TRUNK FLEXION

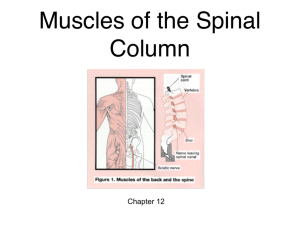
3 Movements of the Trunk
Flexion
Rotation
Extension
TRUNK FLEXION
TRUNK FLEXION: Rectus Abdominalis
• O: Crest of Pubis & ligaments covering front of symphysis pubis.
I: By «3 portions into cartilages of 5th, 6th & 7th ribs.
• N: Lower intercostal nerves.
• Accessory Ms.:
• Internal Obliques & external obliques (reverse action).
TRUNK FLEXION: ROM
• In backlying: flex. of thorax on pelvis is possible until scapulae are raised from the table.
• Motion is mainly at the thoracic spine.
Fixation:
1) Reverse action of hip flexor muscles.
2) Weight of legs and pelvis .
TRUNK FLEXION: Rectus Abdominalis
Limited ROM if:
• Tension of the posterior longitudinal ligament, ligamenta flava & interspinal
& infraspinal ligaments.
• Tension of the spinal extensor muscles.
• Apposition of lower lips of vertebral bodies anteriorly with surfaces of subjacent vertebrae.
• Compression of intervertebral fibocartilages in front.
• Contact of lower ribs with abdomen.
Each vertebra is made up of
TRUNK FLEXION: Testing Grade 1-0
• Note: observe deviation of umbilicus.
• Upward movement indicates stronger contraction of upper section muscle,
& downward movement, stronger contraction of lower section.
Trunk Rotation: Internal & External Oblique
External Oblique:
• O: 8 digitations from external surfaces & inf. borders of lower 8 ribs.
• I: Ant. ½ of iliac crest
& aponeurosis to pubic tubercle.
• N: Lower intercostals.
Trunk Rotation: Internal & External Oblique
Internal Oblique
• O: lateral half of upper surface of inguinal ligament, anterior 2/3 of iliac crest.
• I: Crest of pubis, linea alba, inf. bordres of cartilages of 3 last ribs.
• N: Lower intercostals.
Trunk Rotation: Int. & Ext. Oblique: ROM
ROM in backlying: until scapula on side of forward shoulder is raised from table.
Limited by:
• Tension of annulus fibrosus between vertebrae.
Fixation:
• Reverse action of hip flexors.
• Tension of oblique abdominal muscles on side opposite to those being tested.
• In thoracic area, tension of the costovertebral ligaments.
In Lumbar area, interlocking of articular facets.
• Accessory muscles:
– Lattissimus Dorsi.
– Semispinalis.
– Multifidus.
– Rotatores
– Rectus abdominis
(combined trunk rotation & flexion).
Facet joints:
Inter-vertebral disc (IVD):
Trunk Rotation: Int. & Ext. Oblique: Gr. 1 & 0
• Note: Observe deviation of umbilicus, which will move towards the strongest quadrant if there is a difference in strength of opposing oblique muscles.
Trunk Extension
5 muscles:
• Iliocostalis Dorsalis
• Longissimus dorsi
• Spinalis dorsi
• Iliocostalis lumborum
• Quadratus lumborum
• Sacrospinalis
Accessory muscles:
• Semispinales
• Rotatores
• Multifidus.
Trunk Extension
•
Limitation of ROM:
ROM:
• Thoracic spine extends only to approximately a straight line.
• Lumbar spine extends freely.
• Tension of anterior
Longitudinal ligament of spine.
• Tension of ant. Abdominal
Muscles
Fixation:
• Contraction of gluteus max. & hamstring muscles.
• Weight of pelvis & legs.
• Contact of spinous processes.
• Contact of inf. articular margins with laminae.