network 192.168.1.0
ROUTE v1.0—2-2
Verifying EIGRP Neighbors
R1#show ip eigrp neighbors
IP-EIGRP neighbors for process 110
H
Address
Interface
Hold Uptime
SRTT
(sec)
(ms)
0
192.168.1.102 Se0/0/1
10
00:07:22
10
RTO
Q Seq
Cnt Num
2280 0 5
R2#show ip eigrp neighbors
IP-EIGRP neighbors for process 110
H
Address
Interface
Hold Uptime
SRTT
(sec)
(ms)
0
192.168.1.101 Se0/0/1
10
00:17:02
10
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
RTO
Q Seq
Cnt Num
1380 0 5
ROUTE v1.0—2-3
Verifying EIGRP Neighbors (Cont.)
R1#show ip eigrp neighbors
IP-EIGRP neighbors for process 110
H
Address
Interface
Hold Uptime
SRTT
(sec)
(ms)
0
192.168.1.102 Se0/0/1
10
00:07:22
10
1
2
3
4
5
1.
Neighbor index
2.
Neighbor IP address
3.
Interface on which the neighbor is reachable
4.
Remaining hold time
5.
Neighbor uptime
6.
Smooth round-trip time
7.
Retransmission timeout
8.
Number of packets to send to neighbor
9.
Last sequence received
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
6
RTO
Q Seq
Cnt Num
2280 0 5
7
8
9
ROUTE v1.0—2-4
Verifying EIGRP Neighbors (Cont.)
Total retransmission count
Current retry count
R1#show ip eigrp neighbors detail
IP-EIGRP neighbors for process 110
H
Address
Interface
Hold Uptime
SRTT
RTO Q
Seq
(sec)
(ms)
Cnt Num
0
192.168.1.102 Se0/0/1
14
00:17:55 0
4500 3
274
Last startup serial 569
Version 12.4/1.0, Retrans: 2, Retries: 2, Waiting for Init Ack
UPDATE seq 307 ser 29-569 Sent 8924 Init Sequenced
UPDATE seq 310 ser 570-573 Sequenced
UPDATE seq 312 ser 574-578 Sequenced
Neighbor version of
Cisco IOS
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Current pending packets
ROUTE v1.0—2-5
Verifying EIGRP Routes
Network
EIGRP route type
AD / Metric
Next hop
Route age
R1#show ip route eigrp
D
172.17.0.0/16 [90/40514560] via 192.168.1.102, 00:07:01,
Serial0/0/1
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
D
172.16.0.0/16 is a summary, 00:05:13, Null0
192.168.1.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
D
192.168.1.0/24 is a summary, 00:05:13, Null0
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
ROUTE v1.0—2-6
Verifying EIGRP Operation
R1#show ip protocols
Routing Protocol is "eigrp 110"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Default networks flagged in outgoing updates
Default networks accepted from incoming updates
EIGRP metric weight K1=1, K2=0, K3=1, K4=0, K5=0
K values
EIGRP maximum hopcount 100
EIGRP maximum metric variance 1
Redistributing: eigrp 110
EIGRP NSF-aware route hold timer is 240s
<output omitted>
Load-balancing setting
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
172.16.1.0/24
Networks being announced
192.168.1.0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway
Distance
Last Update
(this router)
90
00:09:38
Gateway
Distance
Last Update
192.168.1.102
90
00:09:40
EIGRP local AD
Distance: internal 90 external 170
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
ROUTE v1.0—2-7
Verifying EIGRP Operation (Cont.)
R1#show ip eigrp interfaces
IP-EIGRP interfaces for process 110
Xmit Queue
Interface
Peers Un/Reliable
Fa0/0
0
0/0
Se0/0/1
1
0/0
Mean
SRTT
0
10
Pacing Time
Un/Reliable
0/10
10/380
Multicast
Flow Timer
0
424
Pending
Routes
0
0
Peer count
Route status
Next hop
R1#show ip eigrp topology
IP-EIGRP Topology Table for AS(110)/ID(192.168.1.101)
Codes: P - Passive, A - Active, U - Update, Q - Query, R - Reply,
r - reply Status, s - sia Status
Feasible
P 192.168.1.96/27, 1 successors, FD is 40512000
distance
via Connected, Serial0/0/1
P 192.168.1.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 40512000
Advertised
via Summary (40512000/0), Null0
distance
P 172.16.0.0/16, 1 successors, FD is 28160
via Summary (28160/0), Null0
P 172.16.1.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 28160
Outgoing
via Connected, FastEthernet0/0
interface
P 172.17.0.0/16, 1 successors, FD is 40514560
via 192.168.1.102 (40514560/28160), Serial0/0/1
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
ROUTE v1.0—2-8
Verifying EIGRP Operation (Cont.)
R1#show ip eigrp traffic
IP-EIGRP Traffic Statistics for AS 110
Hellos sent/received: 429/192
EIGRP packet counters
Updates sent/received: 4/4
Queries sent/received: 1/0
Replies sent/received: 0/1
Acks sent/received: 4/3
Input queue high water mark 1, 0 drops
SIA-Queries sent/received: 0/0
SIA-Replies sent/received: 0/0
Hello Process ID: 113
PDM Process ID: 73
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
ROUTE v1.0—2-9
Using Passive Interfaces
EIGRP announces the directly connected network of an interface
EIGRP does not try to form neighbor relationships over the
interface where only the host is connected
– Reduces traffic overhead
No peer here
R1#
router eigrp 110
passive-interface FastEthernet0/0
network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 192.168.1.0
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
No peer here
R2#
router eigrp 110
passive-interface FastEthernet0/0
network 172.17.2.0 0.0.0.255
network 192.168.1.0
ROUTE v1.0—2-10
Using Passive Interfaces (Cont.)
No need to talk to host by EIGRP
Disables EIGRP on all interfaces by default
Enables EIGRP only on selected interfaces
R1(config)#
router eigrp 110
passive-interface default
no passive-interface Serial0/0/1
network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 192.168.1.0
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
ROUTE v1.0—2-11
Verify Operation with Passive Interfaces
R1#sh ip protocols
Routing Protocol is "eigrp 110"
<output omitted>
Automatic network summarization is in effect
Automatic address summarization:
172.16.0.0/16 for Serial0/0/1
Summarizing with metric 28160
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
172.16.1.0/24
192.168.1.0
Passive Interface(s):
FastEthernet0/0
<output omitted>
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
ROUTE v1.0—2-12
Using the ip default network Command
with EIGRP
Default routes decrease the size of the routing table
Multiple candidates:
– 0.0.0.0 is statically set or advertised by the routing protocol
– Any EIGRP major network route is flagged as a candidate
default with the ip default-network command
EIGRP solution:
Flags network as a default route candidate
Multiple default candidates supported
– Announced with the Exterior flag
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
ROUTE v1.0—2-13
Using the ip default network Command
with EIGRP (Cont.)
Flagging an external network as a default route candidate
R2#
router eigrp 110
network 10.0.0.0
ip default-network 172.31.0.0
ip route 172.31.0.0 255.255.0.0 172.31.1.1
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
ROUTE v1.0—2-14
Verifying Default Network Information
R2#show ip route
Flagged candidate
Flagged candidate
0.0.0.0 via Serial0/0/0
<output omitted>
S*
0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 172.31.1.1
C
172.31.1.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
C
10.64.0.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
R1#show ip route
<output omitted>
Gateway of last resort is 10.64.0.2 to network 0.0.0.0
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 7 subnets, 2 masks
<output omitted>
C
10.64.0.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
D*
172.31.0.0/16 [90/10514560] via 10.64.0.2, 00:07:01, FastEthernet0/0
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
ROUTE v1.0—2-15
Route Summarization
Improves network scalability
– Smaller routing tables
– Fewer updates
Should follow IP addressing
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
ROUTE v1.0—2-16
EIGRP Automatic Route Summarization
Performed on major network boundaries
– Subnetworks are summarized to a single classful (major)
network.
– Automatic summarization occurs by default.
Could result in routing issues—disable auto summarization
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
ROUTE v1.0—2-17
EIGRP Manual Route Summarization
Configurable on a per-interface basis in any router within a
network.
Summarization results in a route pointing to null0.
– Loop prevention mechanism
When the last specific route of the summary goes away, the
summary is deleted.
The minimum metric of the specific routes = metric of the
summary route.
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
ROUTE v1.0—2-18
Configuring Route Summarization
Creating a summary route for 172.16.0.0/16
R1(config)#
router eigrp 110
network 10.0.0.0
network 172.16.0.0
no auto-summary
R2(config)#
router eigrp 110
network 10.0.0.0
network 172.16.0.0
no auto-summary
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
R3(config)#
interface Serial0/0/0
ip address 192.168.4.2 255.255.255.0
ip summary-address eigrp 110 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0
!
router eigrp 110
network 10.0.0.0
network 192.168.4.0
no auto-summary
ROUTE v1.0—2-19
Verifying Route Summarization
R3#show ip route
<output omitted>
Gateway of last resort is not set
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks
D
172.16.0.0/16 is a summary, 00:00:04, Null0
D
172.16.1.0/24 [90/156160] via 10.1.1.2, 00:00:04, FastEthernet0/0
D
172.16.2.0/24 [90/20640000] via 10.2.2.2, 00:00:04, Serial0/0/1
C
192.168.4.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks
C
10.2.2.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1
<output omitted>
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
ROUTE v1.0—2-20
Summary
EIGRP operation can be verified by examining the EIGRP
neighbor relationship information and IP routing table for the
presence of EIGRP routes.
The neighbor command can be used to form the EIGRP neighbor
relationship with only specific neighbors using unicast packets.
EIGRP is, by default, enabled on all interfaces included with the
network command. To prevent unnecessary traffic, interfaces
without neighbors should be made passive.
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
ROUTE v1.0—2-21
Summary (Cont.)
Create and advertise a default route in an EIGRP autonomous
system with the ip default-network network-number command.
EIGRP performs automatic network-boundary summarization, but
administrators can disable automatic summarization and perform
manual route summarization on an interface-by-interface basis.
Summarizing routes results in smaller routing tables.
For manual route summarization, the summary route is advertised
only if a more specific entry of the summary route is present in the
routing table.
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
ROUTE v1.0—2-22
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
ROUTE v1.0—2-23