Lecture 6
advertisement

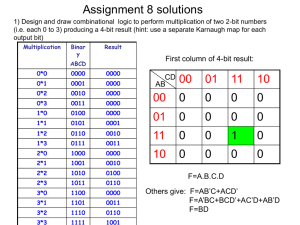
ECE 5367 4436 Multiplication Division ECE 5367 4436 Multiplication concepts Multiplicand Multiplier - Product 1000 1001 1000 0000 0000 1000 1001000ten ECE 5367 4436 Concepts • Product bits > either multiplicand or multiplier bits. • Product bits = # of multiplicand bits + # of multiplier bits. • Multiplication Steps – Place a copy of multiplicand in proper place if multiplier digit = 1. – Place 0 in the proper place if multiplier digit = 0. ECE 5367 4436 Multiplication hardware – Version1 • Multiplicand is 32 bits. • Initialize product = 0. • Need to move multiplicand left one digit during each step. • Here we will move a total of 32 times. • Multiplicand – 64 bit to align with 64 bit product register. ECE 5367 4436 Multiplication algorithm ECE 5367 4436 Multiplication algorithm contd.. Multiply 2ten, 3ten, or 0010two X0011two Iteratio n Step Multiplie r Multiplic and Product 0 Initial values 0011 00000010 00000000 1 1a: 1-> Prod = Prod + Mcand 0011 00000010 00000010 2: Shift left Multiplicand 0011 00000100 00000010 3: Shift right multiplier 0001 00000100 00000010 1a: 1-> Prod = Prod + Mcand 0001 00000100 00000110 2: Shift left Multiplicand 0001 00000100 00000110 3: Shift right multiplier 0000 00001000 00000110 1: 0 -> no operation 0000 00001000 00000110 2: Shift left Multiplicand 0000 00000100 00000110 3: Shift right multiplier 0000 00010000 00000110 1: 0 -> no operation 0000 00010000 00000110 2: Shift left Multiplicand 0000 00100000 00000110 3: Shift right multiplier 0000 00100000 00000110 2 3 4 ECE 5367 4436 Second version of algorithm. • Half of multiplicand bits are wasted. 64-bit ALU not a good idea. • Slow algorithm. • Instead of shifting multiplicand left, shift product right? – Multiplicand fixed relative to product. – Adder need only be 32 bits wide. – Change halves width of ALU and Mcand. – 32-bit sum is formed, only left half of 64-bit product register is changed by the addition. ECE 5367 4436 Second version - hardware ECE 5367 4436 Second version of algorithm. ECE 5367 4436 Second version of algorithm multiply 0010two X 0011two Iteration 0 1 2 3 4 Step Multiplier Multiplicand Product Initial values 0011 0010 00000000 1a:1 => Prod = Prod + Mcand 0011 0010 00100000 2: Shift right product 0011 0010 00010000 3: Shift right multiplier 0001 0010 00010000 1a:1 => Prod = Prod + Mcand 0001 0010 00110000 2: Shift right product 0001 0010 00011000 3: Shift right multiplier 0000 0010 00011000 1: 0=> no operation 0000 0010 00011000 2: Shift right product 0000 0010 00001100 3: Shift right multiplier 0000 0010 00001100 1: 0=> no operation 0000 0010 00001100 2: Shift right product 0000 0010 00000110 3: Shift right multiplier 0000 0010 00000110 ECE 5367 4436 Final version • Product wasted space = size of the multiplier. – As product wasted space disappears, so does the multiplier : gets shifted out… • Suggestion: combination of rightmost half of product with multiplier. ECE 5367 4436 ECE 5367 4436 Final version - hardware ECE 5367 4436 Final version - algorithm ECE 5367 4436 Booth recoding • Observation: many ways to obtain a product. • Purpose: speed – shifting was faster than addition. • Also handles signed numbers. – Replace a string of 1’s in the multiplier with initial subtract when we first see a 1. – Later add when we see the bit after the last 1. ECE 5367 4436 Example 0010two X0110two + 0000 shift (0 in multiplier) - 0010 sub (first 1 in multiplier) + 0000 shift (middle of string of 1’s) + 0010 add (prior step had last 1) 00001100two ECE 5367 4436 ECE 5367 4436 Booth recoding • Key – classification of numbers into groups. End of run middle of run 01 beginning of run 11 10 current bit bit to right Explanation Example 1 0 Beginning of a run of 1’s 000011110002 1 1 Middle of a run of 1’s 000011110002 0 1 End of a run of 1’s 000011110002 0 0 Middle of a run of 1’s 000011110002 ECE 5367 4436 Booth’s algorithm • Depending on the current and previous bits of multiplier: – 00: Middle of a string of 0s so no arithmetic operation. – 01: End of a string of 1’s, so add Mcand to left half of the product. – 10: Beginning of a string of 1’s, so subtract the Mcand from the left half of the product. – 11: Middle of a string of 1’s, so no arithmetic operation. *******when shifting a negative number, always preserve the sign******** ECE 5367 4436 Booth recoding contd. Iterati on Multiplicand Booths algorithm Step Product 0 0010 Initial values 00000110 0 1 0010 1a:00 -> no operation 00000110 0 0010 2: shift right product 00000011 0 0010 1c:10-> Prod=Prod -Mcand 11100011 0 0010 2: shift right product 11110001 1 0010 1d:11 -> no operation 11110001 1 0010 2: shift right product 11111000 1 0010 1b: 01 -> Prod = Prod + Mcand 00011000 1 0010 2: shift right product 00001100 0 2 3 4 ECE 5367 4436 Multiply 2i via shift • 5ten X 2ten using a left shift. • 101two = 5ten – Shift left 1 bit 1010two = 10ten – 5ten X 2ten = 10ten ECE 5367 4436 Division • Long division 1001ten Quotient Divisor 1000ten 1001010ten Dividend -1000 10 101 1010 1000 10ten Remainder Dividend = Quotient X Divisor + Remainder ECE 5367 4436 First version • 32-bit quotient register. • Each step moves the divisor to the right one bit. – Start with divisor placed in the left half of the 64-bit divisor register • Shift it right 1 bit each step to align it with the dividend. • ***Remainder register is initialized with the dividend. ECE 5367 4436 First version • If remainder is +ve, – Step 2a generates a 1 in the quotient. else, – Step 2b generates a 0 in the quotient and adds the divisor to the remainder. • Final shift aligns the divisor. ECE 5367 4436 Divide 710 by 210: 0000 01112 by 00102 Iteration 0 1 2 3 4 5 Step Quotient Divisor Remainder Initial values 0000 0010 0000 0000 0111 1: Rem = Rem – Div 0000 0010 0000 1110 0111 2b: Rem < 0 => +Div, sll Q, Q0 = 0 0000 0010 0000 0000 0111 3: Shift Div right 0000 0001 0000 0000 0111 1: Rem = Rem – Div 0000 0001 0000 1111 0111 2b: Rem < 0 => +Div, sll Q, Q0 = 0 0000 0001 0000 0000 0111 3: Shift Div right 0000 0000 1000 0000 0111 1: Rem = Rem – Div 0000 0000 1000 1111 1111 2b: Rem < 0 => +Div, sll Q, Q0 = 0 0000 0000 1000 0000 0111 3: Shift Div right 0000 0000 0100 0000 0111 1: Rem = Rem – Div 0000 0000 0100 0000 0011 2a: Rem >= 0 => sll Q, Q0 = 1 0001 0000 0100 0000 0011 3: Shift Div right 0001 0000 0010 0000 0011 1: Rem = Rem – Div 0001 0000 0010 0000 0001 2a: Rem >= 0 => sll Q, Q0 = 1 0011 0000 0010 0000 0001 3: Shift Div right 0011 0000 0001 0000 0001 ECE 5367 4436 Second version • Only half the divisor contains useful data at any one time and so the divisor can be split in two. • Shift remainder left and shift divisor right results in alignment needed and also simplifies hardware. ECE 5367 4436 Final version • Eliminate quotient register. Shift quotient into remainder instead of shifting in zeros. • Algorithm has only 2 steps ECE 5367 4436 Final version -hardware • Start by shifting rem. Left. – This serves to shift both the remainder and the quotient. – Consequence: will shift rem. one time too many. • Final correction to shift back only the rem. half of the register. ECE 5367 4436 Divide 000001112 by 00102 Iteration 0 1 2 3 4 Step Divisor Remainder Initial values 0010 00000111 Shift Rem. left by 1 0010 00001110 2: Rem = Rem - Div 0010 11101110 3b: Rem. < 0-> +Div, sll R, R0 = 0 0010 00011100 2: Rem = Rem - Div 0010 11111100 3b: Rem. < 0-> +Div, sll R, R0 = 0 0010 00111000 2: Rem = Rem - Div 0010 00011000 3a: Rem. >= 0-> sll R, R0 = 1 0010 00110001 2: Rem = Rem - Div 0010 00010001 3a: Rem. >= 0-> sll R, R0 = 1 0010 00100011 Shift left half of Rem right by1 0010 00010011