Units of Measurement
advertisement
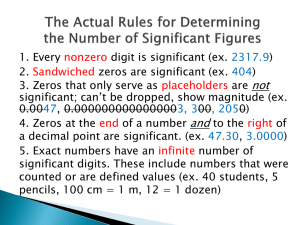
BASIC CHEMISTRY CHM 138 CHAPTER 1: UNITS OF MEASUREMENTS Chemistry is the study of matter and the changes it undergoes Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass. A substance is a form of matter that has a definite composition and distinct properties. liquid nitrogen gold ingots silicon crystals DIMENSIONS Defined as: Any physical quantities that can be measured by measuring devices. There are 2 types of dimension: 1.Basic dimension o o The simplest and the most basic physical quantities There are 7 basic dimensions: - Length (L) - mass (m) - time (t) - temperature (T) - amount of substances (n) - luminous intensity (I) - electrical current 2. Derived dimensions o The compound physical quantities that are obtained by combining basic physical by multiplying / dividing the basic dimensions. Derived dimensions Combination of Basic dimensions Area Length x length Volume Length x length x length Speed Length / time Force (mass x length) / (time x time) Density Mass / (length x length x length) Pressure Mass / (time x time) International System of Units (SI) S.I system of units Dimension Symbol of dimension Name of unit Symbol of unit Definition of unit Basic SI Units length L meter m mass m kilogram Kg time t second s temperature T Kelvin, degree celcius K, °C Amount of substance n mole mol Derived SI Units Energy E Joule J / Nm Kg.m2.s-2 Force F Newton N Kg.m.s-2 Power P watt W /J/s Kg.m2.s-3 Velocity V Meter per second m.s-1 Acceleration a Meter per second squared m.s-2 Pressure P Newton per meter squared, Pascal N.m-2 Pa Density ƿ Kilogram per cubic meter Kg.m-3 American Engineering system of units Dimension Symbol of dimension Name of unit Symbol of unit Basic SI Units length L Feet ft mass m Pound mass Ibm force F Pound force Ibf time t Second S temperature T Degree Rankie, Degree Fahrenheit °R °F Amount of substance n mole Ib mol Derived SI Units Energy E Foot pound force Ft.Ibf Force F Pound force Ibf Power P Horsepower hp Velocity V feet per second ft.s-1 Acceleration a feet per second squared ft.s-2 Pressure P Pound force per second inch Psi Density ƿ Pound mass per cubic foot Ibm.ft-3 Definition of unit Quantity Equivalent Values Mass 1 kg = 1000 g = 0.001 metric ton = 2.20462 Ibm = 35.27392 oz 1 Ibm = 16 oz = 5 x 10-4 ton = 453.593 g = 0.453593 kg Length 1 m = 100 cm = 1000 mm = 106 microns (µm) = 1010 angstroms (A) = 39.37 in. = 3.2808 ft = 1.0936 yd = 0.0006214 mile 1 ft = 12 in. = 1/3 yd = 0.304 m = 30.48 cm Volume 1 m3 = 1000 L = 106 cm3 = 106 mL = 35.3145 ft3 = 220.83 imperial gallons = 264.17 gal = 1056.68 qt 3 1 ft = 1728 in.3 = 7.4805 gal = 0.028317 m3 = 28.317 L = 28,317 cm3 Force 1 N = 1 kg.m/s2 = 105 dynes = 105 g.cm/s2 = 0.22481 Ibf 1 Ibf = 32.174 Ibm.ft/s2 = 4.4482 N = 4.4482 x 105 dynes Pressure 1 atm = 1.01325 x 105 N/m2 (Pa) = 101.325 kPa = 1.01325 bar = 1.01325 x 106 dynes/cm2 = 760 mm Hg = 14.696 Ibf/in.2 (psi) = 33.9 ft = 29.921 in. Hg Energy 1 J = 1 N.m = 107 ergs = 107 dyne.cm = 2.778 x 10-7 kW.h = 0.23901 cal = 0.7376 ft-Ibf = 9.486 x 10-4 Btu power 1 W = 1 J/s = 0.23901 cal/s = 0.7376 ft.Ibf/s = 9.486 x 10-4 Btu/s = 1.341 x 10-3 hp 1 year = 365 days 1 day = 24 hours 1 hour = 60 minutes 1 minute = 60 seconds 30 days = 1 month 1 year = 12 month 1 qt = 0.946 L 1 gal = 3.785 L 1 L = 33.81 fl oz 1 fl oz = 29.57 ml 1 L = 1.057 qt 1 in = 2.54 cm 1 m = 39.37 in 1 mile = 1.609 km 1 mile = 5280 feet 1 mile = 1760 yards 3 feet = 1 yard 12 inches = 1 feet 1 oz = 28.35 g 1 lb = 453.6 g 1 kg = 2.205 lb 1 g = 15.43 grains MASS AND WEIGHT Matter - anything that occupies space and has mass. mass – measure of the quantity of matter SI unit of mass is the kilogram (kg) 1 kg = 1000 g = 1 x 103 g weight – force that gravity exerts on an object weight = c x mass A 1 kg bar will weigh on earth, c = 1.0 1 kg on earth on moon, c ~ 0.1 0.1 kg on moon VOLUME Volume – SI derived unit for volume is cubic meter (m3) 1 cm3 = (1 x 10-2 m)3 = 1 x 10-6 m3 1 dm3 = (1 x 10-1 m)3 = 1 x 10-3 m3 1 L = 1000 mL = 1000 cm3 = 1 dm3 1 mL = 1 cm3 DENSITY Density – SI derived unit for density is kg/m3 1 g/cm3 = 1 g/mL = 1000 kg/m3 m mass d= V density = volume EXAMPLE: A piece of platinum metal with a density of 21.5 g/cm3 has a volume of 4.49 cm3. What is its mass? m d= V m = d x V = 21.5 g/cm3 x 4.49 cm3 = 96.5 g Ex. 1.1 Ex. 1.2 A Comparison of Temperature Scales Three temperature scales: i) 0F – degrees Fahrenheit ii) 0C – degrees Celcius iii) K - Kelvin K = oC + 273.15 oF = oC 9 oF o oF x C + 32 5 oC = (oF – 32oF) x 5 oC 9 oF Example: Convert 172.9 0F to degrees Celsius. = 5 x (0F – 32) 9 0C = 5 x (172.9 – 32) = 78.3 9 0C Scientific Notation The number of atoms in 12 g of carbon: 602,200,000,000,000,000,000,000 6.022 x 1023 The mass of a single carbon atom in grams: 0.0000000000000000000000199 1.99 x 10-23 N x 10n N is a number between 1 and 10 n is a positive or negative integer 568.762 0.00000772 move decimal left move decimal right n>0 n<0 568.762 = 5.68762 x 102 0.00000772 = 7.72 x 10-6 Addition or Subtraction 1. Write each quantity with the same exponent n 2. Combine N1 and N2 3. The exponent, n, remains the same 4.31 x 104 + 3.9 x 103 = 4.31 x 104 + 0.39 x 104 = 4.70 x 104 Multiplication 1. Multiply N1 and N2 2. Add exponents n1 and n2 (4.0 x 10-5) x (7.0 x 103) = ? = (4.0 x 7.0) x (10-5+3) = 28 x 10-2 m) x (b x 10n) = (axb) x 10m+n (a x 10 = 2.8 x 10-1 Division 1. Divide N1 and N2 2. Subtract exponents n1 and n2 8.5 x 104 ÷ 5.0 x 109 = ? = (8.5 ÷ 5.0) x 104-9 m) ÷ (b x 10n) = (a ÷ b) x 10m-n (a x 10 = 1.7 x 10-5 Significant Figures - The meaningful digits in a measured or calculated quantity. RULES: • Any digit that is not zero is significant 1.234 kg 4 significant figures • Zeros between nonzero digits are significant 606 m 3 significant figures • Zeros to the left of the first nonzero digit are not significant 0.08 L 1 significant figure • If a number is greater than 1, then all zeros to the right of the decimal point are significant 2.0 mg 2 significant figures • If a number is less than 1, then only the zeros that are at the end and in the middle of the number are significant 0.00420 g 3 significant figures • Numbers that do not contain decimal points, zeros after the last nonzero digit may or may not be significant. 400 cm 1or 2 or 3 significant figures 4 x 102 1 significant figures 4.0 x 102 2 significant figures How many significant figures are in each of the following measurements? 24 mL 2 significant figures 3001 g 4 significant figures 0.0320 m3 3 significant figures 6.4 x 104 molecules 2 significant figures 560 kg 2 significant figures Significant Figures Addition or Subtraction The answer cannot have more digits to the right of the decimal point than any of the original numbers. 89.332 +1.1 90.432 3.70 -2.9133 0.7867 one significant figure after decimal point round off to 90.4 two significant figures after decimal point round off to 0.79 Significant Figures Multiplication or Division The number of significant figures in the result is set by the original number that has the smallest number of significant figures 4.51 x 3.6666 = 16.536366 = 16.5 3 sig figs round to 3 sig figs 6.8 ÷ 112.04 = 0.0606926 = 0.061 2 sig figs round to 2 sig figs Significant Figures Exact Numbers Numbers from definitions or numbers of objects are considered to have an infinite number of significant figures The average of three measured lengths; 6.64, 6.68 and 6.70? 6.64 + 6.68 + 6.70 = 6.67333 = 6.67 = 7 3 Because 3 is an exact number Dimensional Analysis Method of Solving Problems 1. Determine which unit conversion factor(s) are needed 2. Carry units through calculation 3. If all units cancel except for the desired unit(s), then the problem was solved correctly. given quantity x conversion factor = desired quantity given unit x desired unit given unit = desired unit Dimensional Analysis Method of Solving Problems How many mL are in 1.63 L? Conversion Unit 1 L = 1000 mL 1000 mL 1.63 L x = 1630 mL 1L The speed of sound in air is about 343 m/s. What is this speed in miles per hour? conversion units meters to miles seconds to hours 1 mi = 1609 m 1 min = 60 s 1 mi 60 s m x x 343 s 1609 m 1 min 1 hour = 60 min 60 min mi x = 767 hour 1 hour